RunLoop字面上的意思是,运行循环;
其基本作用:保持程序的持续运行;
处理App中的各种事件(比如:触摸事件、定时器事件、Selector事件)
节省CPU资源,提高程序性能:该做事时做事,该休息时休息
1.main函数中的RunLoop
int main(int argc, char * argv[]) { @autoreleasepool { return UIApplicationMain(argc, argv, nil, NSStringFromClass([AppDelegate class])); } } 在这个main函数中,UIApplicationMain函数内部就启动了一个RunLoop,所以UIApplicationMain函数一直没有返回,保持了程序的持续运行。这个默认启动的RunLoop是跟主线程相关联的。
NSRunLoop 是基于CFRunLoopRef的一层OC包装,所以了解RunLoop内部结构,需要多研究CFRunLoopRef层面的API。
2.RunLoop与线程的关系
每条线程都有唯一的一个与之对应的RunLoop对象
主线程的RunLoop已经自动创建好了,子线程的RunLoop需要主动创建
RunLoop在第一次获取时创建,在线程结束时销毁
获取子线程对应的RunLoop(即,currentRunLoop)该方法本身是懒加载的,如果第一次调用就会创建当前线程对应的RunLoop并保存,以后调用则直接获取
3.RunLoop的获取
#pragma mark - RunLoop - (void)touchesBegan:(NSSet*)touches withEvent:(UIEvent *)event { //OC语言中的API //01 获取主线程对应的runloop对象 NSRunLoop *mainRunloop = [NSRunLoop mainRunLoop]; //02 获取当前的runloop的对象 NSRunLoop *currentRunloop = [NSRunLoop currentRunLoop]; NSLog(@"%p---%p", mainRunloop, currentRunloop); //C语言的API //01 主运行循环 CFRunLoopRef mainRunloopRef = CFRunLoopGetMain(); //02 当前的运行循环 CFRunLoopRef currentRunloopRef = CFRunLoopGetCurrent(); NSLog(@"%p---%p", mainRunloopRef, currentRunloopRef); //转化 NSLog(@"%p----%p", mainRunloop.getCFRunLoop, mainRunloopRef); }
打印的结果:
2019-09-18 15:31:31.176193+0800 NSCach[60622:1117017] 0x60000184c060---0x60000184c060 2019-09-18 15:31:31.176302+0800 NSCach[60622:1117017] 0x600000050600---0x600000050600 2019-09-18 15:31:31.176362+0800 NSCach[60622:1117017] 0x600000050600----0x600000050600
可以看出,当前的主运行循环和当前运行循环是同一个runloop, 最后一行可以看出,OC获取的runloop与C的runloop可以相互转化。
4.RunLoop的模式与Timer的关系
//Runloop的运行模式和Timer - (void)RunLoopModeAndTimer { //创建定时器对象 NSTimer *timer = [NSTimer timerWithTimeInterval:2.0 target:self selector:@selector(run) userInfo:nil repeats:YES]; //添加到runloop中 //Mode:runloo的运行模式(默认|界面跟踪|占位) //把定时器对象添加到runloop中,并制定运行模式为默认--当运行模式为NSDefaultRunLoopMode的时候,定时器才会工作 //[[NSRunLoop currentRunLoop] addTimer:timer forMode:NSDefaultRunLoopMode]; //当滚动textView的时候,主运行循环会切换运行模式:从默认切换成界面跟踪运行模式 //把定时器对象添加到runloop中,并制定运行模式为界面跟踪--当运行模式为UITrackingRunloopMode的时候(即拖拽界面时),定时器才会工作 //[[NSRunLoop