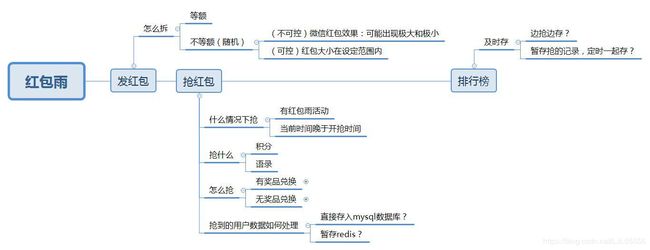
【红包雨】活动红包雨实现逻辑(ionic+springboot)
前言
活动形式:参与活动人员通过红包雨活动抢积分,通过积分可进行相应的奖品兑换
活动当天,我负责完成的功能包括:发红包,红包雨,排行榜
我的考虑
实现逻辑
一、发红包(拆分)
我们采取的是可控情况的不等额金额分配,这种情况下参数共需4个:总金额,红包个数,最大值,最小值,具体拆分形式
多种多样,这里举个栗子(可限定最大值,最小值):
// 每一份随机金额范围(除最后一份),最小值为1,最大值为当前剩余平均金额的3倍
// 当前剩余平均金额=剩余总金额/剩余红包
public ArrayList divide(int totalMoney, int count) {
//创建保存各个红包金额的集合
ArrayList list = new ArrayList <>();
//定义循环次数,总个数‐1次
int time = count‐1;
//创建随机数对象
Random random = new Random();
//循环分配
for (int i = 0; i < time; i++) {
/*
*每次重新计算,生成随机金额
*随机范围:totalMoney/count*3,totalMoney不断的减少,
*count也不断的减少,所以这是一个可变化的范围.
*/
int money = random.nextInt(totalMoney / count * 3) + 1;
//金额添加到集合
list.add(money);
//总金额扣除已分配金额
total Money‐=money;
//红包个数‐1
count‐‐;
}
//剩余的金额,为最后一个红包
list.add(totalMoney);
return list;
}
二、抢红包(含关键逻辑的代码)
(一)逻辑
抢红包的关键点:抢、存
抢:
- 什么时候抢
- 有红包活动
- 当前时间晚于红包开抢时间
- 抢什么
- 积分
- 语录
部分代码
private static AtomicInteger count = new AtomicInteger(0);
//根据次数判断是否要调用抢红包方法
int number = count.incrementAndGet();
model.setNumber(number);
//红包雨每请求2-5次(随机),调用一次抢红包方法
// 起始值(生成随机数的参数)
int start = 2;
// 间隔值(生成随机数的参数)
int interval = 4;
if (number % (new Random().nextInt(interval) + start) == 0) {
// 抢红包方法
IntegralResult result = grabRedPacket(model);
return IntegralResult.build(result.getCode(), result.getMessage(), result.getData());
} else {
redPacketEntity.setIntegral(0);
// 随机的语录,返给前端
redPacketEntity.setReason(quotationList.get(new Random().nextInt(quotationList.size())));
}
- 怎么抢
- 无奖品兑换
- 有奖品兑换(只控制达到最高礼品所需积分的人数)
- 没抢过红包 或 用户红包活动总额< 最高积分的70%,正常抢
- 最高积分的70% < 用户红包活动总额 < 最高积分的90%,抢到积分的概率降低
- 用户红包活动总额 > 最高积分的90%,抢到语录
// 判断用户是否抢到过红包
Boolean userIntegralFlag = redisTemplate.opsForHash().hasKey(activityId + ":" + "userIntegral", userId);
int userIntegral = 0;
if (userIntegralFlag) {
// 用户抢到的红包总额
userIntegral = (int) redisTemplate.opsForHash().get(activityId + ":" + "userIntegral", userId);
}
// 如果该用户 没抢到过红包 或者 用户红包活动总额< 最高积分的70%,正常抢
/* *
* 对用户红包雨活动能够抢到的积分做限制,
* 达到firstLimit = > 抢到积分的概率降低
* 达到secondLimit = > 只能抢到语录
*/
double firstLimit = 0.7;
double secondLimit = 0.9;
if (!userIntegralFlag || userIntegral <= Math.floor(highestUserIntegral * firstLimit)) {
// 将抢红包记录暂存redis
saveRedPacketModel(userId, model.getUserName(), redPacketRainEntity, redPacketEntity, redPacketRainKey, userIntegral);
log.info("用户积分低于最高兑换积分的70%,已抢红包");
} else if (userIntegral > Math.floor(highestUserIntegral * firstLimit) && userIntegral < Math.floor(highestUserIntegral * secondLimit)) {
//红包雨每请求2-5次(随机),调用一次抢红包方法
// 起始值(生成随机数的参数)
int start = 2;
// 间隔值(生成随机数的参数)
int interval = 4;
if (model.getNumber() % (new Random().nextInt(interval) + start) == 0) {
saveRedPacketModel(userId, model.getUserName(), redPacketRainEntity, redPacketEntity, redPacketRainKey, userIntegral);
} else {
redPacketRainEntity.setIntegral(0);
// 随机的语录,返给前端
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(quotationList)) {
quotationList = redisTemplate.opsForList().range("quotation", 0, -1);
