支持向量机(SVM)的SMO算法实现(Python)
最近在学支持向量机,总感觉对SMO理解的不够透彻,就编写程序来检验自己的理解
完全参照John C. Platt《Sequential Minimal Optimization - A Fast Algorithm for Training Support Vector Machines》中的伪代码编写的Python程序(去除了文中的tol)
参考(感谢前辈们^_^):
支持向量机通俗导论(理解SVM的三层境界)
支持向量机(五)SMO算法
Python实现SVM(支持向量机)(数据引用)
代码:
#SVM-SMO
#by ald
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def load_data_set(fileName):
data_sets = []
label_sets = []
with open(fileName) as fr:
for line in fr.readlines():
lineArr = line.strip().split('\t') #去除两边空白符,按制表符分割
data_sets.append([float(lineArr[0]), float(lineArr[1])])
label_sets.append(float(lineArr[2]))
data_sets = np.array(data_sets)
label_sets = np.array([label_sets]).T
return data_sets, label_sets
class OptStruct:
def __init__(self, point, target, C): # point array格式的样本集, target array格式的标签集
self.point = point
self.target = target
self.C = C
self.m = np.shape(point)[0] #样本数量
self.alphas = np.zeros((self.m, 1))
self.b = 0
self.e_cache = np.zeros((self.m, 2)) #储存E
self.Gamma = np.dot(point, point.T)
def cal_Ei(i, opt_struct1):
f_point_i = float(np.dot((opt_struct1.target * opt_struct1.alphas).T, opt_struct1.Gamma[i].T)) + opt_struct1.b
Ei = f_point_i - opt_struct1.target[i]
return Ei
def select_i1_heuristic(i2, opt_struct1, E2):
valid_e_cache = np.nonzero(opt_struct1.e_cache[:, 0])[0]
max_delta_E = np.argmax(np.fabs(opt_struct1.e_cache[valid_e_cache, 1] - E2))
i1 = valid_e_cache[max_delta_E]
return i1
def take_step(i1, i2, opt_struct1):
if i1 == i2:
return False
global y2, alpha2, E2, eps
alpha1 = opt_struct1.alphas[i1]
y1 = opt_struct1.target[i1]
E1 = cal_Ei(i1, opt_struct1)
opt_struct1.e_cache[i1] = [1, E1] #chech in error cache
s = y1 * y2
if y1 == y2:
L = max(0, alpha2 + alpha1 - C)
H = min(C, alpha2 + alpha1)
else:
L = max(0, alpha2 - alpha1)
H = min(C, C + alpha2 + alpha1)
if L == H:
return False
k11 = np.dot(opt_struct1.point[i1], opt_struct1.point[i1].T)
k12 = np.dot(opt_struct1.point[i1], opt_struct1.point[i2].T)
k22 = np.dot(opt_struct1.point[i2], opt_struct1.point[i2].T)
eta = k11 + k22 - 2 * k12
if eta > 0:
a2 = alpha2 + y2 * (E1 - E2) / eta
if a2 < L:
a2 = L
elif a2 > H:
a2 = H
else:
f1 = y1 * (E1 + opt_struct1.b) - alpha1 * k11 - s * alpha2 * k22
f2 = y2 * (E2 + opt_struct1.b) - s * alpha1 * k12 - alpha2 * k22
L1 = alpha1 + s * (alpha2 - L)
H1 = alpha1 + s * (alpha2 - H)
L_obj = L1 * f1 + L * f2 + 0.5 * L1 * L1 * k11 + 0.5 * L * L * k22 + s * L * L1 * k12
H_obj = H1 * f1 + H * f2 + 0.5 * H1 * H1 * k11 + 0.5 * H * H * k22 + s * H * H1 * k12
if L_obj < H_obj - eps:
a2 = L
elif L_obj > H_obj + eps:
a2 = H
else:
a2 = alpha2
if abs(a2 - alpha2) < eps * (a2 + alpha2 + eps):
return False
a1 = alpha1 + s * (alpha2 - a2)
b1 = -E1 - y1 * (a1 - alpha1) * k11 + y2 * (a2 - alpha2) * k12 + opt_struct1.b
b2 = -E2 - y1 * (a1 - alpha1) * k12 + y2 * (a2 - alpha2) * k22 + opt_struct1.b
if 0 < a1 1 and alpha2 > 0): #如果违反KKT条件,选择i1,如果发生更新,返回1
if np.sum((opt_struct1.alphas != 0) * (opt_struct1.alphas != C)) > 1: #如果非界样本数量>1
i1 = select_i1_heuristic(i2, opt_struct1, E2) #启发式方法从非界样本中选择i1
if take_step(i1, i2, opt_struct1 = opt_struct1):
return 1
#如果启发式方法找到的i1不可行,遍历非界样本集寻找可行的i1(随机开始)
non_bound_alphas = np.nonzero((opt_struct1.alphas != 0) * (opt_struct1.alphas != C))[0] #局部变量
np.random.shuffle(non_bound_alphas) #随机打乱
for k in non_bound_alphas:
if take_step(k, i2, opt_struct1):
return 1
#如果仍没有找到可行的i1,遍历边界样本集寻找i1
bound_alphas = np.nonzero((opt_struct1.alphas == 0) + (opt_struct1.alphas == C))[0]
np.random.shuffle(bound_alphas)
for j in bound_alphas:
if take_step(j, i2, opt_struct1):
return 1
return 0 #不违反KKT条件,返回0
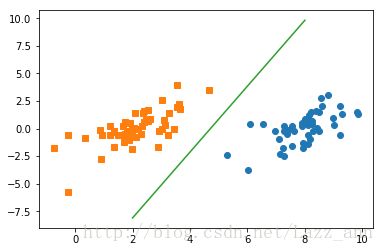
def plot_result(point_sets, target_sets, w, b):
x1_positive = []
x2_positive = []
x1_negeitve = []
x2_negetive = []
for i in range(len(target_sets)):
if int(target_sets[i]) == 1:
x1_positive.append(point_sets[i, 0])
x2_positive.append(point_sets[i, 1])
else:
x1_negeitve.append(point_sets[i, 0])
x2_negetive.append(point_sets[i, 1])
x = np.linspace(2, 8)
y = (-b - w[0] * x) / w[1]
plt.plot(x1_positive, x2_positive, 'o')
plt.plot(x1_negeitve, x2_negetive, 's')
plt.plot(x, y)
point_sets, target_sets = load_data_set('testSet.txt')
opt_struct1 = OptStruct(point_sets, target_sets, 1)
C = 1000
iters = 0 #迭代次数
num_changed = 0 #更新计数
examine_all = True #是否循环所有样本
eps = 0.00001 #允许误差,原文献中取0.001
max_iters = 500
while iters <= max_iters and num_changed > 0 or examine_all:
num_changed = 0
if examine_all:
for i in range(0, opt_struct1.m):
num_changed += examine_example(i, opt_struct1) #检查所有样本
else:
#检查 0 < alpha < C 的样本(非界样本)
non_bound_alphas = np.nonzero((opt_struct1.alphas != 0) * (opt_struct1.alphas != C))[0]
for i in non_bound_alphas:
num_changed += examine_example(i, opt_struct1)
iters += 1
#如果检查了所有样本,下次就只检查非界样本,
#如果非界样本全部合法,下次就要检查全部的样本
if examine_all:
examine_all = False
elif num_changed == 0:
examine_all = True
w = np.dot((target_sets * opt_struct1.alphas).T, point_sets).flatten()
print()
print('w:', w)
print('b:', opt_struct1.b)
plot_result(point_sets, target_sets, w, opt_struct1.b) 结果: