语义分割网络-BiSenet
Sementic Segmentation-BiSenet
- 语义分割网络-BiSenet(Sementic Segmentation-BiSenet)
- 介绍
- 思路来源
- 关于感受野
- 关于空间信息
- 网络框架
- Spatial Path
- Context Path
- BackBone网络
- 注意力优化模块(ARM):
- 特征融合模块(FFM):
- 放大与输出
- Loss Function
- 创新点总结
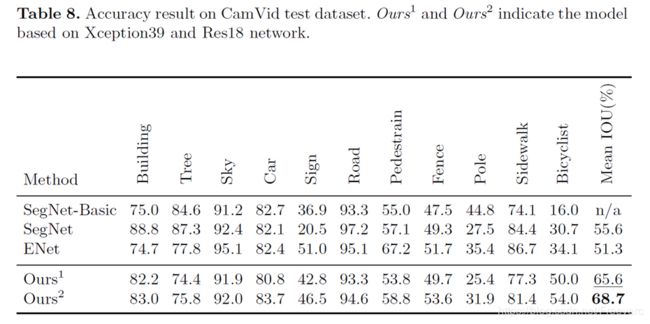
- 分割效果
- 测试结果:
- BiSeNet网络代码
- Tensorboard下的网络
- 
语义分割网络-BiSenet(Sementic Segmentation-BiSenet)
介绍
2018年,BiSeNet模型由旷视科技视觉团队发表于ECCV2018, 在FCN的语义分割任务基础上,搭建编码器-解码器对称结构,实现端到端的像素级别图像分割。
文章链接: BiSeNet. 或参考: ECCV2018
思路来源
语义分割的难点:
- 感受野( Receptive field)太小
- 空间信息(Spatial information)的损失
关于感受野
1.1 What:
在卷积神经网络CNN中,决定某一层输出结果中一个元素所对应的输入层的区域大小,被称作感受野Receptive field。
1.2 Why:
感受野大才能充分考虑图片信息,使得分割结果完整、精确
1.3 How:
网络深,感受野就大,设置Context Path, 采用Resnet, Xception等骨架网络,增加深度,扩大感受野。
关于空间信息
空间信息(Spatial information)主要指的是图像的局部细节信息,尤其是对于边缘丰富的图像。由于卷积网络规模大,一般要求输入图像尺寸较小,需要对原始图像进行Crop或者Resize,这个过程会损失细节的空间信息。通过设置只包含3个网络的Spacial Path,可保留丰富的空间信息,进而将低纬度的空间细节信息与高纬度的信息整合。
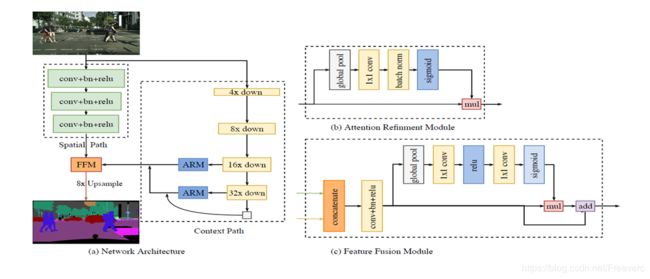
网络框架
Segnet语义分割网络的关键在于下采样和上采样。在上采样的过程中,使用下采样时记录的Max Value像素位置指标。
Spatial Path
包含3个卷积层以及对应的Batch Nornalization 层、ReLU层。输入图像大,输出图像为原图的1/8。
Context Path
包含一个深度骨架网络,用于模型调整的卷积网络,以及一系列注意力优化模块。值得一提的是采用了全局均值化来降低计算量,稳定最大感受野。
BackBone网络
原文采用Xception网络,也可以用Resnet101等。
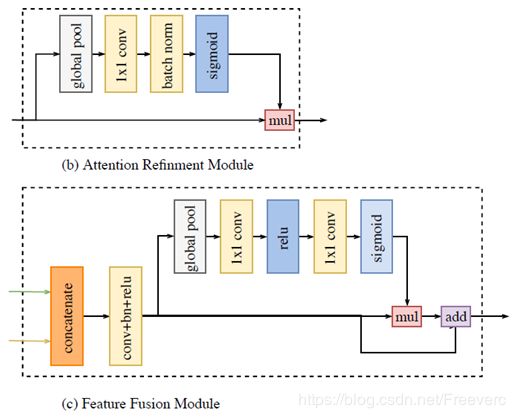
注意力优化模块(ARM):
在 Context Path 中,借助全局平均池化捕获全局语境,计算注意力向量,优化 Context Path 中每一阶段的输出特征,便于整合全局语境信息,大大降低计算成本。
特征融合模块(FFM):
Spatial Path 捕获的空间信息编码了绝大多数的丰富细节信息,Context Path 的输出特征主要编码语境信息。两路网络的特征并不相同,因此不能简单地加权两种特征,要用一个独特的特征融合模块以融合这些特征。
简而言之,两个路径的特征图直接叠加不合适,那就设定个卷积网络,去训练学习一下两部分如何叠加。如图。
放大与输出
这部分原文介绍不多,大致就是不需要上采样,直接用双线性插值把1/8图放大8倍就好了。双线性插值方法简单,无须赘述。
不采用上采样的好处是进一步减少了参数。因为在之前的一部分文章中(如Segnet),作者设置的Decoder部分参数并没有参与训练,因为实验发现Decoder部分对结果影响不大,反而不如降低计算量。
Loss Function
通过辅助损失函数监督模型的训练,
主损失函数监督整个 BiSeNet 的输出(Lp)。
添加两个特殊的辅助损失函数监督 Context Path 的输出(Li)
借助参数 α 以平衡主损失函数与辅助损失函数的权重。

上图中,K=3,α=1,即对Context Path的监督引入了两个辅助损失函数。
创新点总结
-
单独用Spatial path 来保留Spatial information
-
Context Path 直接用经典网络提取深层特征,扩大感受野
-
神奇的使用了一个ARM模块
-
Context Path 与Spatial path的特征整合方式:FFM
-
Loss Function 中,对Context Path 另外做监督
分割效果
测试结果:
BiSeNet网络代码
基于Tensorflow :
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.contrib import slim
from builders import frontend_builder
import numpy as np
import os, sys
def Upsampling(inputs,scale):
return tf.image.resize_bilinear(inputs, size=[tf.shape(inputs)[1]*scale, tf.shape(inputs)[2]*scale])
def ConvUpscaleBlock(inputs, n_filters, kernel_size=[3, 3], scale=2):
"""
Basic conv transpose block for Encoder-Decoder upsampling
Apply successivly Transposed Convolution, BatchNormalization, ReLU nonlinearity
"""
net = tf.nn.relu(slim.batch_norm(inputs, fused=True))
net = slim.conv2d_transpose(net, n_filters, kernel_size=[3, 3], stride=[scale, scale], activation_fn=None)
return net