currentRunLoop] addTimer:timer forMode:UITrackingRunLoopMode]; //当两种模式都可以运行时,均可用 //把定时器对象添加到runloop中,并制定运行模式为NSRunLoopCommonModes--当运行模式为NSDefaultRunLoopMode或者UITrackingRunloopMode的时候,定时器才会工作 //需要注意没有NSRunLoopCommonModes这种模式,NSRunLoopCommonModes是标记NSDefaultRunLoopMode或者UITrackingRunloopMode的集合 [[NSRunLoop currentRunLoop] addTimer:timer forMode:NSRunLoopCommonModes]; } - (void)run { NSLog(@"run----%@", [NSRunLoop currentRunLoop].currentMode); }
注意
//该方法内部会自动创建的定时器对象添加到当前的runloop,并且指定运行模式为默认 // [NSTimer scheduledTimerWithTimeInterval:2.0 target:self selector:@selector(run) userInfo:nil repeats:YES]; //如果想利用上面的那种方法,修改运行模式,可修改成如下 NSTimer *timer = [NSTimer scheduledTimerWithTimeInterval:2.0 target:self selector:@selector(run) userInfo:nil repeats:YES]; [[NSRunLoop currentRunLoop] addTimer:timer forMode:UITrackingRunLoopMode];
注意:上面添加的定时器,如果是添加在主线程中的,所以,不需要开始runloop,定时器就可以工作;但是如果,直接添加到子线程中,例如下面的代码:
- (void)touchesBegan:(NSSet
[self performSelectorInBackground:@selector(RunLoopModeAndTimer) withObject:nil];
}
- (void)RunLoopModeAndTimer { //该方法内部会自动创建的定时器对象添加到当前的runloop,并且指定运行模式为默认 [NSTimer scheduledTimerWithTimeInterval:2.0 target:self selector:@selector(run) userInfo:nil repeats:YES]; } - (void)run { NSLog(@"run----%@", [NSRunLoop currentRunLoop].currentMode); }
那么,点击界面的时候,定时器是不工作的;因为定时器对象添加到当前的runloop中,而当前的runloop在子线程中;子线程中的runloop需要手动创建,所以此时定时器不工作。
解决方式:开启runloop
- (void)RunLoopModeAndTimer { //该方法内部会自动创建的定时器对象添加到当前的runloop,并且指定运行模式为默认 [NSTimer scheduledTimerWithTimeInterval:2.0 target:self selector:@selector(run) userInfo:nil repeats:YES];
[[NSRunLoop currentRunLoop] run];
}
5.GCD的定时器
按照上面那段代码执行后,会发现,timer并没有执行。因为在程序运行到 } 后,代码就执行完了,就被释放了。所以需要添加一个强引用。
修改如下:
总结:
Runloop的相关类
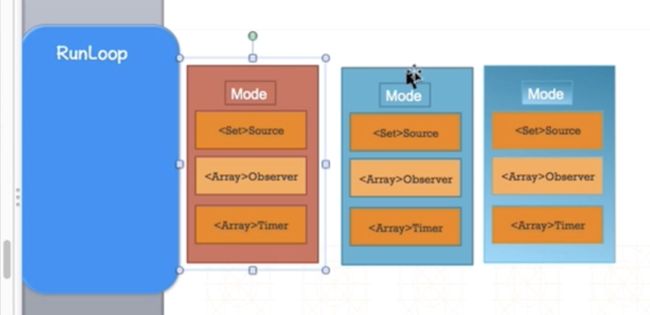
Core Foundation中关于RunLoop的5个类:
CFRunLoopRef
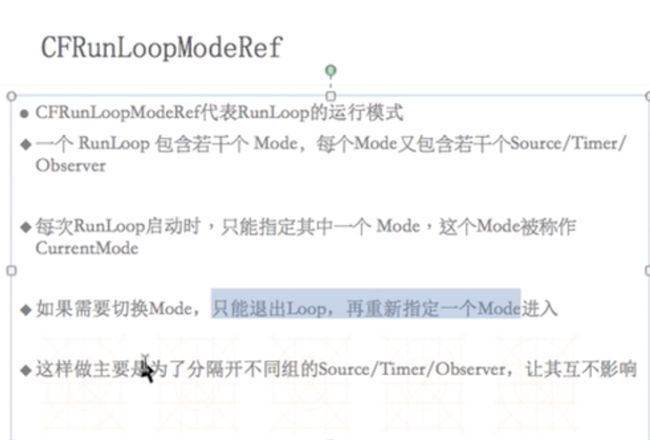
CFRunLoopModeRef
CFRunLoopSourceRef
CFRunLoopTimerRef
CFRunLoopObserverRef
当runloop选择一个运行模式后,需要判断运行模式是否为空,判断的依据是:Source和Timer是否有数据,如果没有数据,runloop立马退出。
选择了一个运行模式后
如果source或者timer有数据时,就开启runloop。
RunLoopObserver简单说明
CFRunLoopObserverRef是观察者,能够监听RunLoop的状态改变。
可以监听的时间点有以下几个: