【线段树学习】POJ-3468-A Simple Problem with Integers
A Simple Problem with Integers
Description
You have N integers, A1, A2, … , AN. You need to deal with two kinds of operations. One type of operation is to add some given number to each number in a given interval. The other is to ask for the sum of numbers in a given interval.
Input
The first line contains two numbers N and Q. 1 ≤ N,Q ≤ 100000.
The second line contains N numbers, the initial values of A1, A2, … , AN. -1000000000 ≤ Ai ≤ 1000000000.
Each of the next Q lines represents an operation.
“C a b c” means adding c to each of Aa, Aa+1, … , Ab. -10000 ≤ c ≤ 10000.
“Q a b” means querying the sum of Aa, Aa+1, … , Ab.
Output
You need to answer all Q commands in order. One answer in a line.
Sample Input
10 5
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
Q 4 4
Q 1 10
Q 2 4
C 3 6 3
Q 2 4
Sample Output
4
55
9
15
#include
#define N 111111
#define LL long long
#define lson l,m,rt<<1
#define rson m+1,r,rt<<1|1
LL add[N<<2];
LL sum[N<<2];
void PushUP(int rt)
{
sum[rt]=sum[rt<<1]+sum[rt<<1|1];
}
void PushDown(int rt,int m)
{
if(add[rt])
{
add[rt<<1]+=add[rt];
add[rt<<1|1]+=add[rt];
sum[rt<<1]+=(m-(m>>1))*add[rt];
sum[rt<<1|1]+=(m>>1)*add[rt];
add[rt]=0;
}
}
void Build(int l,int r,int rt)
{
add[rt]=0;
if(l==r)
{
scanf("%lld",&sum[rt]);
return;
}
int m=(l+r)>>1;
Build(lson);
Build(rson);
PushUP(rt);
}
void Update(int L,int R,int c,int l,int r,int rt)
{
if(L<=l&&R>=r)
{
add[rt]+=c;
sum[rt]+=(LL)c*(r-l+1);
return;
}
PushDown(rt,r-l+1);
int m=(l+r)>>1;
if(L<=m)
Update(L,R,c,lson);
if(R>m)
Update(L,R,c,rson);
PushUP(rt);
}
LL Query(int L,int R,int l,int r,int rt)
{
if(L<=l&&R>=r)
return sum[rt];
PushDown(rt,r-l+1);
int m=(l+r)>>1;
LL ret=0;
if(L<=m) ret+=Query(L,R,lson);
if(R>m) ret+=Query(L,R,rson);
return ret;
}
int main()
{
int m,n;
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
Build(1,n,1);
while(m--)
{
char s[5];
int a,b,c;
scanf("%s",s);
if(s[0]=='Q')
{
scanf("%d%d",&a,&b);
printf("%lld\n",Query(a,b,1,n,1));
}
else
{
scanf("%d%d%d",&a,&b,&c);
Update(a,b,c,1,n,1);
}
}
return 0;
}
模板题,初学,感觉还是很难理解的。
照着大神们的模板学的
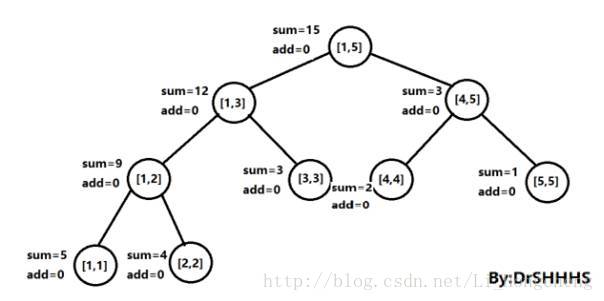
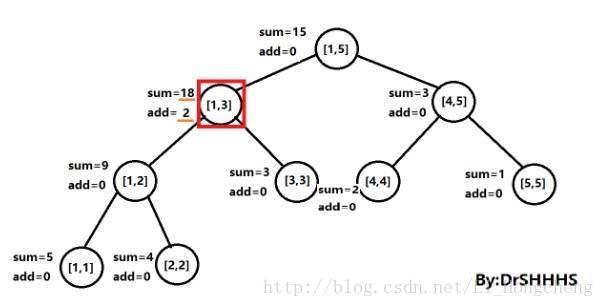
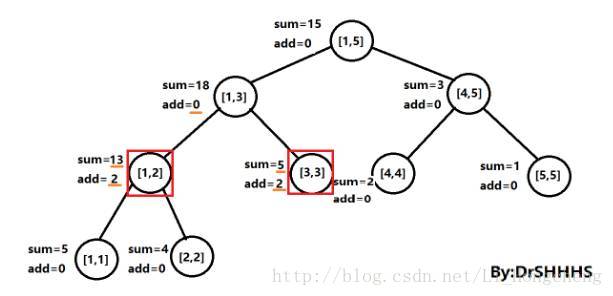
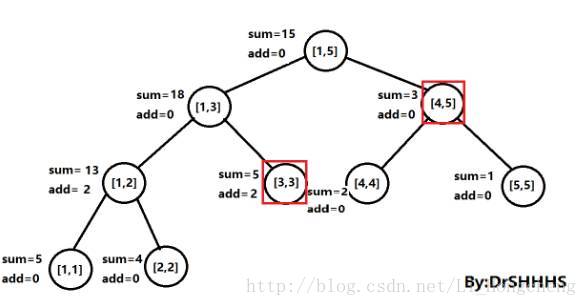
延迟标记在我们需要时,才向下传递信息,如果没有用到,则不再进行操作。这个思想使处理的复杂度依然保持在O(log2(n))左右,相比朴素算法大大地降低了复杂度。
为了完成这种操作,我们可以在结构体中,增加一个add数组存储区间的延迟变化量
比如现在需要对[a,b]区间值进行加c操作,那么就从根节点[1,n]开始调用update函数进行操作,如果刚好执行到一个子节点,它的节点标记为rt,这时tree[rt].l == a && tree[rt].r == b 这时我们可以一步更新此时rt节点的sum[rt]的值,sum[rt] += c * (tree[rt].r - tree[rt].l + 1),注意关键的时刻来了,如果此时按照常规的线段树的update操作,这时候还应该更新rt子节点的sum[]值,而Lazy思想恰恰是暂时不更新rt子节点的sum[]值,到此就return,直到下次需要用到rt子节点的值的时候才去更新,这样避免许多可能无用的操作,从而节省时间 。
#define lson l,m,rt<<1
#define rson m+1,r,rt<<1|1
宏定义左儿子lson和右儿子rson,貌似用宏的速度要慢。
PushUp(rt):通过当前节点rt把值递归向上更新到根节点
PushDown(rt):通过当前节点rt递归向下去更新rt子节点的值
rt表示当前子树的根(root),也就是当前所在的结点