Android 8.0(Oreo) 适配
前阵子,市场中心丢来一个锅,说华为、360、应用宝要求开发者适配 Android P,否则应用将被不推荐、隐藏甚至下架(华为),从 2018 年 8 月 1 日起,所有向 Google Play 首次提交的新应用都必须针对 Android 8.0 (API 等级 26) 开发; 2018 年 11 月 1 日起,所有 Google Play 的现有应用更新同样必须针对 Android 8.0。吓得我赶紧做了下适配,原本觉得应该不难,没想到过程是曲折的,前途终究还是光明的。
适配的第一步,修改targetSdkVersion为26或以上,然后针对Oreo新的行为变更进行适配。
1. 自适应启动图标(非必要)
之前的启动图标都是mipmap中的静态图片ic_launcher。到后来7.1的时候谷歌开始推广圆形图标,在原来android:icon的基础上又添加了android:roundIcon属性来让你的app支持圆形图标。
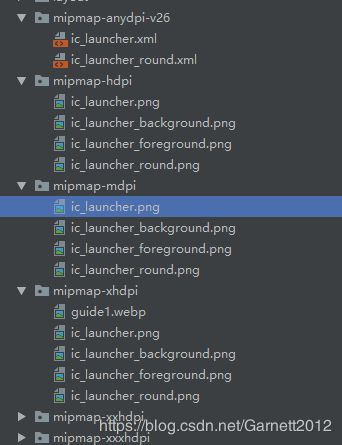
到了8.0,情况又变了,如右图:多了一个mipmap-anydpi-v26文件夹,里面也是启动图,但是不是一张图片,而是xml文件。
该文件中主要是设置两张图片,一个前景色一个背景色。
其实这个还是按照之前的方式处理,并不会出现什么特别的问题,主要是在Android原生的ROM桌面图标显示有问题,图标会变得特别大或者被一个白色的圆包裹着。
2. 通知栏
Android 8.0 引入了通知渠道,其允许您为要显示的每种通知类型创建用户可自定义的渠道。用户界面将通知渠道称之为通知类别。
针对 8.0 的应用,创建通知前需要创建渠道,创建通知时需要传入 channelId,否则通知将不会显示。示例代码如下:
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.O) {
//创建通知渠道
@SuppressLint("WrongConstant")
NotificationChannel mChannel = new NotificationChannel(channelId, "通知渠道名称", NotificationManager.IMPORTANCE_DEFAULT);
mChannel.setDescription("渠道描述");//渠道描述
mChannel.enableLights(false);//是否显示通知指示灯
mChannel.enableVibration(false);//是否振动
mChannel.setImportance(NotificationManager.IMPORTANCE_HIGH);//通知级别
NotificationManager notificationManager = (NotificationManager) context.getSystemService(
NOTIFICATION_SERVICE);
notificationManager.createNotificationChannel(mChannel);//创建通知渠道
NotificationCompat.Builder builder = new NotificationCompat.Builder(this,channelId);
}channelId对应一类渠道通知,mChannel.setImportance()可以设置通知的重要性。
- IMPORTANCE_MIN 开启通知,不会弹出,但没有提示音,状态栏中无显示
- IMPORTANCE_LOW 开启通知,不会弹出,不发出提示音,状态栏中显示
- IMPORTANCE_DEFAULT 开启通知,不会弹出,发出提示音,状态栏中显示
- IMPORTANCE_HIGH 开启通知,会弹出,发出提示音,状态栏中显示
3.后台执行限制
(1)如果针对 Android 8.0 的应用尝试在不允许其创建后台服务的情况下使用 startService() 函数,则该函数将引发一个 IllegalStateException。目前我在实际项目中并没有看到这个Exception的出现,不过为了避免出锅,我们还是try-catch一下比较靠谱。
try {
context.startService(intent);
} catch (Throwable th) {
DebugLog.i("service", "start service: " + intent.getComponent() + "error: " + th);
ExceptionUtils.printExceptionTrace(th);
}(2)静态广播
- 针对 Android 8.0的应用无法继续在其清单中为隐式广播注册广播接收器
- 应用可以继续在它们的清单中注册显式广播
- 应用可以在运行时使用Context.registerReceiver()为任意广播(不管是隐式还是显式)注册接收器
- 需要签名权限的广播不受此限制所限,因为这些广播只会发送到使用相同证书签名的应用,而不是发送到设备上的所有应用
很多人的博客说,8.0只能在代码中注册发送,不能在manifest文件中注册了,其实不然。在manifest中我们依旧可以注册,不过在发送的时候我们需要特殊处理下:
Intent intent = new Intent();
intent.setAction(action);
intent.setComponent(new ComponentName(context.getPackageName(),"receiver的包路径"));
context.sendBroadcast(intent);静态注册的时候我们发送需要添加component,让广播知道发送到哪里。不过最好还是在代码中动态注册,注册了要记得取消注册以免造成内存泄漏。
4. 允许安装未知来源应用
针对 8.0 的应用需要在 AndroidManifest.xml 中声明 REQUEST_INSTALL_PACKAGES 权限,否则将无法进行应用内升级。
5.权限
8.0之前你申请读外部存储的权限READ_EXTERNAL_STORAGE,你会自动被赋予写外部存储的权限WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE,因为他们属于同一组(android.permission-group.STORAGE)权限,但是现在8.0不一样了,读就是读,写就是写,不能混为一谈。不过你授予了读之后,虽然下次还是要申请写,但是在申请的时候,申请会直接通过,不会让用户再授权一次了。
额外篇:Android7.0适配之权限更改
由于之前也没有适配7.0的权限,所以顺带说下7.0适配的问题。
对于面向 Android 7.0 的应用,Android 框架执行的 StrictMode API 政策禁止在您的应用外部公开 file:// URI。如果一项包含文件 URI 的 intent 离开您的应用,则应用出现故障,并出现 FileUriExposedException 异常。对于这种跳转到第三方应用的URI需要使用FileProvider进行处理。
String cachePath = getApplicationContext().getExternalCacheDir().getPath();
File picFile = new File(cachePath, "test.jpg");
Uri picUri = Uri.fromFile(picFile);
Intent intent = new Intent(MediaStore.ACTION_IMAGE_CAPTURE);
intent.putExtra(MediaStore.EXTRA_OUTPUT, picUri);
startActivityForResult(intent, 100);这是常见的打开系统相机拍照的代码,拍照成功后,照片会存储在picFile文件中。
这段代码在Android 7.0之前是没有任何问题,但是如果你尝试在7.0的系统上运行,会抛出FileUriExposedException异常。
使用FileProvider
FileProvider使用大概分为以下几个步骤:
1.manifest中申明FileProvider,android:authorities一般设置为包名+fileProvider。
2.res/xml中定义对外暴露的文件夹路径,即android:resource="@xml/file_paths"
在paths节点内部支持以下几个子节点,分别为:
每个节点都支持两个属性:
name
path
path即为代表目录下的子目录,比如:
name="external"
path="pics" />
代表的目录即为:Environment.getExternalStorageDirectory()/pics,其他同理。
当这么声明以后,代码可以使用你所声明的当前文件
3.生成content://类型的Uri
File imagePath = new File(Context.getFilesDir(), "images");
File newFile = new File(imagePath, "default_image.jpg");
Uri contentUri
// 兼容Android 7.0版本
if(Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.N){
outputFileUri = FileProvider.getUriForFile(mContext,BuildConfig.APPLICATION_ID
+ ".fileProvider",newFile);
}else {
outputFileUri = Uri.fromFile(newFile);
}4.给Uri授予临时权限
intent.addFlags(Intent.FLAG_GRANT_READ_URI_PERMISSION
| Intent.FLAG_GRANT_WRITE_URI_PERMISSION);5.使用Intent传递Uri
File imagePath = new File(Context.getFilesDir(), "images");
if (!imagePath.exists()){imagePath.mkdirs();}
File newFile = new File(imagePath, "default_image.jpg");
Uri contentUri = getUriForFile(getContext(),
"com.mydomain.fileprovider", newFile);
Intent intent = new Intent(MediaStore.ACTION_IMAGE_CAPTURE);
intent.putExtra(MediaStore.EXTRA_OUTPUT, contentUri);
// 授予目录临时共享权限
intent.addFlags(Intent.FLAG_GRANT_READ_URI_PERMISSION
| Intent.FLAG_GRANT_WRITE_URI_PERMISSION);
startActivityForResult(intent, 100); 权限变更影响到的功能有:
1.拍照;
new Intent(MediaStore.ACTION_IMAGE_CAPTURE);2.使用第三方应用打开文件或者链接;
new Intent("android.intent.action.VIEW");3.apk安装
/**
* 安装apk
* @param filePath
*/
public static void installAPK(Context context,String filePath) {
try {
boolean isRight = UtilZipCheck.isErrorZip(filePath);
if (isRight) {
Intent intent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW);
if(Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.N){
intent.setFlags(Intent.FLAG_GRANT_READ_URI_PERMISSION);
Uri contentUri = FileProvider.getUriForFile(context, BuildConfig.APPLICATION_ID
+ ".fileProvider", new File(filePath));
intent.setDataAndType(contentUri, "application/vnd.android.package-archive");
} else {
intent.setFlags(Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK);
intent.setDataAndType(Uri.parse("file://" + filePath), "application/vnd.android.package-archive");
}
context.startActivity(intent);
}
} catch (Exception exception) {
exception.printStackTrace();
}
}