深度学习框架TensorFlow学习与应用(五)——TensorBoard结构与可视化
一、TensorBoard网络结构
举例:
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
#载入数据集
mnist=input_data.read_data_sets("D:\BaiDu\MNIST_data",one_hot=True)
#每个批次的大小
batch_size=100
#计算一共有多少个批次
n_batch=mnist.train.num_examples//batch_size
#命名空间
with tf.name_scope('input'):
#定义两个placeholder
x=tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,784],name='x-input')
y=tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,10],name='y-input')
with tf.name_scope('layer'):
#创建一个简单的神经网络
with tf.name_scope('wights'):
W=tf.Variable(tf.zeros([784,10]))
with tf.name_scope('biases'):
b=tf.Variable(tf.zeros([10]))
with tf.name_scope('xw_plus_b'):
wx_plus_b=tf.matmul(x,W)+b
with tf.name_scope('sofemax'):
prediction=tf.nn.softmax(tf.matmul(x,W)+b)
#二次代价函数
#loss=tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(y-prediction))
loss=tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(labels=y,logits=prediction))
#使用梯度下降法
train_step=tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.2).minimize(loss)
#初始化变量
init=tf.global_variables_initializer()
#结果存放在一个布尔型列表中
correct_prediction=tf.equal(tf.argmax(y,1),tf.argmax(prediction,1))#比较两个参数大小,相同为true。argmax返回一维张量中最大的值所在的位置
#求准确率
accuracy=tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction,tf.float32))#将布尔型转化为32位浮点型,再求一个平均值。true变为1.0,false变为0。
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(init)
write=tf.summary.FileWriter('logs/',sess.graph)#在当前文件中写文件,存的就是图的结构
for epoch in range(1):
for batch in range(n_batch):
batch_xs,batch_ys=mnist.train.next_batch(batch_size)
sess.run(train_step,feed_dict={x:batch_xs,y:batch_ys})
acc=sess.run(accuracy,feed_dict={x:mnist.test.images,y:mnist.test.labels})
print("Iter "+str(epoch)+",Testing Accuracy "+str(acc))运行后打开cmd(TensorFlow环境下):
tensorboard --logdir=C:\Users\JLUTiger\logs #文件的路径得到如下的信息:
TensorBoard 0.4.0rc2 at http://DESKTOP-UEGK0FV:6006 (Press CTRL+C to quit)复制链接在浏览器中打开,便进入TensorBoard,如下所示:
从TensorBoard中可以看出数据是怎么流动的等信息。
二、TensorBoard网络运行
将上面的代码改写为:
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
#载入数据集
tf.reset_default_graph()
mnist=input_data.read_data_sets("D:\BaiDu\MNIST_data",one_hot=True)
#每个批次的大小
batch_size=100
#计算一共有多少个批次
n_batch=mnist.train.num_examples//batch_size
#参数概要
def variable_summaries(var):
with tf.name_scope('summaries'):
mean=tf.reduce_mean(var)
tf.summary.scalar('mean',mean)#平均值
with tf.name_scope('stddev'):
stddev=tf.sqrt(tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(var-mean)))
tf.summary.scalar('stddev',stddev)#标准差
tf.summary.scalar('max',tf.reduce_max(var))#最大值
tf.summary.scalar('min',tf.reduce_min(var))#最小值
tf.summary.histogram('histogram',var)#直方图
#命名空间
with tf.name_scope('input'):
#定义两个placeholder
x=tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,784],name='x-input')
y=tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,10],name='y-input')
with tf.name_scope('layer'):
#创建一个简单的神经网络
with tf.name_scope('wights'):
W=tf.Variable(tf.zeros([784,10]),name='W')
variable_summaries(W)
with tf.name_scope('biases'):
b=tf.Variable(tf.zeros([10]),name='b')
variable_summaries(b)
with tf.name_scope('xw_plus_b'):
wx_plus_b=tf.matmul(x,W)+b
with tf.name_scope('softmax'):
prediction=tf.nn.softmax(wx_plus_b)
#二次代价函数
#loss=tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(y-prediction))
with tf.name_scope('loss'):
loss=tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(labels=y,logits=prediction))
tf.summary.scalar('loss',loss)
#使用梯度下降法
with tf.name_scope('train'):
train_step=tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.2).minimize(loss)
#初始化变量
init=tf.global_variables_initializer()
with tf.name_scope('accuracy'):
with tf.name_scope('correct_prediction'):
#结果存放在一个布尔型列表中
correct_prediction=tf.equal(tf.argmax(y,1),tf.argmax(prediction,1))#比较两个参数大小,相同为true。argmax返回一维张量中最大的值所在的位置
with tf.name_scope('accuracy'):
#求准确率
accuracy=tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction,tf.float32))#将布尔型转化为32位浮点型,再求一个平均值。true变为1.0,false变为0。
tf.summary.scalar('accuracy',accuracy)
#合并所有的summary
merged=tf.summary.merge_all()
#以下的与结构没什么关系
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(init)
writer=tf.summary.FileWriter('logs/',sess.graph)#在当前文件中写文件,存的就是图的结构
for epoch in range(51):
for batch in range(n_batch):
batch_xs,batch_ys=mnist.train.next_batch(batch_size)
summary,_=sess.run([merged,train_step],feed_dict={x:batch_xs,y:batch_ys})#每训练一次都统计一次
writer.add_summary(summary,epoch)
acc=sess.run(accuracy,feed_dict={x:mnist.test.images,y:mnist.test.labels})
print("Iter "+str(epoch)+",Testing Accuracy "+str(acc))注意:
起初运行时会报错:InvalidArgumentError: You must feed a value for placeholder tensor ‘inputs/x_input’ 。
引用别人的方法: if you’re using IPython or Jupyter, it’ll cause that problem after running repeatedly.there are two main ways that you could fix that:
A.
tf.reset_default_graph()
call firstly, before your tf operations code
B.
using
with tf.Graph().as_default() as g:
your tf operations code
如果有别的错误也可以参考这篇博文:
网络结构:
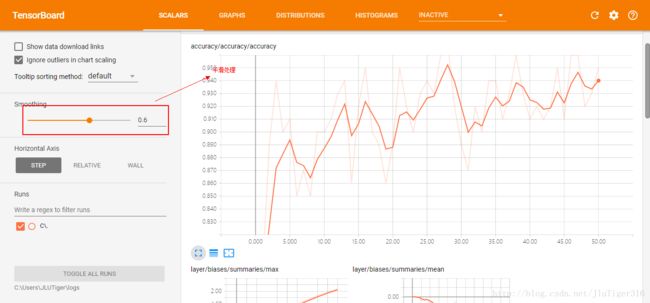
准确率:
偏置值分布图:
权值分布图:
权值直方图:
如果感觉图中的点比较少,可以改用下列类似代码:
for i in range(2001):
#m每个批次100个样本
batch_xs,batch_xs=mnist.train.next_batch(100)
summary,_=sess.run([merged,train_step],feed_dict={x:batch_xs,y:batch_xs})
writer.add_summary(summary,i)
if i%500==0:
print(sess.run(accuracy,feed_dict={x:mnist.test.images,y:mnist.test.labels}))通过查看TensorBoard中各个图像,可以分析出程序是否存在问题,从而便于进一步的优化改进。