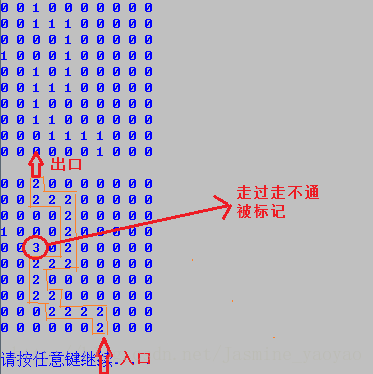
【数据结构】迷宫(递归)
代码如下:
#include 这样,一个简易的递归实现迷宫就完成了。