Pytorch LSTM 时间序列预测
Pytorch LSTM 时间序列预测
https://github.com/pytorch/examples/blob/master/time_sequence_prediction/generate_sine_wave.py
Pytorch官网提供初学者入门的一个例子,有助于学习Pytorch时间序列预测。本例中使用两个LSTMCell单元学习从不同相位开始的一些正弦波信号,LSTM网络在学习了正弦波之后,试图预测未来的信号值。
generate_sine_wave.py生成模拟数据:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import numpy as np
import torch
np.random.seed(2)
T = 20
L = 1000
N = 100
x = np.empty((N, L), 'int64')
x[:] = np.array(range(L)) + np.random.randint(-4 * T, 4 * T, N).reshape(N, 1)
data = np.sin(x / 1.0 / T).astype('float64')
torch.save(data, open('traindata.pt', 'wb'))
LSTM数据序列预测:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from __future__ import print_function
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.optim as optim
import numpy as np
import matplotlib
matplotlib.use('Agg')
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
class Sequence(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Sequence, self).__init__()
self.lstm1 = nn.LSTMCell(1, 51)
self.lstm2 = nn.LSTMCell(51, 51)
self.linear = nn.Linear(51, 1)
def forward(self, input, future = 0):
outputs = []
h_t = torch.zeros(input.size(0), 51, dtype=torch.double)
c_t = torch.zeros(input.size(0), 51, dtype=torch.double)
h_t2 = torch.zeros(input.size(0), 51, dtype=torch.double)
c_t2 = torch.zeros(input.size(0), 51, dtype=torch.double)
for i, input_t in enumerate(input.chunk(input.size(1), dim=1)):
h_t, c_t = self.lstm1(input_t, (h_t, c_t))
h_t2, c_t2 = self.lstm2(h_t, (h_t2, c_t2))
output = self.linear(h_t2)
outputs += [output]
for i in range(future):# if we should predict the future
h_t, c_t = self.lstm1(output, (h_t, c_t))
h_t2, c_t2 = self.lstm2(h_t, (h_t2, c_t2))
output = self.linear(h_t2)
outputs += [output]
outputs = torch.stack(outputs, 1).squeeze(2)
return outputs
if __name__ == '__main__':
# set random seed to 0
np.random.seed(0)
torch.manual_seed(0)
# load data and make training set
data = torch.load('traindata.pt')
input = torch.from_numpy(data[3:, :-1])
target = torch.from_numpy(data[3:, 1:])
test_input = torch.from_numpy(data[:3, :-1])
test_target = torch.from_numpy(data[:3, 1:])
# build the model
seq = Sequence()
seq.double()
criterion = nn.MSELoss()
# use LBFGS as optimizer since we can load the whole data to train
optimizer = optim.LBFGS(seq.parameters(), lr=0.8)
#begin to train
for i in range(15):
print('STEP: ', i)
def closure():
optimizer.zero_grad()
out = seq(input)
loss = criterion(out, target)
print('loss:', loss.item())
loss.backward()
return loss
optimizer.step(closure)
# begin to predict, no need to track gradient here
with torch.no_grad():
future = 1000
pred = seq(test_input, future=future)
loss = criterion(pred[:, :-future], test_target)
print('test loss:', loss.item())
y = pred.detach().numpy()
# draw the result
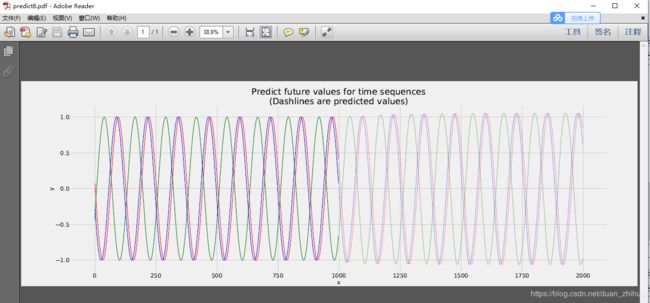
plt.figure(figsize=(30,10))
plt.title('Predict future values for time sequences\n(Dashlines are predicted values)', fontsize=30)
plt.xlabel('x', fontsize=20)
plt.ylabel('y', fontsize=20)
plt.xticks(fontsize=20)
plt.yticks(fontsize=20)
def draw(yi, color):
plt.plot(np.arange(input.size(1)), yi[:input.size(1)], color, linewidth = 2.0)
plt.plot(np.arange(input.size(1), input.size(1) + future), yi[input.size(1):], color + ':', linewidth = 2.0)
draw(y[0], 'r')
draw(y[1], 'g')
draw(y[2], 'b')
plt.savefig('predict%d.pdf'%i)
plt.close()运行结果: