相机标定(二)——图像坐标与世界坐标转换
因本文存在错误与模糊之处,为此进行重写修改,但因CSDN不支持富文本转换Markdown,所以重写发布新的博文:
https://blog.csdn.net/Kalenee/article/details/99207102
一、坐标变换详解
1.1 坐标关系
相机中有四个坐标系,分别为world,camera,image,pixel
world为世界坐标系,可以任意指定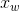 轴和
轴和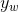 轴,为上图P点所在坐标系。
轴,为上图P点所在坐标系。camera为相机坐标系,原点位于小孔,z轴与光轴重合,轴和轴平行投影面,为上图坐标系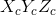 。
。image为图像坐标系,原点位于光轴和投影面的交点,轴和轴平行投影面,为上图坐标系xy。pixel为像素坐标系,从小孔向投影面方向看,投影面的左上角为原点,uv轴和投影面两边重合,该坐标系与图像坐标系处在同一平面,但原点不同。
1.2 坐标转换
下式为像素坐标pixel与世界坐标world的转换公式,左侧第一个矩阵为相机内参数矩阵,第二个矩阵为相机外参数矩阵。假设图像坐标已知,同时相机内参数矩阵通过标定已获取,还需计算比例系数s和外参数矩阵。
- 比例系数s
转换公式可简化为:
M为相机内参数矩阵,R为旋转矩阵,t为平移矩阵,![]() 为世界坐标系高度,可设置为0。
为世界坐标系高度,可设置为0。
通过矩阵变换可得下式:
求解出旋转矩阵和平移矩阵即可算得s。
- 外参数矩阵
Perspective-n-Point是通过n组给定点的世界坐标与像素坐标估计相机位置的方法。OpenCV内部提供的函数为solvePnP(),函数介绍如下:
bool solvePnP(InputArray objectPoints,
InputArray imagePoints,
InputArray cameraMatrix,
InputArray distCoeffs,
OutputArray rvec,
OutputArray tvec,
bool useExtrinsicGuess=false,
int flags=ITERATIVE )objectPoints,输入世界坐标系中点的坐标;imagePoints,输入对应图像坐标系中点的坐标;cameraMatrix, 相机内参数矩阵;distCoeffs, 畸变系数;rvec, 旋转向量,需输入一个非空Mat,需要通过cv::Rodrigues转换为旋转矩阵;tvec, 平移向量,需输入一个非空Mat;useExtrinsicGuess, 默认为false,如果设置为true则输出输入的旋转矩阵和平移矩阵;flags,选择采用的算法;- CV_ITERATIVE Iterative method is based on Levenberg-Marquardt optimization. In this case the function finds such a pose that minimizes reprojection error, that is the sum of squared distances between the observed projections
imagePointsand the projected (usingprojectPoints())objectPoints. - CV_P3P Method is based on the paper of X.S. Gao, X.-R. Hou, J. Tang, H.-F. Chang “Complete Solution Classification for the Perspective-Three-Point Problem”. In this case the function requires exactly four object and image points.
- CV_EPNP Method has been introduced by F.Moreno-Noguer, V.Lepetit and P.Fua in the paper “EPnP: Efficient Perspective-n-Point Camera Pose Estimation”.
- CV_ITERATIVE Iterative method is based on Levenberg-Marquardt optimization. In this case the function finds such a pose that minimizes reprojection error, that is the sum of squared distances between the observed projections
注意:solvePnP的参数rvec和tvec应该都是double类型的
二、程序实现
(1)计算参数s和旋转平移矩阵,需要输入一系列的世界坐标系的点及其对应的图像坐标系的点。
//输入参数
Mat cameraMatrix = Mat(3, 3, CV_32FC1, Scalar::all(0)); /* 摄像机内参数矩阵 */
Mat distCoeffs = Mat(1, 5, CV_32FC1, Scalar::all(0)); /* 摄像机的5个畸变系数:k1,k2,p1,p2,k3 */
double zConst = 0;//实际坐标系的距离,若工作平面与相机距离固定可设置为0
//计算参数
double s;
Mat rotationMatrix = Mat (3, 3, DataType::type);
Mat tvec = Mat (3, 1, cv::DataType::type);
void calcParameters(vector imagePoints, vector objectPoints)
{
//计算旋转和平移
Mat rvec(3, 1, cv::DataType::type);
cv::solvePnP(objectPoints, imagePoints, cameraMatrix, distCoeffs, rvec, tvec);
cv::Rodrigues(rvec, rotationMatrix);
} (2)根据输入的图像坐标计算世界坐标。
Point3f getWorldPoints(Point2f inPoints)
{
//获取图像坐标
cv::Mat imagePoint = cv::Mat::ones(3, 1, cv::DataType::type); //u,v,1
imagePoint.at(0, 0) = inPoints.x;
imagePoint.at(1, 0) = inPoints.y;
//计算比例参数S
cv::Mat tempMat, tempMat2;
tempMat = rotationMatrix.inv() * cameraMatrix.inv() * imagePoint;
tempMat2 = rotationMatrix.inv() * tvec;
s = zConst + tempMat2.at(2, 0);
s /= tempMat.at(2, 0);
//计算世界坐标
Mat wcPoint = rotationMatrix.inv() * (s * cameraMatrix.inv() * imagePoint - tvec);
Point3f worldPoint(wcPoint.at(0, 0), wcPoint.at(1, 0), wcPoint.at(2, 0));
return worldPoint;
}
参考
http://answers.opencv.org/question/62779/image-coordinate-to-world-coordinate-opencv/
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/12299870/computing-x-y-coordinate-3d-from-image-point
https://docs.opencv.org/2.4/modules/calib3d/doc/camera_calibration_and_3d_reconstruction.html
《视觉SLAM十四讲》——相机与图像


