剑指offer题解(十):C++&java
二叉搜索树的后序遍历序列
题目描述
输入一个整数数组,判断该数组是不是某二叉搜索树的后序遍历的结果。假设输入的数组的任意两个数字都互不相同。
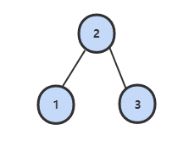
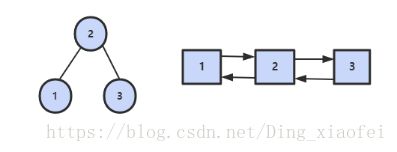
例如,下图是后序遍历序列 3,1,2 所对应的二叉搜索树。
解题思路
BST的后序序列的合法序列是,对于一个序列S,最后一个元素是x (也就是根),如果去掉最后一个元素的序列为T,那么T满足:T可以分成两段,前一段(左子树)小于x,后一段(右子树)大于x,且这两段(子树)都是合法的后序序列。完美的递归定义
c++
class Solution {
private:
bool func(vector<int>&a, int l, int r)
{
if(l >= r) return true;
int i = r;
while(i > l && a[i - 1] > a[r]) --i;
for(int j = i - 1; j >= l; --j) if(a[j] > a[r]) return false;
return func(a, l, i - 1)&&func(a,i,r-1);
}
public:
bool VerifySquenceOfBST(vector<int> sequence) {
if(!sequence.size()) return false;
return func(sequence, 0, sequence.size() - 1);
}
};java
public boolean VerifySquenceOfBST(int[] sequence) {
if (sequence == null || sequence.length == 0)
return false;
return verify(sequence, 0, sequence.length - 1);
}
private boolean verify(int[] sequence, int first, int last) {
if (last - first <= 1)
return true;
int rootVal = sequence[last];
int cutIndex = first;
while (cutIndex < last && sequence[cutIndex] <= rootVal)
cutIndex++;
for (int i = cutIndex + 1; i < last; i++)
if (sequence[i] < rootVal)
return false;
return verify(sequence, first, cutIndex - 1) && verify(sequence, cutIndex, last - 1);
}二叉树中和为某一值的路径
题目描述
输入一颗二叉树和一个整数,打印出二叉树中结点值的和为输入整数的所有路径。路径定义为从树的根结点开始往下一直到叶结点所经过的结点形成一条路径。
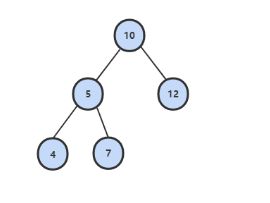
下图的二叉树有两条和为 22 的路径:10, 5, 7 和 10, 12
解题思路
class Solution {
private:
void dfs(TreeNode* root,int s,vector<vector<int>> &ret,vector<int> &trace)
{
trace.push_back(root->val);
if(root->left == NULL&& root->right==NULL)
{
if(root->val == s)
ret.push_back(trace);
}
if(root->left != NULL)
dfs(root->left, s-root->val, ret, trace);
if(root->right != NULL)
dfs(root->right, s-root->val, ret, trace);
trace.pop_back();
}
public:
vector<vector<int> > FindPath(TreeNode* root,int expectNumber) {
vector<vector<int>> res;
vector<int> trace;
if(root) dfs(root,expectNumber,res,trace);
return res;
}
};java
private ArrayList> ret = new ArrayList<>();
public ArrayList> FindPath(TreeNode root, int target) {
backtracking(root, target, new ArrayList<>());
return ret;
}
private void backtracking(TreeNode node, int target, ArrayList path) {
if (node == null)
return;
path.add(node.val);
target -= node.val;
if (target == 0 && node.left == null && node.right == null) {
ret.add(new ArrayList(path));
} else {
backtracking(node.left, target, path);
backtracking(node.right, target, path);
}
path.remove(path.size() - 1);
} python
def pathSum(self, root, sum):
if not root:
return []
res = []
self.dfs(root, sum, [], res)
return res
def dfs(self, root, sum, ls, res):
