407-Trapping Rain Water II
Description:
Given an m x n matrix of positive integers representing the height of each unit cell in a 2D elevation map, compute the volume of water it is able to trap after raining.
Note:
Both m and n are less than 110. The height of each unit cell is greater than 0 and is less than 20,000.
Example:
Given the following 3x6 height map:
[
[1,4,3,1,3,2],
[3,2,1,3,2,4],
[2,3,3,2,3,1]
]
Return 4.
The above image represents the elevation map [[1,4,3,1,3,2],[3,2,1,3,2,4],[2,3,3,2,3,1]] before the rain.
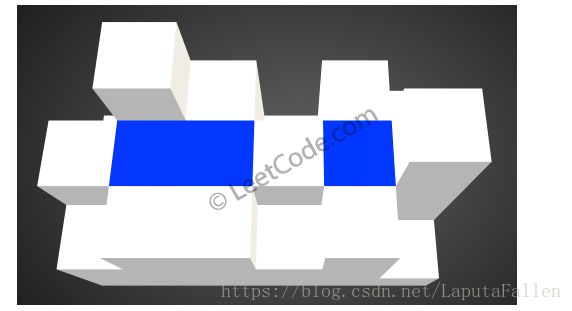
After the rain, water is trapped between the blocks. The total volume of water trapped is 4.
问题描述:
给定一个二维数组,其中每个元素为单位方块(长宽为1)的高度,求下雨后,这个立体空间能盛的水的体积。
例子:
[
[1,4,3,1,3,2],
[3,2,1,3,2,4],
[2,3,3,2,3,1]
]
(1,3)和(1,2)下标的元素变为3,(1,5)变为3,总计为4
关于这个题目,先说一下自己的想法:
如果单纯的想每一个方块如何变化,然后加起来,那完蛋了,比较困难。列一个不太形象的比喻,木桶原理,把整个空间想象为一个整体,除去边缘处(因为雨不可能盛放在边缘,只能从边缘往里流),每个方块最终的结果为其”观察”周围后能够达到的最大的高度。
有两种解法,都是用的优先级队列。
解法1:
/*
使用优先级队列,优先级判断条件为方块的高度。先把边缘处方块加入优先级队列,优先处理高度最低的。
每取出一个方块,可以看到四个方向的方块,首先排除到已经看过或者行列不满足条件的方块,
如果新方块比当前方块矮,那么最终结果加上两者之差,将新方块的高度改为当前方块高度后加入队列。
如果新方块的高度大于等于当前方块,那么不作处理,将其加入队列。依次处理,直到优先级队列没有元素,
返回最终结果。
*/
class Solution {
private int[][] dirs = {{0, -1}, {-1, 0}, {0, 1}, {1, 0}};
//方块类,实现了Comparable接口,用于优先级队列排序
private class Cell implements Comparable<Cell>{
int row;
int col;
int height;
public Cell(int row, int col, int height){
this.row = row;
this.col = col;
this.height = height;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Cell cell1){
return height - cell1.height;
}
}
public int trapRainWater(int[][] heightMap) {
if(heightMap == null || heightMap.length == 0 || heightMap[0].length == 0) return 0;
int m = heightMap.length, n = heightMap[0].length;
//由于方块类Cell实现了Comparable,优先级队列不需要定义匿名内部类comparator
Queue queue = new PriorityQueue| ();
boolean[][] visited = new boolean[m][n];
//首先放入边缘方块
for(int i = 0;i < m;i++){
visited[i][0] = true;
visited[i][n - 1] = true;
queue.add(new Cell(i, 0, heightMap[i][0]));
queue.add(new Cell(i, n - 1, heightMap[i][n - 1]));
}
for(int j = 1;j < n - 1;j++){
visited[0][j] = true;
visited[m - 1][j] = true;
queue.add(new Cell(0, j, heightMap[0][j]));
queue.add(new Cell(m - 1, j, heightMap[m - 1][j]));
}
int res = 0;
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
Cell cell = queue.poll();
for(int[] dir : dirs){
int i = cell.row + dir[0], j = cell.col + dir[1];
//排除不合条件的方块后分情况处理,为了方便,直接使用了两个Math.max()
if(i >= 0 && i < m && j >= 0 && j < n && !visited[i][j]){
visited[i][j] = true;
res += Math.max(0, cell.height - heightMap[i][j]);
queue.offer(new Cell(i, j, Math.max(heightMap[i][j], cell.height)));
}
}
}
return res;
}
} | | 解法2:
/*
与解法1差异在于加了fill方法。实际上我认为解法2更好理解,可以想象成水面慢慢上升
实际上自习分析解法1,我们也可以看出解法2。如果边缘高度为2,3,4,那么会先处理2,而若2的四个方向
(实际上由于边缘,只有1个方向)中有一个方块高度比它小,那么将其放入优先级队列后会继续处理这个方块,
因为这个方块现在高度变为了2,还是最小的那个,所以实际上是一个递归,于是就有了fill()。直到把
高度为2的连通分量方块处理完它才会结束递归,转回优先级队列
*/
public class Solution {
private static class Cell implements Comparable {
private int row;
private int col;
private int value;
public Cell(int r, int c, int v) {
this.row = r;
this.col = c;
this.value = v;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Cell other) {
return value - other.value;
}
}
private int water;
private boolean[][] visited1;
public int trapRainWater(int[][] heightMap) {
if (heightMap.length == 0) return 0;
PriorityQueue walls = new PriorityQueue();
water = 0;
visited1 = new boolean[heightMap.length][heightMap[0].length];
int rows = heightMap.length, cols = heightMap[0].length;
//build wall;
for (int c = 0; c < cols; c++) {
walls.add(new Cell(0, c, heightMap[0][c]));
walls.add(new Cell(rows - 1, c, heightMap[rows - 1][c]));
visited1[0][c] = true;
visited1[rows - 1][c] = true;
}
for (int r = 1; r < rows - 1; r++) {
walls.add(new Cell(r, 0, heightMap[r][0]));
walls.add(new Cell(r, cols - 1, heightMap[r][cols - 1]));
visited1[r][0] = true;
visited1[r][cols - 1] = true;
}
//end build wall;
while(walls.size() > 0) {
Cell min = walls.poll();
//变化在这里
visit(heightMap, min, walls);
}
return water;
}
private void visit(int[][] height, Cell start, PriorityQueue walls) {
fill(height, start.row + 1, start.col, walls, start.value);
fill(height, start.row - 1, start.col, walls, start.value);
fill(height, start.row, start.col + 1, walls, start.value);
fill(height, start.row, start.col - 1, walls, start.value);
}
//注意fill,是一个递归的函数
private void fill(int[][] height, int row, int col, PriorityQueue| walls, int min) {
if (row < 0 || col < 0) return;
else if (row >= height.length || col >= height[0].length) return;
else if (visited1[row][col]) return;
else if (height[row][col] >= min) {
walls.add(new Cell(row, col, height[row][col]));
visited1[row][col] = true;
return;
} else {
water += min - height[row][col];
visited1[row][col] = true;
fill(height, row + 1, col, walls, min);
fill(height, row - 1, col, walls, min);
fill(height, row, col + 1, walls, min);
fill(height, row, col - 1, walls, min);
}
}
} | | | | |