JAVA学习笔记整理五(JAVA常用类库)
常用包介绍
java.lang: ava语言核心包,包含java 最基础的类
java.util:包含一系列的工具类, 数据结构的支持工具
java.io:包含着支持输入/输出操作的类
java.net:Network,TCP/IP,socket网络编程
java.awt:AWT GUI 设计,事件操作
java.text :提供国际化(i18n)支持
java.security :支持密文安全性
java.rmi :RMI,支持分布式编程
java.sql :包含支持使用标准sql的数据库访问功能的类
java.applet: Applet类库
Javax.*: java类库扩展
Java.lang包介绍:是Java语言的核心包,其中包括了一些最重要的基本类,没有java.lang就无法编写最基本的程序,java.lang包是唯一不需要在程序中用import引入的包
1. Obejct:所有类的父类
2. 类型包装类:由基本的数据类型扩展来,如int--Integer等,八大基本类型的包装类
类型包装类的作用:
1、保存一个对应类型的数据范围:最大值、最小值
2、完成不同数据类型间的转换
String s =Double.toString(0.08);
int i =Integer.parseInt(“123”);
doubled=Double.valueOf(“12.16”).doubleValue();
3、需要执行对象操作的地方:如List,Map,HttpSession等
4、封装对应类型的特殊功能:如:Integer.toBinaryString(123);
public class TestBoxing {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "";
test(str);
int a = 0;
test(a);// 自动装箱, 就是将int类型的a变量转换为Integer
Integer i =new Integer(a);//将int类型的a变量转换为Integer
test(i);
Integer i1 = 10;
long l = 20;
Long l1 = 20L;//需要加上L
double d = 3.12;
Double d1 = 3.12D;//需要加上D
a = i1 + 20;// 自动插箱 自动将i1转化位int类型(即a=i1.intValue()+20)
System.out.println("a=i1.intValue()+20" + a);
System.out.println("利用*.valueof()方法转换后计算:" + Integer.valueOf("100")+10);
//利用*.valueof()方法可将格式符合的字符串转换为对应类型
String str1=String.valueOf(10);//或者将基本数据类型等转换为字符串形式
boolean b1 = new Boolean(true);
Boolean b2 = new Boolean(true);
System.out.println("b1==b2地址比较:" + (b1 == b2));//直接比较的是地址
System.out.println("b1==b2值比较:" + (b1 == b2.booleanValue()));//b1与b2的值进行比较
Boolean b3 = new Boolean(true);
System.out.println("b2==b3地址比较:" + (b2 == b3));//地址比较
System.out.println("b2==b3值比较:" + (b2.booleanValue() == b3.booleanValue()));//值比较
int x=100;
System.out.println("二进制:"+Integer.toBinaryString(x));//转换为二进制
System.out.println("十六进制:"+Integer.toHexString(x));//转换为十六进制
System.out.println("八进制:"+Integer.toOctalString(x));//转换为八进制
}
private static void test(Object obj) {
System.out.println("对象的类型为:" + obj.getClass().getName());
}
}
//对象的类型为:java.lang.String
//对象的类型为:java.lang.Integer
//对象的类型为:java.lang.Integer
//a=i1.intValue()+2030
//利用*.valueof()方法转换后计算:10010
//b1==b2地址比较:true
//b1==b2值比较:true
//b2==b3地址比较:false
//b2==b3值比较:true
//二进制:1100100
//十六进制:64
//八进制:144
3. Math类:数学计算,声明为final,构造方法为私有的,不能实例化,所有方法都是static型的,用来完成常用的数学运算
public class TestMath {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Math类中的方法都是静态方法,直接使用“类名称.方法名称()的形式即可调用”
System.out.println("在(10, 20)中返回大数:"+Math.max(10, 20));//在(10, 20)中返回大数:20
System.out.println("在(10, 20)中返回小数:"+Math.min(10, 20));//在(10, 20)中返回小数:10
System.out.println("求10的3次方:"+Math.pow(10, 3));//求10的3次方:1000.0
System.out.println("求100的平方根:"+Math.sqrt(100));//求100的平方根:10.0
System.out.println("3.54舍去小数:"+Math.floor(3.54));//3.54舍去小数:3.0
System.out.println("3.14小数部分舍去后+1:"+Math.ceil(3.14));//3.14小数部分舍去后+1:4.0
System.out.println("3.51四舍五入:"+Math.round(3.51));//3.51四舍五入:4
}
}
// 在(10, 20)中返回大数:20
// 在(10, 20)中返回小数:10
// 求10的3次方:1000.0
// 求100的平方根:10.0
// 3.54舍去小数:3.0
// 3.14小数部分舍去后+1:4.0
// 3.51四舍五入:4
4. System类:系统功能类,主要提供下列功能
1) 系统的标准输入、输出:System.in,System.out,System.err
2) 获取系统信息:System.currentTimeMillis()
3) 执行系统操作:System.exit(0)、System.gc();
public class TestSystem {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("使用System输出内容");
// System.gc();//垃圾回收,强制性释放空间
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();//获取当前系统的时间
for (int i = 0; i < 1000000000L; i++) {
double d = 1.1233432 * 0.98992734;
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();//执行计算后的系统时间
System.out.println("end-start=" + (end - start));//计算所用去的时间
System.err.println("红色的");//“标准”错误输出流。
System.exit(0);// 表示结束当前程序,之后的代码不再执行
Properties pro = System.getProperties();//返回当前的系统属性
pro.list(System.out);//以列表形式返回
System.out.println("--------------");
}
}
//使用System输出内容
//红色的end-start=4664
5. String与StringBuffer:
String一旦声明则不可更改,如果要改变则肯定改变的是String的引用地址,所以一个字符串经常改变,就必须用StringBuffer类,而StringBuffer只能使用append方法进行字符串的连接,性能较高。StringBuffer类中定义的大部分方法名称都与String一样。
public class StringBufferTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
StringBuffer buf = new StringBuffer();
buf.append("Hello ").append("World").append("!");
System.out.println("buf:" + buf);
System.out.println("在指定的首位添加内容:" + (buf.insert(0, "My ")));
System.out.println("在指定的末位添加内容:" + (buf.insert(buf.length(), "!!")));
String str = buf.reverse().toString();//转换为String类型输出
System.out.println("字符串反转操作:" + str);
buf.reverse();//反转回来
System.out.println("利用replace()替换指定内容:" + buf.replace(9, 14, "wxq"));//指定要替换的内容的起始位置
String str1 = buf.substring(9, 12);//指定截取范围,截取内容并转换为String类型
System.out.println("截取的内容:" + str1);
System.out.println("截取之后的buf:" + buf);
String str2 = buf.delete(8, 12).toString();//删除指定范围内的内容后转为String
System.out.println("删除之后的内容:" + str2);
System.out.println("删除之后的内容:" + buf);
if (buf.indexOf("Hello") == -1) {// 没有查找到会返回-1
System.out.println("没有查找到指定内容");
}else{//不为-1表示查找到指定内容
System.out.println("可以查找到指定内容");
}
}
}
//buf:Hello World!
//在指定的首位添加内容:My Hello World!
//在指定的末位添加内容:My Hello World!!!
//字符串反转操作:!!!dlroW olleH yM
//利用replace()替换指定内容:My Hello wxq!!!
//截取的内容:wxq
//截取之后的buf:My Hello wxq!!!
//删除的内容:My Hello!!!
//删除之后的内容:My Hello!!!
//可以查找到指定内容Java.uitl包介绍:是Java组件中最有用的包,这个包中包含着多个常用类,可以用于在你的程序中以不同的方式管理数据和完成一些常用操作,该包中包含的类主要有:
1. Date:表示日期和时间,大部分方法已过期(deprecated)(日期操作类1,代码见Java.text包处)
2. Calendar:日历,获取当前日期和时间,完成对日期和时间的各种操作,是抽象类不能被实例化(日期操作类2,代码见Java.text包处)
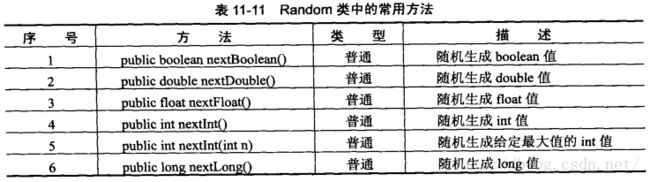
3. Random:用于生成各种类型的随机数
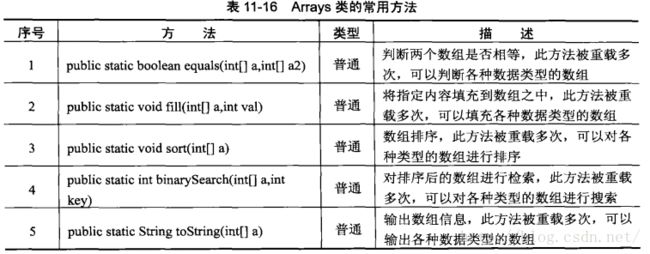
4. Arrays:用于对数组的操作
5. Locale:封装了各个国家,用于支持国际化,一般不需实例化,如:Locale china=Locale.CHINA
各个国家都有对应的ISO编码,例如,中国编码为zh-CN、英语-美国编码为en-US、法语编码为fr-FR(获取:【工具】→【Internrt选项】→【常规】→【语言】→【添加】)
6. ResourceBundle :读取属性文件,一般与Locale一起使用
import java.util.Locale;
import java.util.ResourceBundle;
public class ResBundleDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//通过指定属性文件实现国际化
Locale zhLocale = new Locale("zh", "CN");//指定语言与国家,此处表示中国地区
Locale enLocale = new Locale("en", "US");//表示美国地区
Locale frLocale = new Locale("fr", "FR");//表示法国地区
ResourceBundle zhBundle = ResourceBundle.getBundle("org.wxq.t14_colection.Message", zhLocale);//找到中文的属性文件
ResourceBundle enBundle = ResourceBundle.getBundle("org.wxq.t14_colection.Message", enLocale);//找到英文的属性文件
ResourceBundle frBundle = ResourceBundle.getBundle("org.wxq.t14_colection.Message", frLocale);//找到法文的属性文件
System.out.println("指定中文:" + zhBundle.getString("message.hello"));
System.out.println("指定英文:" + enBundle.getString("message.hello"));
System.out.println("指定法文:" + frBundle.getString("message.hello"));
}
}
//指定中文:你好世界!
//指定英文:Hello World!
//指定法文:Bonjour!
7. 数据结构类:封装了对各种数据结构的操作,形成一个完整的框架,包括Collection,List,Set,Map,Iterator等接口和对应的实现类
Java.text包介绍:
1. DateFormat:用于将日期对象格式化成对应国家的标准日期格式,该类不能被实例化(日期操作类3,代码见下)
2. SimpleDateFormat:该类可以根据指定的掩码(pattern)格式将日期格式化成任意的格式,提供了非常灵活的定制功能,可以被实例化(日期操作类4)
Date_Calendar_DateFormat_SimpleDateFormat 实例
import java.text.DateFormat;
import java.text.ParseException;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Calendar;
import java.util.Date;
public class TestDate {
public static void main(String[] args) {
testDate();
testCalendar();
testDateFormat();
testSimpleDateFormat();
parseDate();// 将字符串转换为日期
}
private static void testDate() {
long now = System.currentTimeMillis();//得到地系统的日期时间,因为没有转换为规范的格式,所以的一长串数字
Date date = new Date();//直接得到的日期时间信息,格式不太符合要求,可以格式化得到所需或者直接使用Calendar类
System.out.println("利用System得到的时间:" + now);
System.out.println("利用Date得到的时间:" + date);
System.out.println("返回的数字可以进行计算:" + (now - 1000 * 60 * 60 * 24));
Date date1 = new Date(now - 1000 * 60 * 60 * 24);//将计算后的数字转换为日期格式
System.out.println("date是否是在date1之前:" + date.before(date1));
System.out.println("date是否是在date1之后:" + date.after(date1));
String datestr = String.format("%tF %
3. NumberFormat:用于将一个数字按不同国家不同信息的显示形式进行格式化,不能实例化
4. DecimalFormat:用于将一个数字按指定的掩码格式进行格式化,可以实例化
NumberFormat_DecimalFormat 实例
import java.text.DecimalFormat;
import java.text.NumberFormat;
import java.util.Locale;
public class TestNumberFormat {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 100;
double b = 3.141592657;
String s = "Hello world!";
System.out.println(String.format("a=%d,d=%f,s=%s", a, b, s));
System.out.println(String.format("a=%5d,d=%5.2f,s=%S", a, b, s));
//符号d前的数字表示默认的位数,不足则在左边以空格表示
//5.2f中,5代表的是默认一共5位,.2表示显示2位小数,大写S表示将s中的字母全部以大写输出
System.out.println(String.format("a10=%d,a8=%o,a16=%X,d=%5.2f,s=%S", a, a, a, b, s));
//可以将十进制数转换为八进制以及十六进制数
System.out.println(String.format("a10=%d,a8=%