android 自定义View之继承ViewGroup实现流式布局
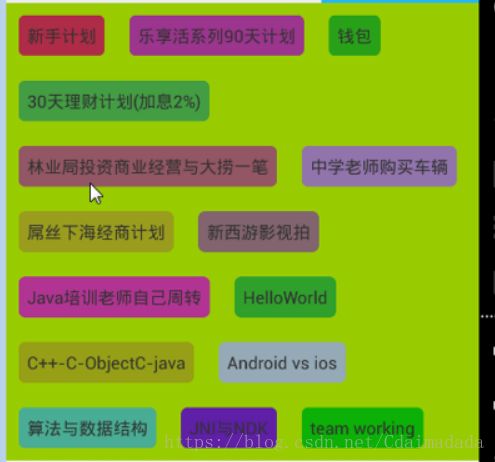
主要实现效果如下:
接下来讲述如何实现:
xml布局
xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical">
android:id="@+id/flow"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="@android:color/holo_green_light">
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/hello_world"/>
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="你好"/>
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="javaandroidjkdsajl"/>
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="笑話不好笑吧dsadasda"/>
通过自定义ViewGroup实现:
1:onMeasure:测量view的宽高--
在重写的onMeasure方法中,会传入2个参数,他们分别代表“宽的测量规格”,“高的测量规格”,如下所示(spec:规格)
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
测量规格由测量模式和测量值组成,得到了测量规格就可以得到测量模式和测量值,如下所示:
int widthMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec); int widthSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec); int heightMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec); int heightSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
测量模式
1.EXACTLY:精确模式,eg:100dp,match_parent;
2.AT_MOST:至多模式,view最多可以获得的宽高值,它需要计算所有包含的子View的宽高,最后计算出来的宽高总和值,eg:wrap_content;
3.UNSPECIFFIED:未指定模式,想设置多宽多高,就给你多宽多高,一般的控件不会指定这种模式,单页存在,eg:scrollView的宽高测量就是使用这种模式
在我们的流式布局内,应该怎么设置布局的宽高呢?
1:如果布局指定的宽是match_parent或者精确的宽度值,那么直接就可以从父控件传入的测量规格中直接获取布局宽度,高度同理
2:如果布局指定的宽高不是EXACTLY,而是wrap_content,那么这时候,就需要计算每一个子View的宽高,来决定布局的宽高了。
宽度:摆放的所有子View占据宽度最多的一行,作为布局宽度
高度:摆放的所有子View共占据几行的高度总和
宽度=子View最多的那行的宽度=每一个子View的宽度+leftMargin+RightMargin
高度=所有行的高度=每一行的高度+topMargin+bottomMargin;
setMeasureDimenSion() ---->设置流式布局的宽高。
具体代码如下:
@Override protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) { int widthMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec); int widthSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec); int heightMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec); int heightSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec); int width = 0; int height = 0; int lineWidth = 0; int lineHeight = 0; //求取at_most模式下的布局宽、高值 int cCount = getChildCount();//返回此布局下的View的个数 for (int i = 0; i < cCount; i++) { View child = getChildAt(i);
//这个函数是viewGroup提供的方法,供其子类使用测量child尺寸
measureChild(child
, widthMeasureSpec
, heightMeasureSpec)
;
int childWidth = child.getMeasuredWidth()
;
int childHeight = child.getMeasuredHeight()
;
MarginLayoutParams mp = ((MarginLayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams())
;/*通过MarginLayoutParams得到leftMargin等边距,注意下面
@Override public LayoutParams generateLayoutParams(AttributeSet attrs) {
MarginLayoutParams mp = new MarginLayoutParams(getContext(), attrs); return mp; }的实现
