random_device在windows上的实现
A random number generator that produces non-deterministic random numbers, if supported.
也就是说,这个类能产生不可预测的真随机数。
不过在搜random_device的时候,却发现Linux上的实现是读取dev/urandom设备,而windows上的实现是调用rand_s。如果真的是这样的话,那windows上的random_device就与一般伪随机数发生器无异了。
查MSDN(https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/bb982250.aspx),MS对这个类的说明:
Generates a random sequence from an external device.
Remarks
The class describes a source of random numbers, and is allowed but not required to be non-deterministic or cryptographically secure by the ISO C++ Standard. In the Visual Studio implementation the values produced are non-deterministic and cryptographically secure, but runs more slowly than generators created from engines and engine adaptors
也就是说MS声称VS里的random_device实现能产生不可预测的,具有加密强度的随机数
另外stackoverflow上有人问过这个问题The implementation of random_device in VS2010?
高票答案说windows上的实现是调用RtlGenRandom函数(详见https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/windows/desktop/aa387694(v=vs.85).aspx)
既然这样,只能自己动手调试了。环境:win8.1 x64+VS2015
测试代码:
#include
int main()
{
using namespace std;
random_device rd;
unsigned int rnd = rd();
return 0; }在unsigned int rnd = rd()处下断点,开始调试
整个调用链是这样的 random_device::operator() => _Random_device() => rand_s()
最后果然是调用了rand_s()。难道windows上random_device真的只是个伪随机数发生器?
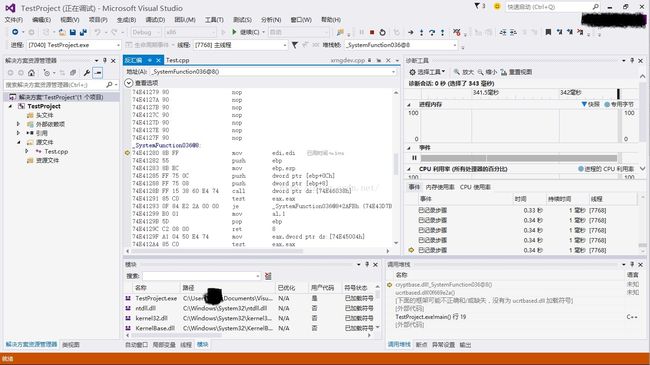
先别急,转到反汇编,继续单步运行。在ucrtbased.dll里绕来绕去之后,跳到了cryptbase.dll里一个名为SystemFunction036的API,如图
根据上面给出的链接,SystemFunction036是RtlGenRandom的一个别名
那RtlGenRandom能否产生不可预测的随机数序列呢?
上面stackoverflow的问题里提到一个MSDN博客的链接Cryptographically Secure Random number on Windows without using CryptoAPI
在博客后面作者自己的评论中,他提到了RtlGenRandom的熵来源于
The current process ID (GetCurrentProcessID).
The current thread ID (GetCurrentThreadID).
The ticks since boot (GetTickCount).
The current time (GetLocalTime).
Various high-precision performance counters (QueryPerformanceCounter).
An MD4 hash of the user's environment block, which includes username, computer name, and search path. MD4 is a hashing algorithm that creates a 128-bit message digest from input data to verify data integrity.
High-precision internal CPU counters, such as RDTSC, RDMSR, RDPMC
Low-level system information: Idle Process Time, Io Read Transfer Count, I/O Write Transfer Count, I/O Other Transfer Count, I/O Read Operation Count, I/O Write Operation Count, I/O Other Operation Count, Available Pages, Committed Pages, Commit Limit, Peak Commitment, Page Fault Count, Copy On Write Count, Transition Count, Cache Transition Count, Demand Zero Count, Page Read Count, Page Read I/O Count, Cache Read Count, Cache I/O Count, Dirty Pages Write Count, Dirty Write I/O Count, Mapped Pages Write Count, Mapped Write I/O Count, Paged Pool Pages, Non Paged Pool Pages, Paged Pool Allocated space, Paged Pool Free space, Non Paged Pool Allocated space, Non Paged Pool Free space, Free System page table entry, Resident System Code Page, Total System Driver Pages, Total System Code Pages, Non Paged Pool Lookaside Hits, Paged Pool Lookaside Hits, Available Paged Pool Pages, Resident System Cache Page, Resident Paged Pool Page, Resident System Driver Page, Cache manager Fast Read with No Wait, Cache manager Fast Read with Wait, Cache manager Fast Read Resource Missed, Cache manager Fast Read Not Possible, Cache manager Fast Memory Descriptor List Read with No Wait, Cache manager Fast Memory Descriptor List Read with Wait, Cache manager Fast Memory Descriptor List Read Resource Missed, Cache manager Fast Memory Descriptor List Read Not Possible, Cache manager Map Data with No Wait, Cache manager Map Data with Wait, Cache manager Map Data with No Wait Miss, Cache manager Map Data Wait Miss, Cache manager Pin-Mapped Data Count, Cache manager Pin-Read with No Wait, Cache manager Pin Read with Wait, Cache manager Pin-Read with No Wait Miss, Cache manager Pin-Read Wait Miss, Cache manager Copy-Read with No Wait, Cache manager Copy-Read with Wait, Cache manager Copy-Read with No Wait Miss, Cache manager Copy-Read with Wait Miss, Cache manager Memory Descriptor List Read with No Wait, Cache manager Memory Descriptor List Read with Wait, Cache manager Memory Descriptor List Read with No Wait Miss, Cache manager Memory Descriptor List Read with Wait Miss, Cache manager Read Ahead IOs, Cache manager Lazy-Write IOs, Cache manager Lazy-Write Pages, Cache manager Data Flushes, Cache manager Data Pages, Context Switches, First Level Translation buffer Fills, Second Level Translation buffer Fills, and System Calls.
System exception information consisting of Alignment Fix up Count, Exception Dispatch Count, Floating Emulation Count, and Byte Word Emulation Count.
System lookaside information consisting of Current Depth, Maximum Depth, Total Allocates, Allocate Misses, Total Frees, Free Misses, Type, Tag, and Size.
System interrupt information consisting of context switches, deferred procedure call count, deferred procedure call rate, time increment, deferred procedure call bypass count, and asynchronous procedure call bypass count.
System process information consisting of Next Entry Offset, Number Of Threads, Create Time, User Time, Kernel Time, Image Name, Base Priority, Unique Process ID, Inherited from Unique Process ID, Handle Count, Session ID, Page Directory Base, Peak Virtual Size, Virtual Size, Page Fault Count, Peak Working Set Size, Working Set Size, Quota Peak Paged Pool Usage, Quota Paged Pool Usage, Quota Peak Non Paged Pool Usage, Quota Non Paged Pool Usage, Page file Usage, Peak Page file Usage, Private Page Count, Read Operation Count, Write Operation Count, Other Operation Count, Read Transfer Count, Write Transfer Count, and Other Transfer Count.
可见,windows下的random_device能产生统计意义上的真随机数。