GBDT回归的python官方例子详解
简单的GBDT调用见官方例子:
方法地址:http://scikit-learn.org/stable/auto_examples/ensemble/plot_gradient_boosting_regression.html#sphx-glr-auto-examples-ensemble-plot-gradient-boosting-regression-py
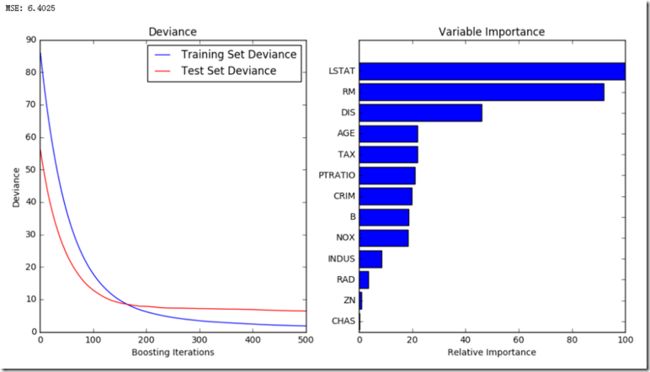
输出:
结论:LSTAT>RM>DIS………
房产的数据结构:
- CRIM per capita crime rate by town
- ZN proportion of residential land zoned for lots over 25,000 sq.ft.
- INDUS proportion of non-retail business acres per town
- CHAS Charles River dummy variable (= 1 if tract bounds river; 0 otherwise)
- NOX nitric oxides concentration (parts per 10 million)
- RM average number of rooms per dwelling
- AGE proportion of owner-occupied units built prior to 1940
- DIS weighted distances to five Boston employment centres
- RAD index of accessibility to radial highways
- TAX full-value property-tax rate per $10,000
- PTRATIO pupil-teacher ratio by town
- B 1000(Bk - 0.63)^2 where Bk is the proportion of blacks by town
- LSTAT % lower status of the population
- MEDV Median value of owner-occupied homes in $1000's
源代码读取csv文件方法详解:
def load_boston(): """Load and return the boston house-prices dataset (regression). ============== ============== Samples total 506 Dimensionality 13 Features real, positive Targets real 5. - 50. ============== ============== Returns ------- data : Bunch Dictionary-like object, the interesting attributes are: 'data', the data to learn, 'target', the regression targets, and 'DESCR', the full description of the dataset. Examples -------- >>> from sklearn.datasets import load_boston >>> boston = load_boston() >>> print(boston.data.shape) (506, 13) """ module_path = dirname(__file__) fdescr_name = join(module_path, 'descr', 'boston_house_prices.rst') with open(fdescr_name) as f: #with用法可以自动关闭,读取文件声明 descr_text = f.read() data_file_name = join(module_path, 'data', 'boston_house_prices.csv') with open(data_file_name) as f: data_file = csv.reader(f) #csv读取文件,获得迭代器 temp = next(data_file) #读取文件头,获得总行数和字段名 n_samples = int(temp[0]) n_features = int(temp[1]) data = np.empty((n_samples, n_features)) #建立矩阵 target = np.empty((n_samples,)) temp = next(data_file) # names of features feature_names = np.array(temp) for i, d in enumerate(data_file): #一行一行通过迭代器读取文件设置到矩阵中 data[i] = np.asarray(d[:-1], dtype=np.float) target[i] = np.asarray(d[-1], dtype=np.float) return Bunch(data=data, target=target, # last column is target value feature_names=feature_names[:-1], DESCR=descr_text)
方法说明:
1、with是python的一种用法,可以自动关闭对应的资源
2、next(iterator[, default]) 迭代器遍历方法
3、reader(csvfile, dialect='excel', **fmtparams) :返回一个迭代器
Return a reader object which will iterate over lines in the given csvfile.
类的主要方法介绍:
构造函数:
loss
learning_rate
n_estimators
max_depth
criterion
min_samples_split
min_samples_leaf
min_weight_fraction_leaf
subsample
max_features
max_leaf_nodes
min_impurity_split
alpha
init
verbose
warm_start
random_state
presort
属性
方法
feature_importances_ :重要的特性
oob_improvement_:
train_score_ :训练分数
loss_ :损失函数
`init` : 评估期
estimators_ : ndarray of DecisionTreeRegressor, shape = [n_estimators, 1]
方法:
后续待补充详细参数说明