FAST算法解析
一、FAST特征点
在像素点的周围邻域内有足够多的像素点与该点处于不同的灰度区域。在灰度图像中,也就是有足够多的像素点的灰度值大于该点的灰度值或者小于该点的灰度值。
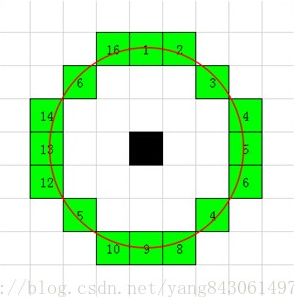
通常选取以像素点为中心的半径为3的离散化的Bresenham元形区域。
在OpenCV中,当patternSize为16时,用以下数组表示这16个点相对于圆心的坐标:
static const int offsets16[][2] =
{
{0, 3}, { 1, 3}, { 2, 2}, { 3, 1}, { 3, 0}, { 3, -1}, { 2, -2}, { 1, -3},
{0, -3}, {-1, -3}, {-2, -2}, {-3, -1}, {-3, 0}, {-3, 1}, {-2, 2}, {-1, 3}
};
OpenCV用函数来计算圆周上的点相对于圆心坐标在原图像中的位置:
void makeOffsets(int pixel[25], int rowStride, int patternSize)
{
//分别定义三个数组,用于表示patternSize为16,12和8时,圆周像素对于圆心的相对坐标位置
static const int offsets16[][2] =
{
{0, 3}, { 1, 3}, { 2, 2}, { 3, 1}, { 3, 0}, { 3, -1}, { 2, -2}, { 1, -3},
{0, -3}, {-1, -3}, {-2, -2}, {-3, -1}, {-3, 0}, {-3, 1}, {-2, 2}, {-1, 3}
};
static const int offsets12[][2] =
{
{0, 2}, { 1, 2}, { 2, 1}, { 2, 0}, { 2, -1}, { 1, -2},
{0, -2}, {-1, -2}, {-2, -1}, {-2, 0}, {-2, 1}, {-1, 2}
};
static const int offsets8[][2] =
{
{0, 1}, { 1, 1}, { 1, 0}, { 1, -1},
{0, -1}, {-1, -1}, {-1, 0}, {-1, 1}
};
//根据patternSize值,得到具体应用上面定义的哪个数组
const int (*offsets)[2] = patternSize == 16 ? offsets16 :
patternSize == 12 ? offsets12 :
patternSize == 8 ? offsets8 : 0;
CV_Assert(pixel && offsets);
int k = 0;
//代入输入图像每行的像素个数,得到圆周像素的绝对坐标位置
for( ; k < patternSize; k++ )
pixel[k] = offsets[k][0] + offsets[k][1] * rowStride;
for( ; k < 25; k++ )//由于要计算连续的像素,因此要循环的多列出一些值
pixel[k] = pixel[k - patternSize];
} 一个候选点是否为特征点可由下面公式判断:
I(x)为圆周上的任意一点像素值;
I(p)为候选点像素值;
N为圆周上有N个点满足则为角点,如N=12
二、OpenCV的FAST源代码解析
来源:http://blog.csdn.net/zhaocj/article/details/40301561
template
void FAST_t(InputArray _img, std::vector& keypoints, int threshold, bool nonmax_suppression)
{
//http://blog.csdn.net/zhaocj/article/details/40301561
Mat img = _img.getMat();
//K为圆周连续像素的个数
//N用于循环圆周的像素点,因为要首尾连接,所以N要比实际圆周像素数量多K+1个
const int K = patternSize/2, N = patternSize + K + 1;
#if CV_SSE2
const int quarterPatternSize = patternSize/4;
(void)quarterPatternSize;
#endif
int i, j, k, pixel[25];
//找到圆周像素点相对于圆心的偏移量
makeOffsets(pixel, (int)img.step, patternSize);
keypoints.clear();
//保证阈值不大于255,不小于0
threshold = std::min(std::max(threshold, 0), 255);
#if CV_SSE2
__m128i delta = _mm_set1_epi8(-128), t = _mm_set1_epi8((char)threshold), K16 = _mm_set1_epi8((char)K);
(void)K16;
(void)delta;
(void)t;
#endif
// threshold_tab为阈值列表,在进行阈值比较的时候,只需查该表即可
uchar threshold_tab[512];
/*
阈值列表赋值,
该表分为三段:
第一段从threshold_tab[0]至threshold_tab[255 - threshold],值为1,落在该区域的值表示满足角点判断条件:
集合S由圆周上N个连续的像素x组成,Ix < Ip - t;
第二段从threshold_tab[255 – threshold]至threshold_tab[255 + threshold],值为0,落在该区域的值表示不是角点;
第三段从threshold_tab[255 + threshold]至threshold_tab[511],值为2,落在该区域的值表示满足角点判断条件:
集合S由圆周上N个连续的像素x组成,Ix > Ip + t;
*/
for( i = -255; i <= 255; i++ )
threshold_tab[i+255] = (uchar)(i < -threshold ? 1 : i > threshold ? 2 : 0);
AutoBuffer _buf((img.cols+16)*3*(sizeof(int) + sizeof(uchar)) + 128);
/*
buf[0、buf[1]和buf[2]分别表示图像的前一行、当前行和后一行。
因为在非极大值抑制的步骤2中,是要在3×3的角点邻域内进行比较,
因此需要三行的图像数据。
*/
uchar* buf[3];
buf[0] = _buf; buf[1] = buf[0] + img.cols; buf[2] = buf[1] + img.cols;
int* cpbuf[3];
/*
alignPtr:对齐指针
在某些架构上,只有能被指定数(如4,16)整除的内存地址才能够被访问,否则程序会crash,或者出现错误的结果,或者数据的访问变慢。
举个例子来说,很多系统都要求interger的地址从偶数开始。
template < typename _Tp > static inline _Tp* alignPtr ( _Tp* ptr , int n = ( int ) sizeof ( _Tp ) ) {
return ( _Tp* ) ( ( ( size_t ) ptr + n - 1 ) & - n ) ;
}
& - n:
n是2的幂,其二进制也就只有一个1,比如n默认为16的时候为00010000,取负数得到111110000,效果是对于2^k,得到一个低k为为0,其他
位为1的数,拿这个数(-n)和别的数做与操作,等于把别的数的低k位截没了。这样得到的数必然是2^k的倍数(低k位为0的数必然是2^k的
倍数)。这一效果仅对n=2^k成立。
*/
//cpbuf存储角点的坐标位置,也是需要连续三行的数据
cpbuf[0] = (int*)alignPtr(buf[2] + img.cols, sizeof(int)) + 1;//+1腾出一个位置存放角点的数目:cornerpos[-1] = ncorners;
cpbuf[1] = cpbuf[0] + img.cols + 1;
cpbuf[2] = cpbuf[1] + img.cols + 1;
memset(buf[0], 0, img.cols*3);
for(i = 3; i < img.rows-2; i++)//防止越界
{
const uchar* ptr = img.ptr(i) + 3;//得到图像行的首地址指针
//得到buf、cpbuf的某行数组,用于存储当前行的得分函数的值V
uchar* curr = buf[(i - 3)%3];
int* cornerpos = cpbuf[(i - 3)%3];
memset(curr, 0, img.cols);
int ncorners = 0; //检测到的角点数量
if( i < img.rows - 3 )
{
j = 3;
#if CV_SSE2
if( patternSize == 16 )
{
for(; j < img.cols - 16 - 3; j += 16, ptr += 16)
{
__m128i m0, m1;
__m128i v0 = _mm_loadu_si128((const __m128i*)ptr);
__m128i v1 = _mm_xor_si128(_mm_subs_epu8(v0, t), delta);
v0 = _mm_xor_si128(_mm_adds_epu8(v0, t), delta);
