吴恩达_两层神经网络实战(第一课~第三周)
本次实现具有一个隐藏层的神经网络(实现二分类)
1.planar_utils模块
一个初始化模块,提供一些共用的方法,画图函数,激活函数,不同数据生成的函数
#coding:utf-8
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import sklearn.datasets
from matplotlib.font_manager import FontProperties
'''
①提供画图函数
②提供激活函数
③提供数据生成函数
④提供数据生成函数
'''
#画图函数
def plot_decision_boundary(model,X,y):
x_min, x_max = X[0, :].min() - 1, X[0, :].max() + 1
y_min, y_max = X[1, :].min() - 1, X[1, :].max() + 1
h = 0.01
#xx和yy是两个大小相等的矩阵
#xx和yy是提供坐标(xx,yy)
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.arange(x_min, x_max, h), np.arange(y_min, y_max, h))
#print xx.shape
#print yy.shape
#列扩展,每个点是一行
Z = model(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()])
#print Z.shape
Z = Z.reshape(xx.shape)
#轮廓,等高线,预测值相等的点描绘成一个轮廓,把图像进行分割
#contour 没有颜色填充,只是分割
#contourf 会进行颜色填充
plt.contourf(xx, yy, Z, cmap=plt.cm.Spectral)
font = FontProperties(fname=r"c:\windows\fonts\simsun.ttc", size=14)
plt.ylabel(u'y轴',fontproperties=font)
plt.xlabel(u'x轴',fontproperties=font)
plt.scatter(X[0, :], X[1, :], c=y[0,:], cmap=plt.cm.Spectral)
#激活函数
def sigmoid(x):
s = 1/(1+np.exp(-x))
return s
#生成数据
def load_planar_dataset():
np.random.seed(1)
m = 400
N = int(m/2)
D = 2
X = np.zeros((m,D))
Y = np.zeros((m,1))
a = 4
for j in range(2):
ix = range(N*j,N*(j+1))
t = np.linspace(j*3.12,(j+1)*3.12,N) + np.random.randn(N)*0.2 # theta
r = a*np.sin(4*t) + np.random.randn(N)*0.2 # radius
X[ix] = np.c_[r*np.sin(t), r*np.cos(t)]
Y[ix] = j
X = X.T
Y = Y.T
return X, Y
#生成数据
def load_extra_datasets():
N = 1000
noisy_circles = sklearn.datasets.make_circles(n_samples=N, factor=.5, noise=.1)
noisy_moons = sklearn.datasets.make_moons(n_samples=N, noise=.2)
blobs = sklearn.datasets.make_blobs(n_samples=N, random_state=5, n_features=2, centers=6)
gaussian_quantiles = sklearn.datasets.make_gaussian_quantiles(mean=None, cov=0.5, n_samples=N, n_features=2, n_classes=2, shuffle=True, random_state=None)
no_structure = np.random.rand(N, 2), np.random.rand(N, 2)
return noisy_circles, noisy_moons, blobs, gaussian_quantiles, no_structuredemo1模块
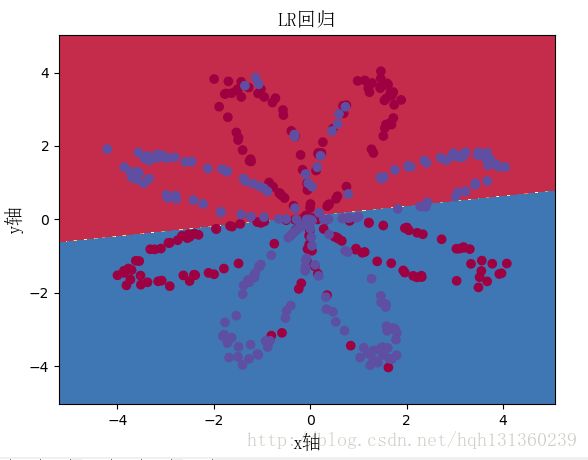
用sklearn模块中包装的方法实现LR回归
#coding:utf-8
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import sklearn.linear_model
from planar_utils import plot_decision_boundary, sigmoid, load_planar_dataset, load_extra_datasets
from matplotlib.font_manager import FontProperties
'''
使用sklearn包的LogisticRegression做二分类
①生成的数据X是多个列向量,Y是一个行向量
②clf.fit需要转置
③predict需要转置
'''
X, Y = load_planar_dataset()
print X.shape
print Y.shape
m = X.shape[1]
clf = sklearn.linear_model.LogisticRegressionCV();
clf.fit(X.T, Y.T.ravel());
#clf.fit填入数据进行训练
#clf.predict进行测试
