浅拷贝和深拷贝,List拷贝总结
最近在项目中看到Collections.copy的使用,于是想对Java的拷贝相关知识有更深入的了解,便有了本篇文章的总结。
Java的拷贝可以分为三种:浅拷贝(Shallow Copy)、深拷贝(Deep Copy)、延迟拷贝(Lazy Copy)。
在java中除了基本数据类型之外(int,long,short等),还存在引用数据类型,例如String以及对象实例。
对于基本数据类型,实际上是拷贝它的值,而对于引用数据类型,拷贝的就是它的引用,并没有创建一个新的对象,即没有分配新的内存空间。这样的拷贝就称作浅拷贝。
深拷贝就是在引用类型进行拷贝时,创建了新的对象,即分配了新的内存空间给拷贝对象。下面就来具体看看浅拷贝和深拷贝的区别。
浅拷贝
对于对象的创建有两种方式
1 使用new操作符创建一个对象
2 使用clone方法复制一个对象
我们常用的方式就是
Object O = new Object();
Object C = O;通过这样的方式里进行对象的复制,实际上传递的就是对象O的地址
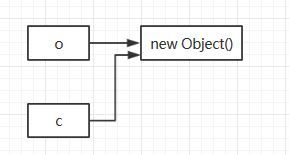
具体例子如下
class Person implements Serializable {
String name;
int age;
public Person(String name, int age) {
this.age = age;
this.name = name;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args){
Person p = new Person("张三", 11);
Person p1 = p;
System.out.println(p);
System.out.println(p1);
}打印结果是两个对象的地址相同
test.Person@15db9742
test.Person@15db9742接下来我们使用clone来复制对象,使用前需要让对象实现Cloneable接口
class Person implements Serializable,Cloneable {
String name;
int age;
public Person(String name, int age) {
this.age = age;
this.name = name;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
return super.clone();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws CloneNotSupportedException
{
Person p = new Person("张三", 11);
Person p1 = (Person) p.clone();
System.out.println(p);
System.out.println(p1);
}
结果
test.Person@15db9742
test.Person@6d06d69c可以看到两个对象是不一样的。此时我们再打印String类型的name,查看一下
System.out.println("p.name == p1.name:"+(p.name == p1.name));结果为true说明,String 的引用类型仍然引用了原来的地址
p.name == p1.name:true这张图表明了使用clone时对于对象中含有引用类型时,并没有给引用类型创建新的内存空间,而是引用了其地址。这样使用clone,也只是实现了浅拷贝。
深拷贝
通过上面的例子我们已经了解到使用clone 的方式,只能对当前对象进行浅拷贝,引用类型依然是在传递引用。那么如何进行深拷贝呢?
常用的方式有两种:
1 序列化这个对象再反序列化回来,就可以得到新的对象
2 继续使用clone方法,让内部的引用类型实现Cloneable接口,重写clone。
下面是修改clone实现深拷贝的方式
class ChildClass implements Cloneable {
public int age;
@Override
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
return super.clone();
}
}
class FatherClass implements Cloneable {
public int age;
public ChildClass child;
@Override
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
FatherClass cloneFather = (FatherClass) super.clone();
cloneFather.child = (ChildClass) this.child.clone();
return cloneFather;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws CloneNotSupportedException
FatherClass fatherClass = new FatherClass();
fatherClass.age = 10;
fatherClass.child = new ChildClass();
fatherClass.child.age = 3;
FatherClass fatherClass2 = (FatherClass) fatherClass.clone();
System.out.println("fatherClass == fatherClass2 "+(fatherClass == fatherClass2));
System.out.println("fatherClass.child == fatherClass2.child "+(fatherClass.child == fatherClass2.child));
}运行结果
fatherClass == fatherClass2 false
fatherClass.child == fatherClass2.child false可以看到父类的引用对象的拷贝实例,也重新分配了新的内存空间。

使用序列化的方式来进行深拷贝
public static T deepCopy(T t) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
ObjectOutputStream objectOutputStream = null;
ObjectInputStream objectInputStream = null;
ByteArrayOutputStream byteArrayOutputStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
objectOutputStream = new ObjectOutputStream(byteArrayOutputStream);
objectOutputStream.writeObject(t);
ByteArrayInputStream byteArrayInputStream = new ByteArrayInputStream(byteArrayOutputStream.toByteArray());
objectInputStream = new ObjectInputStream(byteArrayInputStream);
T copy = (T) objectInputStream.readObject();
if (objectInputStream!=null) {
objectInputStream.close();
}
if (objectInputStream!=null) {
objectOutputStream.close();
}
return copy;
} 要进行序列化的对象必须要实现Serializable的接口
class Person implements Serializable, Cloneable {
String name;