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(quotationList)) {
queryRelation();
}
}
redPacketRainEntity.setReason(quotationList.get(new Random().nextInt((quotationList).size())));
}
log.info("用户积分介于最高兑换积分的70%-90%,已抢红包");
} else if (userIntegral >= Math.floor(highestUserIntegral * secondLimit)) {
redPacketRainEntity.setIntegral(0);
// 随机的语录,返给前端
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(quotationList)) {
quotationList = redisTemplate.opsForList().range("quotation", 0, -1);
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(quotationList)) {
queryRelation();
}
}
redPacketRainEntity.setReason(quotationList.get(new Random().nextInt((quotationList).size())));
log.info("用户积分高于最高兑换积分的90%,已抢红包");
}
- 抢到的数据如何处理
- 暂存redis
private void saveRedPacketModel(String userId, String userName, ExhibitionPacketRecordEntity
redPacketRainEntity, ExhibitionSendPacketEntity redPacketEntity, String redPacketRainKey, int userIntegral) {
/**
* 加锁(redis分布式锁)
*/
RLock rlock = redissonClient.getLock("redisson:lock:redPacketId" + redPacketEntity.getId());
//设置锁超时时间,防止异常造成死锁
rlock.lock(2, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
List list = redisTemplate.opsForList().range(redPacketRainKey, 0, -1);
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(list)) {
log.warn("{} redis记录为空", redPacketRainKey);
//解锁
rlock.unlock();
return;
}
try {
redPacketRainEntity
.setUserId(userId)
.setUserName(userName)
.setIntegral(list.get(0))
.setReason("红包雨")
.setRedPacketId(redPacketEntity.getId())
.setActivityId(redPacketEntity.getActivityId());
String alreadyGrabKey = redPacketEntity.getActivityId() + ":" + redPacketEntity.getId() + ":" + "1";
redisTemplate.opsForList().leftPush(alreadyGrabKey, redPacketRainEntity);
redisTemplate.opsForList().leftPop(redPacketRainKey);
redisTemplate.opsForHash().put(redPacketEntity.getActivityId() + ":" + "userIntegral", userId, userIntegral + list.get(0));
} finally {
//解锁
rlock.unlock();
}
(二)需要注意的地方
1.统计所有用户访问抢红包后端的次数应该使用AtomicInteger 而不是int
int不是线程安全的,但AtommicInteger是。
❤AtommicInteger的使用过程:
在并发环境下,某个线程对共享变量先进行操作,如果没有其他线程争用共享数据那操作就成功;如果存在数据的争用冲突,那就才去补偿措施,比如不断的重试机制,直到成功为止,这种并发策略不需要把线程挂起。
❤代码
private static AtomicInteger count = new AtomicInteger(0);
// incrementAndGet()方法在一个无限循环体内,不断尝试将一个比当前值大1的新值赋给自己,如果失败则说明在执行"获取-设置"操作的时候已经被其它线程修改过了,于是便再次进入循环下一次操作,直到成功为止。
int number = count.incrementAndGet();
2.用户抢红包信息存入redis使用redis锁(redission)
❤redission的特点:
1-互斥性。在任意时刻,只有一个客户端能持有锁。
2-可靠性。要保证系统的稳定性,不能产生死锁
3-容错性。只要大部分的Redis节点正常运行,客户端就可以加锁和解锁。
4-一致性。加锁和解锁必须是同一个客户端,客户端自己不能把别人加的锁给解了。
❤代码:
RLock rlock = redissonClient.getLock("redisson:lock");
//设置锁超时时间,防止异常造成死锁
rlock.lock(2, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
try {
// 要执行的逻辑
} finally {
//解锁
rlock.unlock();
}
3.redis使用
❤红包过程用到的redis:
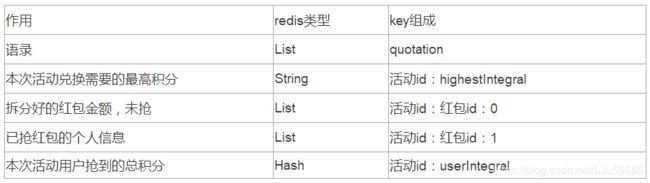
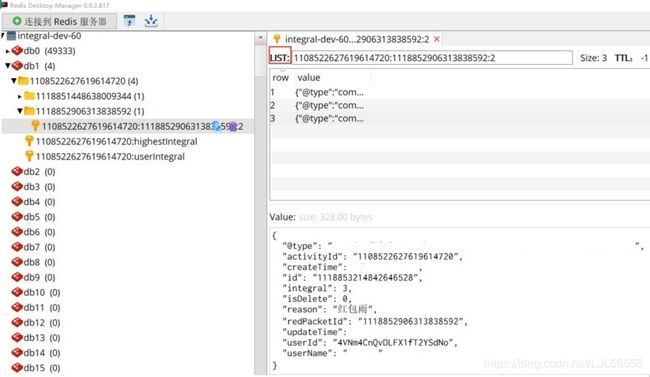
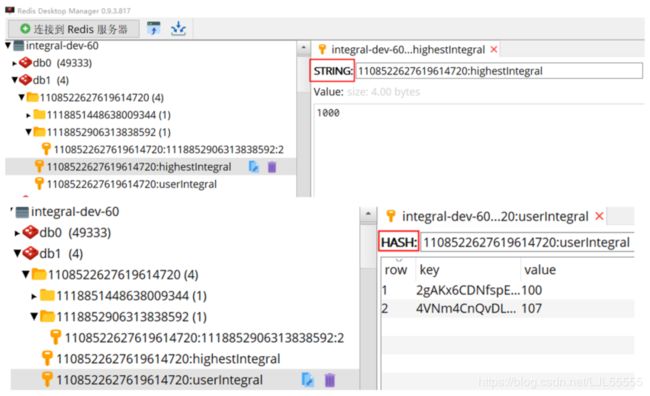
❤redis中的存储情况:
三、排行榜
红包雨被抢完后,自动跳转到排行榜页面
为了保证用户可以看到最新的红包记录结果,采用的是定时器5秒执行一次,将redis中的红包记录存入数据库
定时器才用的是xxl-job。