plot_decision_boundary(lambda x: clf.predict(x), X, Y)
font = FontProperties(fname=r"c:\windows\fonts\simsun.ttc", size=14)
plt.title(u"LR回归",fontproperties=font)
plt.show()
LR_predictions = clf.predict(X.T)
print '准确率=%d%%'%float((np.dot(Y,LR_predictions)+np.dot(1-Y,1-LR_predictions))/float(Y.size)*100)
print '准确率=%d%%'%(100 - 100*np.mean(np.abs(Y-LR_predictions)))
2层神经网络实现2分类,主要就是反向传播有点绕,注意不同的激活函数,反向求导公式也不一样
本神经网络第一个激活函数是tanh,第二个激活函数是sigmod
#coding:utf-8
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from planar_utils import plot_decision_boundary, sigmoid, load_planar_dataset, load_extra_datasets
from matplotlib.font_manager import FontProperties
X, Y = load_planar_dataset()
m = X.shape[1]
#输入个输出的特征个数,2个输入,1个输出
def layer_size(X,Y):
n_x=X.shape[0] #2行400列
n_y=Y.shape[0] #1行400列
return (n_x,n_y)
#正向传播函数
def foward_propagation(X,parameters):
W1=parameters["W1"]
b1=parameters["b1"]
W2=parameters["W2"]
b2=parameters["b2"]
Z1=np.dot(W1,X)+b1
#激活函数
A1=np.tanh(Z1)
Z2=np.dot(W2,A1)+b2
#激活函数
A2=1/(1+np.exp(-Z2))
assert(A2.shape==(1,X.shape[1]))
cache = {"Z1": Z1,
"A1": A1,
"Z2": Z2,
"A2": A2}
return A2,cache
#代价函数
def compute_cost(A2,Y):
m=Y.shape[1]
logprobs=np.multiply(np.log(A2),Y)+np.multiply(np.log(1-A2),1-Y)
cost=-np.sum(logprobs)/m
cost=np.squeeze(cost)
assert (isinstance(cost, float))
return cost
#反向传播函数
def backward_propagation(parameters,cache,X,Y):
m=X.shape[1]
W1=parameters["W1"]
W2=parameters["W2"]
A1 = cache["A1"]
A2 = cache["A2"]
dZ2 = A2 - Y
dW2 = np.dot(dZ2, A1.T) / m
'''
#这里的w已经是转置过的,在本次实验中,w从初始化的时候就已经是转置过的了。
#所以注意区别dW2 = np.dot(A1,dZ2.T)/m
'''
'''
dW1 5*2
db1 5*1
dZ1 5*n
dW2 1*5
db2 1*1
dZ2 1*n
'''
db2 = np.sum(dZ2, keepdims=True) / m
#dw2是个1行5列的向量
#db2是个行向量
#dZ1将作为下一个输入5*n
dZ1 = np.multiply(np.dot(W2.T, dZ2), (1 - np.power(A1, 2)))
#dW1是5*2
dW1 = np.dot(dZ1, X.T) / m
#1表示水平方向求和
#dw1是个5行2列的向量
#db1是个列向量
db1 = np.sum(dZ1, axis=1, keepdims=True) / m
grads = {"dW1": dW1,
"db1": db1,
"dW2": dW2,
"db2": db2}
return grads
#更新函数
def update_parameter(parameters,grads,learning_rate=1.2):
W1 = parameters["W1"]
b1 = parameters["b1"]
W2 = parameters["W2"]
b2 = parameters["b2"]
dW1 = grads["dW1"]
db1 = grads["db1"]
dW2 = grads["dW2"]
db2 = grads["db2"]
W1 = W1 - learning_rate * dW1
b1 = b1 - learning_rate * db1
W2 = W2 - learning_rate * dW2
b2 = b2 - learning_rate * db2
parameters = {"W1": W1,
"b1": b1,
"W2": W2,
"b2": b2}
return parameters
#初始化函数
def initialize_parameters(n_x, n_h, n_y):
np.random.seed(2)
#5个神经元,每个对应2个特征(这里面的w都是已经转置之后的)
W1=np.random.randn(n_h,n_x)*0.01
b1=np.zeros((n_h,1))
#1个结果,对应5个输入
W2=np.random.randn(n_y,n_h)*0.01
b2=np.zeros((n_y,1))
assert (W1.shape == (n_h, n_x))
assert (b1.shape == (n_h, 1))