def ConvBlock(inputs, n_filters, kernel_size=[3, 3], strides=1):
"""
Basic conv block for Encoder-Decoder
Apply successivly Convolution, BatchNormalization, ReLU nonlinearity
"""
net = slim.conv2d(inputs, n_filters, kernel_size, stride=[strides, strides], activation_fn=None, normalizer_fn=None)
net = tf.nn.relu(slim.batch_norm(net, fused=True))
return net
def AttentionRefinementModule(inputs, n_filters):
# Global average pooling
net = tf.reduce_mean(inputs, [1, 2], keep_dims=True)
net = slim.conv2d(net, n_filters, kernel_size=[1, 1])
net = slim.batch_norm(net, fused=True)
net = tf.sigmoid(net)
net = tf.multiply(inputs, net)
return net
def FeatureFusionModule(input_1, input_2, n_filters):
inputs = tf.concat([input_1, input_2], axis=-1)
inputs = ConvBlock(inputs, n_filters=n_filters, kernel_size=[3, 3])
# Global average pooling
net = tf.reduce_mean(inputs, [1, 2], keep_dims=True)
net = slim.conv2d(net, n_filters, kernel_size=[1, 1])
net = tf.nn.relu(net)
net = slim.conv2d(net, n_filters, kernel_size=[1, 1])
net = tf.sigmoid(net)
net = tf.multiply(inputs, net)
net = tf.add(inputs, net)
return net
def build_bisenet(inputs, num_classes, preset_model='BiSeNet', frontend="ResNet101", weight_decay=1e-5, is_training=True, pretrained_dir="models"):
"""
Builds the BiSeNet model.
Arguments:
inputs: The input tensor=
preset_model: Which model you want to use. Select which ResNet model to use for feature extraction
num_classes: Number of classes
Returns:
BiSeNet model
"""
### The spatial path
### The number of feature maps for each convolution is not specified in the paper
### It was chosen here to be equal to the number of feature maps of a classification
### model at each corresponding stage
spatial_net = ConvBlock(inputs, n_filters=64, kernel_size=[3, 3], strides=2)
spatial_net = ConvBlock(spatial_net, n_filters=128, kernel_size=[3, 3], strides=2)
spatial_net = ConvBlock(spatial_net, n_filters=256, kernel_size=[3, 3], strides=2)
### Context path
logits, end_points, frontend_scope, init_fn = frontend_builder.build_frontend(inputs, frontend, is_training=is_training)
net_4 = AttentionRefinementModule(end_points['pool4'], n_filters=512)
net_5 = AttentionRefinementModule(end_points['pool5'], n_filters=2048)
global_channels = tf.reduce_mean(net_5, [1, 2], keep_dims=True)
net_5_scaled = tf.multiply(global_channels, net_5)
### Combining the paths
net_4 = Upsampling(net_4, scale=2)
net_5_scaled = Upsampling(net_5_scaled, scale=4)
context_net = tf.concat([net_4, net_5_scaled], axis=-1)
net = FeatureFusionModule(input_1=spatial_net, input_2=context_net, n_filters=num_classes)
### Final upscaling and finish
net = Upsampling(net, scale=8)
net = slim.conv2d(net, num_classes, [1, 1], activation_fn=None, scope='logits')
return net, init_fn
Tensorboard下的网络
作者:Freeverc
来源:CSDN