__m128i x0 = _mm_sub_epi8(_mm_loadu_si128((const __m128i*)(ptr + pixel[0])), delta);
__m128i x1 = _mm_sub_epi8(_mm_loadu_si128((const __m128i*)(ptr + pixel[quarterPatternSize])), delta);
__m128i x2 = _mm_sub_epi8(_mm_loadu_si128((const __m128i*)(ptr + pixel[2*quarterPatternSize])), delta);
__m128i x3 = _mm_sub_epi8(_mm_loadu_si128((const __m128i*)(ptr + pixel[3*quarterPatternSize])), delta);
m0 = _mm_and_si128(_mm_cmpgt_epi8(x0, v0), _mm_cmpgt_epi8(x1, v0));
m1 = _mm_and_si128(_mm_cmpgt_epi8(v1, x0), _mm_cmpgt_epi8(v1, x1));
m0 = _mm_or_si128(m0, _mm_and_si128(_mm_cmpgt_epi8(x1, v0), _mm_cmpgt_epi8(x2, v0)));
m1 = _mm_or_si128(m1, _mm_and_si128(_mm_cmpgt_epi8(v1, x1), _mm_cmpgt_epi8(v1, x2)));
m0 = _mm_or_si128(m0, _mm_and_si128(_mm_cmpgt_epi8(x2, v0), _mm_cmpgt_epi8(x3, v0)));
m1 = _mm_or_si128(m1, _mm_and_si128(_mm_cmpgt_epi8(v1, x2), _mm_cmpgt_epi8(v1, x3)));
m0 = _mm_or_si128(m0, _mm_and_si128(_mm_cmpgt_epi8(x3, v0), _mm_cmpgt_epi8(x0, v0)));
m1 = _mm_or_si128(m1, _mm_and_si128(_mm_cmpgt_epi8(v1, x3), _mm_cmpgt_epi8(v1, x0)));
m0 = _mm_or_si128(m0, m1);
int mask = _mm_movemask_epi8(m0);
if( mask == 0 )
continue;
if( (mask & 255) == 0 )
{
j -= 8;
ptr -= 8;
continue;
}
__m128i c0 = _mm_setzero_si128(), c1 = c0, max0 = c0, max1 = c0;
for( k = 0; k < N; k++ )
{
__m128i x = _mm_xor_si128(_mm_loadu_si128((const __m128i*)(ptr + pixel[k])), delta);
m0 = _mm_cmpgt_epi8(x, v0);
m1 = _mm_cmpgt_epi8(v1, x);
c0 = _mm_and_si128(_mm_sub_epi8(c0, m0), m0);
c1 = _mm_and_si128(_mm_sub_epi8(c1, m1), m1);
max0 = _mm_max_epu8(max0, c0);
max1 = _mm_max_epu8(max1, c1);
}
max0 = _mm_max_epu8(max0, max1);
int m = _mm_movemask_epi8(_mm_cmpgt_epi8(max0, K16));
for( k = 0; m > 0 && k < 16; k++, m >>= 1 )
if(m & 1)
{
cornerpos[ncorners++] = j+k;
if(nonmax_suppression)
curr[j+k] = (uchar)cornerScore(ptr+k, pixel, threshold);
}
}
}
#endif
for( ; j < img.cols - 3; j++, ptr++ )
{
int v = ptr[0];//当前像素的灰度值
const uchar* tab = &threshold_tab[0] - v + 255;//由当前像素的灰度值,确定其在阈值列表中的位置
/*
pixel[0]表示圆周上编号为0的像素相对于圆心坐标的偏移量
ptr[pixel[0]表示圆周上编号为0的像素值
tab[ptr[pixel[0]]]表示相对于当前像素(即圆心)圆周上编号为0的像素值在阈值列表threshold_tab中所查询得到的值
*/
//检查在位置1、9、5和13四个位置的像素,把一个减法和比较操作变成查表方式
int d = tab[ptr[pixel[0]]] | tab[ptr[pixel[8]]];
/*
d的四种情况:
d=0 说明编号为0和8的值都是0;
d=1 说明编号为0和8的值至少有一个为1,而另一个不能为2;
d=2 说明编号为0和8的值至少有一个为2,而另一个不能为1;
d=3 说明编号为0和8的值有一个为1,另一个为2。
*/
//1和9与中点比较不符合特征点条件
if( d == 0 )//d=0说明圆周上不可能有连续12个像素满足角点条件,因此当前值一定不是角点
continue;
//继续进行其他直径上两个像素点的判断
d &= tab[ptr[pixel[2]]] | tab[ptr[pixel[10]]];
d &= tab[ptr[pixel[4]]] | tab[ptr[pixel[12]]];
d &= tab[ptr[pixel[6]]] | tab[ptr[pixel[14]]];
/*
d=0
说明上述d中至少有一个d为0,所以肯定不是角点;
另一种情况是一个d为2,而另一个d为1,相与后也为0,这说明一个是满足角点条件1,而另一个满足角点条件2,
所以肯定也不会有连续12个像素满足同一个角点条件的,因此也一定不是角点。
*/
if( d == 0 )
continue;
d &= tab[ptr[pixel[1]]] | tab[ptr[pixel[9]]];
d &= tab[ptr[pixel[3]]] | tab[ptr[pixel[11]]];
d &= tab[ptr[pixel[5]]] | tab[ptr[pixel[13]]];
d &= tab[ptr[pixel[7]]] | tab[ptr[pixel[15]]];
if( d & 1 )
{
//vt为真正的角点条件,即Ip – t,count为连续像素的计数值
int vt = v - threshold, count = 0;
//遍历整个圆周
for( k = 0; k < N; k++ )
{
int x = ptr[pixel[k]];//提取出圆周上的像素值
if(x < vt)
{
if( ++count > K )//连续计数,并判断是否大于K(K为圆周像素的一半)
{
cornerpos[ncorners++] = j;//保存该点的位置,并把当前行的角点数加1
if(nonmax_suppression)//进行非极大值抑制的第一步,计算得分函数
curr[j] = (uchar)cornerScore(ptr, pixel, threshold);
break;//得到一个角点,退出循环
}//++count > K
}//x < vt
else
count = 0;
}//k
}//d & 1
if( d & 2 )
{
int vt = v + threshold, count = 0;
for( k = 0; k < N; k++ )
{
int x = ptr[pixel[k]];
if(x > vt)
{
if( ++count > K )
{
cornerpos[ncorners++] = j;
if(nonmax_suppression)
curr[j] = (uchar)cornerScore(ptr, pixel, threshold);
break;
}//++count > K
}//x > vt
else
count = 0;
}//k
}//d & 2
}//j
}//i < img.rows - 3
cornerpos[-1] = ncorners;//保存当前行所检测到的角点数
if( i == 3 )//i=3说明只仅仅计算了一行的数据,还不能进行非极大值抑制的第二步,所以不进行下面代码的操作,直接进入下一次循环
continue;
//非极大值抑制
//提取出上一行和上两行的图像像素
const uchar* prev = buf[(i - 4 + 3)%3];//3行的第1行地址
const uchar* pprev = buf[(i - 5 + 3)%3];//3行的第3行地址
cornerpos = cpbuf[(i - 4 + 3)%3];//提取出上一行所检测到的角点位置
ncorners = cornerpos[-1];//提取出上一行的角点数
for( k = 0; k < ncorners; k++ )
{
j = cornerpos[k];
int score = prev[j];
if( !nonmax_suppression ||
(score > prev[j+1] && score > prev[j-1] &&
score > pprev[j-1] && score > pprev[j] && score > pprev[j+1] &&
score > curr[j-1] && score > curr[j] && score > curr[j+1]) )
{
keypoints.push_back(KeyPoint((float)j, (float)(i-1), 7.f, -1, (float)score));
}//if
}//k
}//i
}