TensorFlow之线性回归
通过tensorflow实现一个简易的线性回归,代码如下:
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
#定义训练数据
train_x = np.linspace(-1,1,100)
train_y = 3*train_x + np.random.randn(*train_x.shape)*0.33 + 10
#定义输入输出
x = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.float32)
y_ = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.float32)
#定义权值和偏置
w = tf.Variable(0.0,name="weight")
b = tf.Variable(0.0,name="bias")
#定义预测输出
y = w*x + b
#定义损失函数和反向传播算法
loss = tf.square(y-y_)
train_step = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.01).minimize(loss)
#创建会话
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(tf.initialize_all_variables())
for i in range(10):
for (X,Y) in zip(train_x,train_y):
_,w_value,b_value = sess.run([train_step,w,b],feed_dict={x:X,y_:Y})
print("step:{},w:{},b:{}".format(i+1,w_value,b_value))
#绘图
plt.plot(train_x,train_y,'+')
plt.plot(train_x,w.eval()*train_x+b.eval())
plt.show()
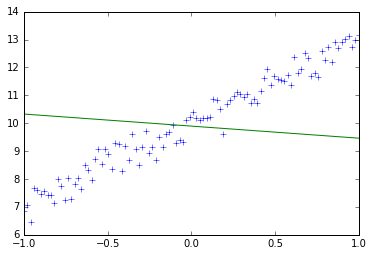
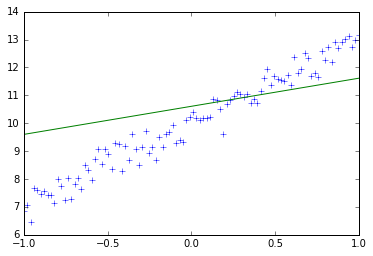
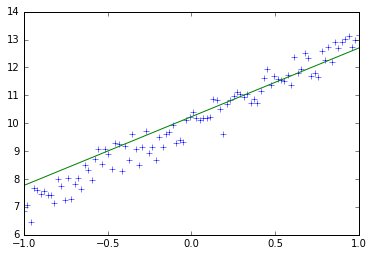
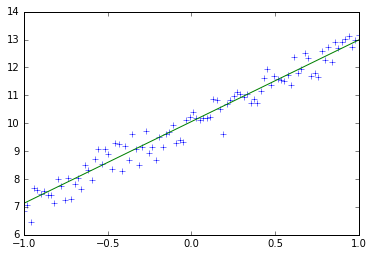
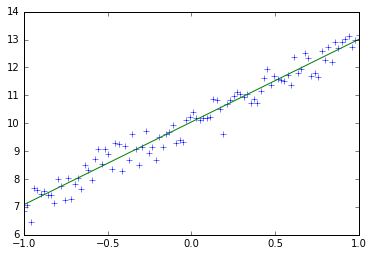
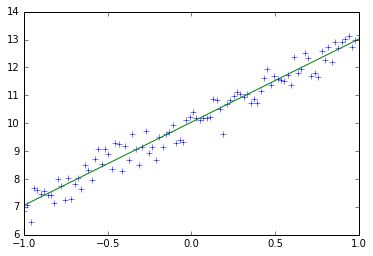
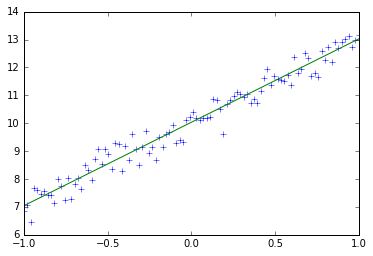
训练10次后,w接近为3,b接近为10,这和上述代码定义训练数据中的train_y的定义十分接近,10次迭代训练的每一次权值和偏置变化以及图形变化如下所示:
step:1,w:-0.4323926568031311,b:9.895733833312988
step:2,w:1.006221890449524,b:10.605839729309082
step:3,w:1.9528942108154297,b:10.40628719329834
step:4,w:2.4621810913085938,b:10.232091903686523
step:5,w:2.7247731685638428,b:10.134077072143555
step:6,w:2.8587703704833984,b:10.083012580871582
step:7,w:2.926967144012451,b:10.056891441345215
step:8,w:2.961653470993042,b:10.043588638305664
step:9,w:2.9792935848236084,b:10.036816596984863
step:10,w:2.9882631301879883,b:10.03337574005127