Day 20: 斯坦福CoreNLP —— 用Java给Twitter进行情感分析
今天学习如何使用斯坦福CoreNLP Java API来进行情感分析(sentiment analysis)。前几天,我还写了一篇关于如何使用TextBlob API在Python里做情感分析,我已经开发了一个应用程序,会筛选出给定关键词的推文(tweets)的情感,现在看看它能做什么。
应用
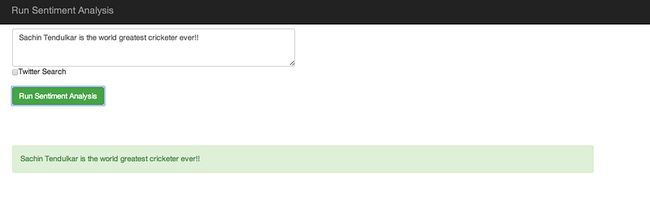
该演示应用程序在OpenShift http://sentiments-t20.rhcloud.com/ 运行,它有两个功能:
什么是斯坦福CoreNLP?
斯坦福CoreNLP是一个Java自然语言分析库,它集成了所有的自然语言处理工具,包括词性的终端(POS)标注器,命名实体识别(NER),分析器,对指代消解系统,以及情感分析工具,并提供英语分析的模型文件。
准备
- 基本的Java知识是必需的,安装最新的Java开发工具包(JDK ),可以是OpenJDK 7或Oracle JDK 7。
- 从官方网站下载斯坦福CoreNLP包。
- 注册一个OpenShift帐户,它是完全免费的,可以分配给每个用户1.5 GB的内存和3 GB的磁盘空间。
- 安装RHC客户端工具,需要有ruby 1.8.7或更新的版本,如果已经有ruby gem,输入
sudo gem install rhc,确保它是最新版本。要更新RHC的话,执行命令sudo gem update rhc,如需其他协助安装RHC命令行工具,请参阅该页面: https://www.openshift.com/developers/rhc-client-tools-install - 通过
rhc setup命令设置您的OpenShift帐户,此命令将帮助你创建一个命名空间,并上传你的SSH keys到OpenShift服务器。
Github仓库
今天的演示应用程序的代码可以在GitHub找到:day20-stanford-sentiment-analysis-demo
在两分钟内启动并运行SentimentsApp
开始创建应用程序,名称为sentimentsapp。
$ rhc create-app sentimentsapp jbosseap --from-code=https://github.com/shekhargulati/day20-stanford-sentiment-analysis-demo.git
还可以使用如下指令:
$ rhc create-app sentimentsapp jbosseap -g medium --from-code=https://github.com/shekhargulati/day20-stanford-sentiment-analysis-demo.git
这将为应用程序创建一个容器,设置所有需要的SELinux政策和cgroup的配置,OpenShift也将创建一个私人git仓库并克隆到本地。然后,它会复制版本库到本地系统。最后,OpenShift会给外界提供一个DNS,该应用程序将在http://newsapp-{domain-name}.rhcloud.com/ 下可以访问(将 domain-name 更换为自己的域名)。
该应用程序还需要对应Twitter应用程序的4个环境变量,通过去https://dev.twitter.com/apps/new 创建一个新的Twitter应用程序,然后创建如下所示的4个环境变量。
$ rhc env set TWITTER_OAUTH_ACCESS_TOKEN= -a sentimentsapp
$ rhc env set TWITTER_OAUTH_ACCESS_TOKEN_SECRET= -a sentimentsapp
$rhc env set TWITTER_OAUTH_CONSUMER_KEY= -a sentimentsapp
$rhc env set TWITTER_OAUTH_CONSUMER_SECRET= -a sentimentsapp
重新启动应用程序,以确保服务器可以读取环境变量。
$ rhc restart-app --app sentimentsapp
开始在pom.xml中为stanford-corenlp和twitter4j增加Maven的依赖关系,使用3.3.0版本斯坦福corenlp作为情感分析的API。
<dependency>
<groupId>edu.stanford.nlpgroupId>
<artifactId>stanford-corenlpartifactId>
<version>3.3.0version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.twitter4jgroupId>
<artifactId>twitter4j-coreartifactId>
<version>[3.0,)version>
dependency>
该twitter4j依赖关系需要Twitter搜索。
通过更新 pom.xml 文件里的几个特性将Maven项目更新到Java 7:
<maven.compiler.source>1.7maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>1.7maven.compiler.target>
现在就可以更新Maven项目了(右键单击>Maven>更新项目)。
启用CDI
使用CDI来进行依赖注入。CDI、上下文和依赖注入是一个Java EE 6规范,能够使依赖注入在Java EE 6的项目中。
在 src/main/webapp/WEB-INF 文件夹下建一个名为beans.xml中一个新的XML文件,启动CDI
<beans xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/beans_1_0.xsd">
beans>
搜索Twitter的关键字
创建了一个新的类TwitterSearch,它使用Twitter4J API来搜索Twitter关键字。该API需要的Twitter应用程序配置参数,使用的环境变量得到这个值,而不是硬编码。
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List;
import twitter4j.Query;
import twitter4j.QueryResult;
import twitter4j.Status;
import twitter4j.Twitter;
import twitter4j.TwitterException;
import twitter4j.TwitterFactory;
import twitter4j.conf.ConfigurationBuilder;
public class TwitterSearch {
public List search(String keyword) {
ConfigurationBuilder cb = new ConfigurationBuilder();
cb.setDebugEnabled(true).setOAuthConsumerKey(System.getenv("TWITTER_OAUTH_CONSUMER_KEY"))
.setOAuthConsumerSecret(System.getenv("TWITTER_OAUTH_CONSUMER_SECRET"))
.setOAuthAccessToken(System.getenv("TWITTER_OAUTH_ACCESS_TOKEN"))
.setOAuthAccessTokenSecret(System.getenv("TWITTER_OAUTH_ACCESS_TOKEN_SECRET"));
TwitterFactory tf = new TwitterFactory(cb.build());
Twitter twitter = tf.getInstance();
Query query = new Query(keyword + " -filter:retweets -filter:links -filter:replies -filter:images");
query.setCount(20);
query.setLocale("en");
query.setLang("en");;
try {
QueryResult queryResult = twitter.search(query);
return queryResult.getTweets();
} catch (TwitterException e) {
// ignore
e.printStackTrace();
}
return Collections.emptyList();
}
}
在上面的代码中,筛选了Twitter的搜索结果,以确保没有转推(retweet)、或带链接的推文、或有图片的推文,这样做的原因是为了确保我们得到的是有文字的推。
情感分析器(SentimentAnalyzer)
创建了一个叫SentimentAnalyzer的类,这个类就是对某一条推文进行情感分析的。
public class SentimentAnalyzer {
public TweetWithSentiment findSentiment(String line) {
Properties props = new Properties();
props.setProperty("annotators", "tokenize, ssplit, parse, sentiment");
StanfordCoreNLP pipeline = new StanfordCoreNLP(props);
int mainSentiment = 0;
if (line != null && line.length() > 0) {
int longest = 0;
Annotation annotation = pipeline.process(line);
for (CoreMap sentence : annotation.get(CoreAnnotations.SentencesAnnotation.class)) {
Tree tree = sentence.get(SentimentCoreAnnotations.AnnotatedTree.class);
int sentiment = RNNCoreAnnotations.getPredictedClass(tree);
String partText = sentence.toString();
if (partText.length() > longest) {
mainSentiment = sentiment;
longest = partText.length();
}
}
}
if (mainSentiment == 2 || mainSentiment > 4 || mainSentiment < 0) {
return null;
}
TweetWithSentiment tweetWithSentiment = new TweetWithSentiment(line, toCss(mainSentiment));
return tweetWithSentiment;
}
}
复制 englishPCFG.ser.gz 和 sentiment.ser.gz 模型到src/main/resources/edu/stanford/nlp/models/lexparser 和src/main/resources/edu/stanford/nlp/models/sentiment 文件夹下。
创建SentimentsResource
最后,创建了JAX-RS资源类。
public class SentimentsResource {
@Inject
private SentimentAnalyzer sentimentAnalyzer;
@Inject
private TwitterSearch twitterSearch;
@GET
@Produces(value = MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)
public List sentiments(@QueryParam("searchKeywords") String searchKeywords) {
List results = new ArrayList<>();
if (searchKeywords == null || searchKeywords.length() == 0) {
return results;
}
Set keywords = new HashSet<>();
for (String keyword : searchKeywords.split(",")) {
keywords.add(keyword.trim().toLowerCase());
}
if (keywords.size() > 3) {
keywords = new HashSet<>(new ArrayList<>(keywords).subList(0, 3));
}
for (String keyword : keywords) {
List statuses = twitterSearch.search(keyword);
System.out.println("Found statuses ... " + statuses.size());
List sentiments = new ArrayList<>();
for (Status status : statuses) {
TweetWithSentiment tweetWithSentiment = sentimentAnalyzer.findSentiment(status.getText());
if (tweetWithSentiment != null) {
sentiments.add(tweetWithSentiment);
}
}
Result result = new Result(keyword, sentiments);
results.add(result);
}
return results;
}
}
上述代码执行以下操作:
- 检查搜索关键字(searchkeywords)是否“不是无效且不为空”,然后将其拆分到一个数组里,只考虑三个搜索条件。
- 然后对每一个搜索条件找到对应的推文,并做情感分析。
- 最后将返回结果列表给用户。
今天就是这些,欢迎反馈。
原文 Day 20: Stanford CoreNLP--Performing Sentiment Analysis of Twitter using Java
翻译整理 SegmentFault