int age;
public Person(String name, int age) {
this.age = age;
this.name = name;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
return super.clone();
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return name + ":" + age;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws CloneNotSupportedException, ClassNotFoundException, IOException
{
Person person = new Person("張三", 20);
Person person2 = deepCopy(person);
System.out.println(person2);
System.out.println("person == person2 "+ (person == person2));
System.out.println("person.name == person2.name "+(person.name == person2.name));
}运行结果
張三:20
person == person2 false
person.name == person2.name false可以看到通过序列化的方式,拷贝对象中的引用类型也分配了新的内存空间,所以是深拷贝。
选择
如果对象的属性全是基本类型的,那么可以使用浅拷贝,但是如果对象有引用属性,那就要基于具体的需求来选择浅拷贝还是深拷贝。如果对象引用经常改变就用深拷贝,不经常改变就用浅拷贝。
List 拷贝
List浅拷贝
1.使用循环遍历的方式
使用上面的Person类,通过循环遍历的方式来进行List的拷贝
public static void main(String[] args)
{
List srcList = new ArrayList<>();
srcList.add(new Person("小红", 12));
srcList.add(new Person("王五", 23));
srcList.add(new Person("李四", 33));
List copyList = new ArrayList<>();
for(Person person : srcList){
copyList.add(person);
}
System.out.println("copyList "+ copyList);
srcList.get(0).setAge(4);
System.out.println("srcList "+ srcList);
System.out.println("copyList "+ copyList);
} 在复制完成后,修改原始数据中第一个对象的年龄,结果如下
copyList [小红:12, 王五:23, 李四:33]
srcList [小红:4, 王五:23, 李四:33]
copyList [小红:4, 王五:23, 李四:33]从结果可以看到,原始数据更改后,拷贝对象的数据内容也相应改变。
2.List实现类的构造方法
List srcList = new ArrayList<>();
srcList.add(new Person("小红", 12));
srcList.add(new Person("王五", 23));
srcList.add(new Person("李四", 33));
List copyList = new ArrayList<>(srcList);
System.out.println("copyList "+ copyList);
srcList.get(0).setAge(4);
System.out.println("srcList "+ srcList);
System.out.println("copyList "+ copyList); 运行结果一样
copyList [小红:12, 王五:23, 李四:33]
srcList [小红:4, 王五:23, 李四:33]
copyList [小红:4, 王五:23, 李四:33]- 使用list .addAll
List copyList = new ArrayList<>();
copyList.addAll(srcList);
System.out.println("copyList "+ copyList);
srcList.get(0).setAge(4);
System.out.println("srcList "+ srcList);
System.out.println("copyList "+ copyList); 结果也是一样的
copyList [小红:12, 王五:23, 李四:33]
srcList [小红:4, 王五:23, 李四:33]
copyList [小红:4, 王五:23, 李四:33]- 使用Collections.copy
使用Collections.copy方法时需要注意,使用时它的capacity必须要指定大于等于原始数据的大小。而且new ArrayList(NUM)指定值时,初始化时它的大小仍为0,只有进行add和remove等相关操作才能改变List的大小。
为此我们使用的方式是指定一个值为null的和原List相同大小的List
System.out.println(Arrays.asList(new String[srcList.size()]));
List copyList = new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(new
Person[srcList.size()]));
Collections.copy(copyList, srcList);
System.out.println(copyList);
srcList.get(0).setAge(4);
System.out.println("srcList " + srcList);
System.out.println("copyList " + copyList);
结果
[null, null, null]
[小红:12, 王五:23, 李四:33]
srcList [小红:4, 王五:23, 李四:33]
copyList [小红:4, 王五:23, 李四:33]List深拷贝
public static List deepCopy(List src) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
ByteArrayOutputStream byteArrayOutputStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
ObjectOutputStream outputStream = new ObjectOutputStream(byteArrayOutputStream);
outputStream.writeObject(src);
ByteArrayInputStream byteArrayInputStream = new ByteArrayInputStream(byteArrayOutputStream.toByteArray());
ObjectInputStream inputStream = new ObjectInputStream(byteArrayInputStream);
List dest = (List) inputStream.readObject();
if (outputStream!=null) {
outputStream.close();
}
if (inputStream!=null) {
inputStream.close();
}
return dest;
} 参考文章
详解java中的clone
java深拷贝和浅拷贝
细说java深拷贝和浅拷贝
javaList深度复制的方法
java Collections.copy的使用
简析Java的浅拷贝和深拷贝
java的浅拷贝和深拷贝