*/if (lineWidth + childWidth + mp. leftMargin + mp. rightMargin > widthSize) { // 换行 : 宽度 -- 对比获取 width = Math. max(width , lineWidth) ; height += lineHeight ; // 重置一下 lineWidth = childWidth + mp. leftMargin + mp. rightMargin ; lineHeight = childHeight + mp. topMargin + mp. bottomMargin ; } else { // 不换行 : 行高 -- 对比获得 lineWidth += childWidth + mp. leftMargin + mp. rightMargin ; lineHeight = Math. max(lineHeight , childHeight + mp. topMargin + mp. bottomMargin) ; } // 最后一次还要再参与计算一次 if (i == cCount - 1) { width = Math. max(width , lineWidth) ; height += lineHeight ; } } Log. e( "zoubo" , "width:" + width + "----heigth:" + height) ; setMeasuredDimension(widthMode == MeasureSpec. EXACTLY ? widthSize : width , heightMode == MeasureSpec. EXACTLY ? heightSize : height) ;}
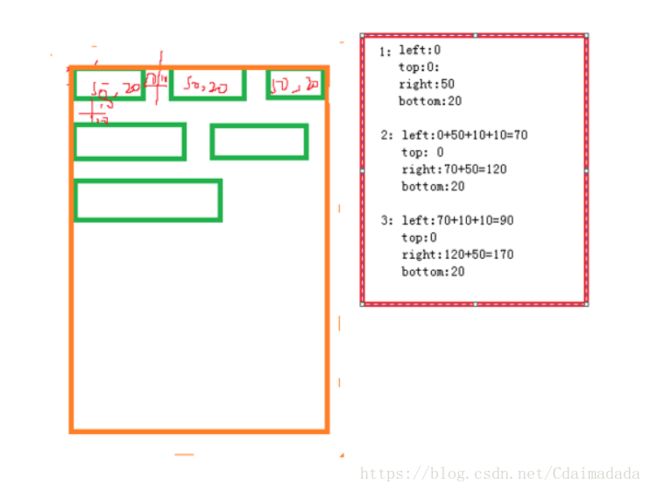
如果测量模式选择至多模式的话:
依图,有如下
布局的行宽取第一行和第二行的最大值作为行宽
布局的高度取第一行和第二行的高度和最为列高
这样,view的宽高就确定下来了。
接下来就是onLayout()的实现了。
onLayout用于设置viewGroup内包含的所有子View的位置
获取到每一行的每一个子View,计算出它的left、top、right和bottom,调用layout方法设置其在流式布局当中的位置。
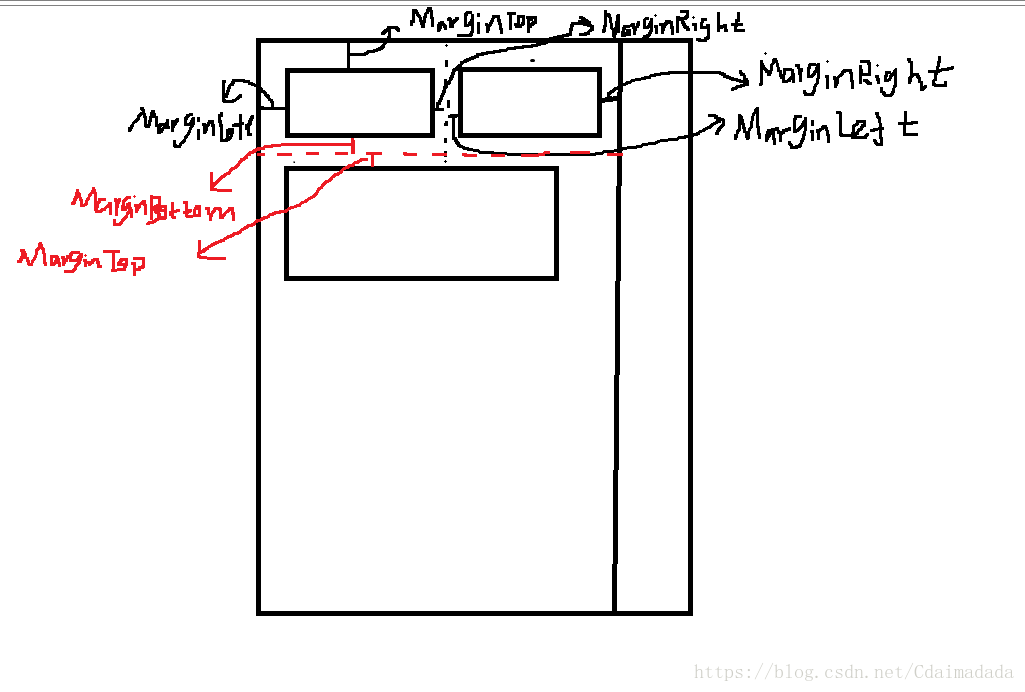
首先理解了下面这个图,下面的代码就好理解了。
left、top、right和bottom都是根据父布局的左上角顶点来衡量的。
代码如下:
//每一行所包含的所有子view
private List> allViews = new ArrayList<>();
private List allHeights = new ArrayList<>();
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
int width = getWidth();
int cCount = getChildCount();
int lineWidth = 0;
int lineHeight = 0;
List lineViews = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < cCount; i++) {
View child = getChildAt(i);
int childWidth = child.getMeasuredWidth();//因为在onMeasure()中已经调用了 measureChild(child,
// widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);,所以这里可以直接取值
int childHeight = child.getMeasuredHeight();
MarginLayoutParams mp = ((MarginLayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams());
if (lineWidth + childWidth + mp.leftMargin + mp.rightMargin > width) {
//换行
allViews.add(lineViews);
allHeights.add(lineHeight);
//重置一下变量
lineViews = new ArrayList<>();
lineWidth = 0;
lineHeight = childHeight + mp.topMargin + mp.bottomMargin;
}
//不换行
lineWidth += childWidth + mp.leftMargin + mp.rightMargin;
lineHeight = Math.max(lineHeight, childHeight + mp.topMargin + mp.bottomMargin);
lineViews.add(child);
if (i == cCount - 1) {
allViews.add(lineViews);
allHeights.add(lineHeight);
}
}
//通过计算每一行的每一个子view的left,top,right,bottom,摆放每一行的每一个子view的位置
int left = 0;
int top = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < allViews.size(); i++) {
int curLineHeight = allHeights.get(i);
//当前行的所有子view
List views = allViews.get(i);
for (View view : views) {
int viewWidth = view.getMeasuredWidth();
int viewHeight = view.getMeasuredHeight();
MarginLayoutParams mp = ((MarginLayoutParams) view.getLayoutParams());
int lc = left + mp.leftMargin;
int tc = top + mp.topMargin;
int rc = lc + viewWidth;
int bc = tc + viewHeight;
view.layout(lc, tc, rc, bc);
left += viewWidth + mp.rightMargin + mp.leftMargin;
}
left = 0;
top += curLineHeight;
}
} 这里有一个比较值得参考的就是:
private List> allViews = new ArrayList<>();