if not root.left and not root.right and sum == root.val:
ls.append(root.val)
res.append(ls)
if root.left:
self.dfs(root.left, sum-root.val, ls+[root.val], res)
if root.right:
self.dfs(root.right, sum-root.val, ls+[root.val], res)复杂链表的复制
题目描述
输入一个复杂链表(每个节点中有节点值,以及两个指针,一个指向下一个节点,另一个特殊指针指向任意一个节点),返回结果为复制后复杂链表的 head。
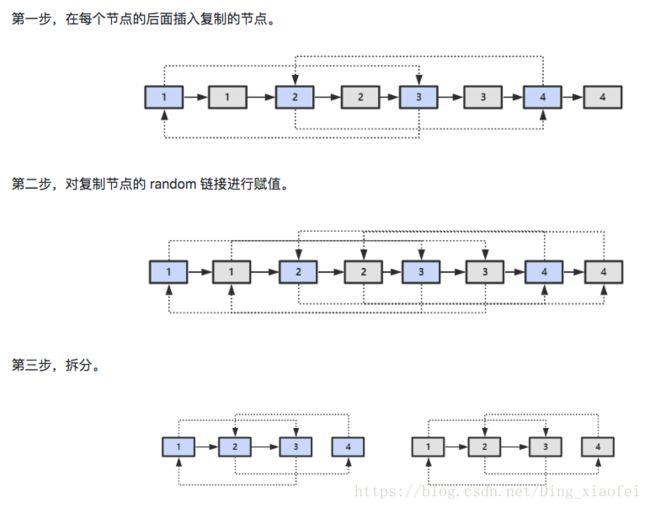
解题思路
c++
/*
struct RandomListNode {
int label;
struct RandomListNode *next, *random;
RandomListNode(int x) :
label(x), next(NULL), random(NULL) {
}
};
*/
class Solution {
public:
RandomListNode* Clone(RandomListNode* pHead)
{
if(pHead == NULL)
return NULL;
RandomListNode * cur = pHead;
//插入新节点
while(cur!=NULL)
{
RandomListNode *newnode = new RandomListNode(cur->label);
newnode->next = cur->next;
cur->next = newnode;
cur = newnode->next;
}
//建立random链接
cur = pHead;
while(cur!=NULL)
{
RandomListNode *newnode = cur->next;
if(cur->random != NULL)
newnode->random = cur->random->next;
cur = newnode -> next;
}
//拆分
cur = pHead;
RandomListNode *pclonehead = pHead->next;
while(cur->next != NULL)
{
RandomListNode *next = cur->next;
cur->next = next ->next;
cur = next;
}
return pclonehead;
}
};java
public RandomListNode Clone(RandomListNode pHead) {
if (pHead == null)
return null;
// 插入新节点
RandomListNode cur = pHead;
while (cur != null) {
RandomListNode clone = new RandomListNode(cur.label);
clone.next = cur.next;
cur.next = clone;
cur = clone.next;
}
// 建立 random 链接
cur = pHead;
while (cur != null) {
RandomListNode clone = cur.next;
if (cur.random != null)
clone.random = cur.random.next;
cur = clone.next;
}
// 拆分
cur = pHead;
RandomListNode pCloneHead = pHead.next;
while (cur.next != null) {
RandomListNode next = cur.next;
cur.next = next.next;
cur = next;
}
return pCloneHead;
}二叉搜索树与双向链表
题目描述
输入一棵二叉搜索树,将该二叉搜索树转换成一个排序的双向链表。要求不能创建任何新的结点,只能调整树中结点指针的指向。
java
private TreeNode pre = null;
private TreeNode head = null;
public TreeNode Convert(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null)
return null;
inOrder(root);
return head;
}
private void inOrder(TreeNode node) {
if (node == null)
return;
inOrder(node.left);
node.left = pre;
if (pre != null)
pre.right = node;
pre = node;
if (head == null)
head = node;
inOrder(node.right);
}c++
//直接用中序遍历
public class Solution {
TreeNode head = null;
TreeNode realHead = null;
public TreeNode Convert(TreeNode pRootOfTree) {
ConvertSub(pRootOfTree);
return realHead;
}
private void ConvertSub(TreeNode pRootOfTree) {
if(pRootOfTree==null) return;
ConvertSub(pRootOfTree.left);
if (head == null) {
head = pRootOfTree;
realHead = pRootOfTree;
} else {
head.right = pRootOfTree;
pRootOfTree.left = head;
head = pRootOfTree;
}
ConvertSub(pRootOfTree.right);
}
}