【Object Detection】目标检测综述
【Object Detection】目标检测综述
- 基础知识
- 目标检测模型中的性能评估
- NMS(非极大抑制算法)
- 目标检测中的数据增强
- 目标检测流程
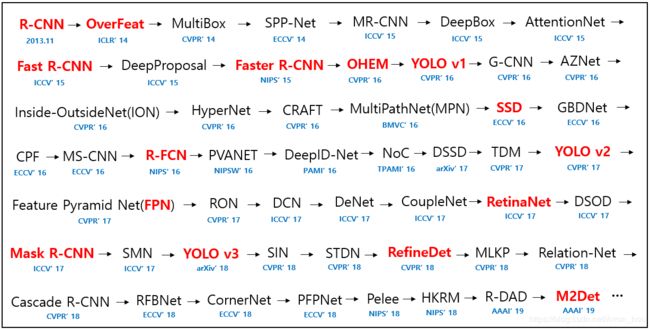
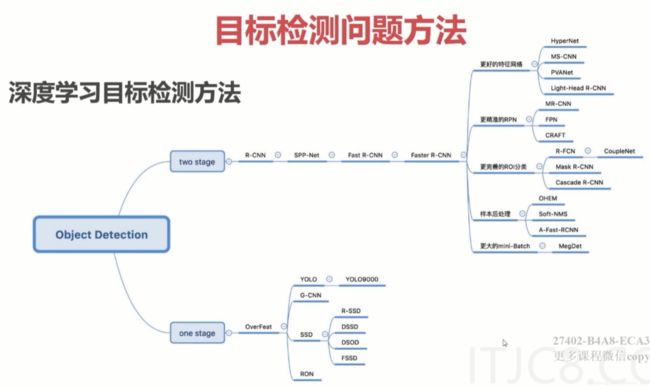
- 各个阶段的目标检测算法
- two-stage
- [R-CNN]
- Bottom-up Object Detection by Grouping Extreme and Center Points
- one-stage
- [YOLO]
- [RefineDet]
- anchor free
- [DenseBox]
- [CornerNet]
- [ExtremeNet]
- [FSAF]
- [FCOS]
- [FoveaBox]
记录一下看过的目标检测论文。
主要来源:
-
吴恩达老师的DeepLearningAI
-
github上相当火的深度学习指导路线
-
国外大神的汇总
-
微信号:我爱计算机视觉计算机视觉开源代码汇总
-
基础知识
目标检测模型中的性能评估
MAP(Mean Average Precision)
https://blog.csdn.net/katherine_hsr/article/details/79266880
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/56961620
https://medium.com/@jonathan_hui/map-mean-average-precision-for-object-detection-45c121a31173
NMS(非极大抑制算法)
IOU(区域交并比)IOU的原称为Intersection over Union,也就是两个box区域的交集比上并集,下面的示意图就很好理解,用于确定两个框的位置像素距离~思路:(注意维度一致)首先计算两个box左上角点坐标的最大值和右下角坐标的最小值然后计算交集面积最后把交集面积除以对应的并集面积其Pytorch源码为:(注意矩阵维度的变化)
IOU计算
def iou(self, box1, box2):
'''
假设box1维度为[N,4] box2维度为[M,4]
'''
N = box1.size(0)
M = box2.size(0)
lt = torch.max( # 左上角的点
box1[:, :2].unsqueeze(1).expand(N, M, 2), # [N,2]->[N,1,2]->[N,M,2]
box2[:, :2].unsqueeze(0).expand(N, M, 2), # [M,2]->[1,M,2]->[N,M,2]
)
rb = torch.min(
box1[:, 2:].unsqueeze(1).expand(N, M, 2),
box2[:, 2:].unsqueeze(0).expand(N, M, 2),
)
wh = rb - lt # [N,M,2]
wh[wh < 0] = 0 # 两个box没有重叠区域
inter = wh[:,:,0] * wh[:,:,1] # [N,M]
area1 = (box1[:,2]-box1[:,0]) * (box1[:,3]-box1[:,1]) # (N,)
area2 = (box2[:,2]-box2[:,0]) * (box2[:,3]-box2[:,1]) # (M,)
area1 = area1.unsqueeze(1).expand(N,M) # (N,M)
area2 = area2.unsqueeze(0).expand(N,M) # (N,M)
iou = inter / (area1+area2-inter)
return iou
其中:
torch.unsqueeze(1) 表示增加一个维度,增加位置为维度1
torch.squeeze(1) 表示减少一个维度
NMS算法一般是为了去掉模型预测后的多余框,其一般设有一个nms_threshold=0.5,具体的实现思路如下:选取这类box中scores最大的哪一个,记为box_best,并保留它计算box_best与其余的box的IOU如果其IOU>0.5了,那么就舍弃这个box(由于可能这两个box表示同一目标,所以保留分数高的哪一个)从最后剩余的boxes中,再找出最大scores的哪一个,如此循环往复
NMS算法
def nms(self, bboxes, scores, threshold=0.5):
'''
bboxes维度为[N,4],scores维度为[N,], 均为tensor
'''
x1 = bboxes[:,0]
y1 = bboxes[:,1]
x2 = bboxes[:,2]
y2 = bboxes[:,3]
areas = (x2-x1)*(y2-y1) # [N,] 每个bbox的面积
_, order = scores.sort(0, descending=True) # 降序排列
keep = []
while order.numel() > 0: # torch.numel()返回张量元素个数
if order.numel() == 1: # 保留框只剩一个
i = order.item()
keep.append(i)
break
else:
i = order[0].item() # 保留scores最大的那个框box[i]
keep.append(i)
# 计算box[i]与其余各框的IOU(思路很好)
xx1 = x1[order[1:]].clamp(min=x1[i]) # [N-1,]
yy1 = y1[order[1:]].clamp(min=y1[i])
xx2 = x2[order[1:]].clamp(max=x2[i])
yy2 = y2[order[1:]].clamp(max=y2[i])
inter = (xx2-xx1).clamp(min=0) * (yy2-yy1).clamp(min=0) # [N-1,]
iou = inter / (areas[i]+areas[order[1:]]-inter) # [N-1,]
idx = (iou <= threshold).nonzero().squeeze() # 注意此时idx为[N-1,] 而order为[N,]
if idx.numel() == 0:
break
order = order[idx+1] # 修补索引之间的差值
return torch.LongTensor(keep)
Pytorch的索引值为LongTensor
其中:torch.numel() 表示一个张量总元素的个数
torch.clamp(min, max) 设置上下限
tensor.item() 把tensor元素取出作为numpy数字
链接:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/54709759
NMS各种变种,主要用于文字检测
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/50126479
soft-NMS
https://blog.csdn.net/lanyuxuan100/article/details/78767818
softer-NMS
https://blog.csdn.net/lcczzu/article/details/86518615
目标检测中的数据增强
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/54566524
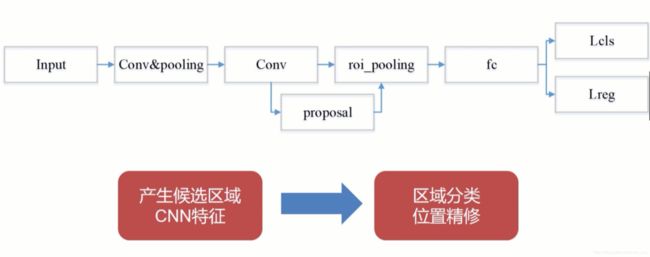
目标检测流程
各个阶段的目标检测算法
深度学习前:
- Viola-Jones
- HOG+SVM
- DPM
深度学习:
two-stage
- CNN 提取特征
- 在faster RCNN 后,基本上使用RPN(region proposal network)网络 + ROI (region of interest pooling)提取检测区域。(第一步)
- 然后对检测区域回归边框,分类。(第二步)
[R-CNN]
Bottom-up Object Detection by Grouping Extreme and Center Points
[翻译] https://alvinzhu.xyz/2017/10/09/r-cnn/
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_35451572/article/details/80249259
https://www.cnblogs.com/zyly/p/9246221.html
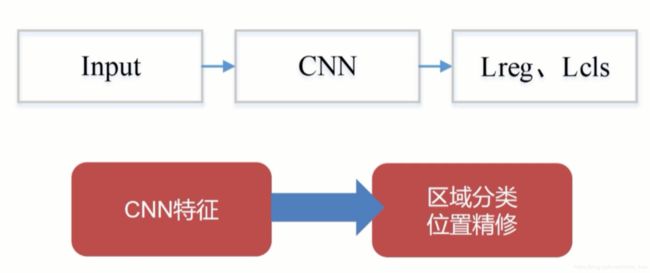
one-stage
- CNN 提取特征
- 直接对feature map 进行分类预测以及位置回归。所以是一步到位,称为one stage。
- 与one-stage 相比,速度快,精度差。
基本流程
常见one stage 算法

[YOLO]
[RefineDet]
https://arxiv.org/abs/1506.02640
anchor free
1.早期探索:
- DenseBox
- YOLO
2.基于关键点:
- CornerNet
- ExtremeNet
3.密集预测
- FSAF
- FCOS
- FoveaBox
[DenseBox]
https://arxiv.org/abs/1509.04874
[CornerNet]
https://arxiv.org/abs/1808.01244
[ExtremeNet]
https://arxiv.org/abs/1901.08043
[FSAF]
https://arxiv.org/abs/1903.00621
[FCOS]
https://arxiv.org/abs/1904.01355
[FoveaBox]
https://arxiv.org/abs/1904.03797v1