assert (W2.shape == (n_y, n_h))
assert (b2.shape == (n_y, 1))
parameters={'W1':W1,
'b1':b1,
'W2':W2,
'b2':b2}
return parameters
#迭代函数,迭代1万次,代价函数在不断变小
def nn_model(X,Y,n_h,num_iterations=10000,print_cost=False):
n_x=layer_size(X,Y)[0]
n_y=layer_size(X,Y)[1]
parameters=initialize_parameters(n_x,n_h,n_y)
for i in range(0,num_iterations):
#向前传播
A2,cache=foward_propagation(X,parameters)
#代价函数
cost=compute_cost(A2,Y)
#向后传播
grads=backward_propagation(parameters,cache,X,Y)
#更新参数
parameters=update_parameter(parameters,grads)
if print_cost and i%1000==0:
print("迭代 %i次,损失函数的值:%f"%(i,cost))
return parameters
#预测函数(还是0/1判断)
def predict(parameters,X):
A2,cache=foward_propagation(X, parameters)
prediction=(A2 > 0.5)
return prediction
parameters = nn_model(X, Y, n_h = 5, num_iterations = 10000, print_cost=True)
plot_decision_boundary(lambda x: predict(parameters, x.T), X, Y)
font = FontProperties(fname=r"c:\windows\fonts\simsun.ttc", size=14)
plt.title(u"隐含层神经元个数=" + str(5),fontproperties=font)
plt.show()
predictions=predict(parameters,X)
print '准确率=%d%%'%(100 - 100*np.mean(np.abs(Y-predictions)))
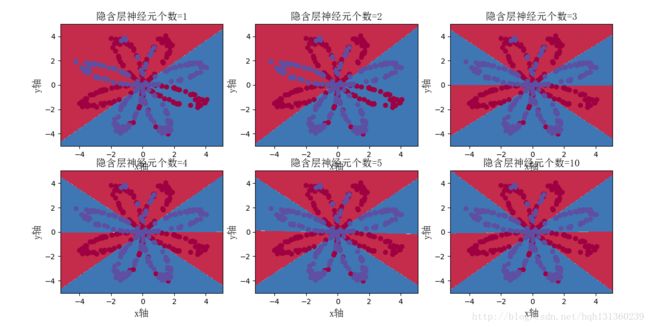
hidden_layer_sizes = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 10]
for i, n_h in enumerate(hidden_layer_sizes):
plt.subplot(2, 3, i+1)
plt.title(u'隐含层神经元个数=%d' % n_h,fontproperties=font)
parameters = nn_model(X, Y, n_h, num_iterations = 5000)
plot_decision_boundary(lambda x: predict(parameters, x.T), X, Y)
predictions = predict(parameters, X)
print '隐含层神经元个数为%d时,准确率=%d%%'%(n_h,100 - 100*np.mean(np.abs(Y-predictions)))
plt.show()针对sklearn中自带的数据生成方法,利用这些数据实现二分
#coding:utf-8
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from planar_utils import plot_decision_boundary, sigmoid, load_planar_dataset, load_extra_datasets
from matplotlib.font_manager import FontProperties
#测试不同的测试集
noisy_circles, noisy_moons, blobs, gaussian_quantiles, no_structure = load_extra_datasets()
datasets = {"noisy_circles": noisy_circles,
"noisy_moons": noisy_moons,
"blobs": blobs,
"gaussian_quantiles": gaussian_quantiles}
dataset = "blobs"
X, Y = datasets[dataset]
X, Y = X.T, Y.reshape(1,-1)
print X.shape
print Y.shape
# make blobs binary
print Y
if dataset == "blobs":
Y = Y%2总结:
#提供画图时候,显示汉字
from matplotlib.font_manager import FontProperties
#提供数据生成
import sklearn.datasets
#提供LR回归方法
import sklearn.linear_model
#模块对应方法使用
font = FontProperties(fname=r"c:\windows\fonts\simsun.ttc", size=14)
plt.ylabel(u'y轴',fontproperties=font)
#固定随机数生成
np.random.seed(1)
#轮廓,等高线,预测值相等的点描绘成一个轮廓,把图像进行分割
#contour 没有颜色填充,只是分割
#contourf 会进行颜色填充
plt.contourf(xx, yy, Z, cmap=plt.cm.Spectral)
#注意两个激活函数,以及激活函数的求导
#注意本神经网络中的W以及是转置之后处理过的