CUDA: 共享存储器实现矩阵相乘
共享存储器使用__shared__限定词分配。
相关阅读:
CUDA编程接口:运行初始化与设备存储器
CUDA编程接口:使用nvcc编译器的兼容性
CUDA编程接口:如何用nvcc编译CUDA程序
CUDA编程模型:存储器层次和异构编程
CUDA编程模型:内核与线程层次概述
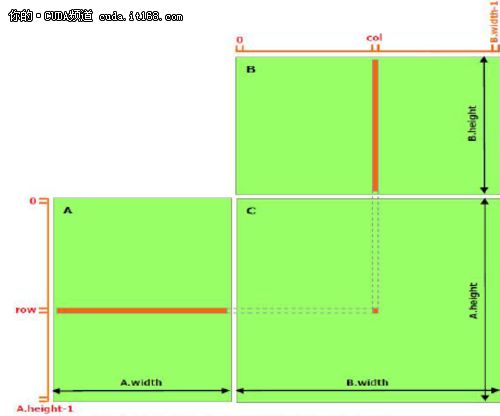
正如在前面的文章提到的,共享存储器应当比全局存储器更快,详细内容将在后续文章中介绍。任何用访问共享存储器取代访问全局存储器的机会应当被发掘,如下面的矩阵相乘例子展示的那样。 下面的代码是矩阵相乘的一个直接的实现,没有利用到共享存储器。每个线程读入A的一行和B的一列,然后计算C中对应的元素,如图1所示。这样,A读了B.width次,B读了A.height次。
#include
#pragma comment(lib, "cudart.lib") #pragma comment(lib, "cutil32.lib")
bool InitCUDA(void) { int count = 0; int i = 0;
cudaGetDeviceCount(&count); if(count == 0) { fprintf(stderr, "There is no device.\n"); return false; }
for(i = 0; i < count; i++) { cudaDeviceProp prop; if(cudaGetDeviceProperties(&prop, i) == cudaSuccess) { if(prop.major >= 1) { break; } } } if(i == count) { fprintf(stderr, "There is no device supporting CUDA.\n"); return false; } cudaSetDevice(i);
printf("CUDA initialized.\n"); return true; } /////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// #define THREAD_NUM 256
#define MATRIX_SIZE 100 //方阵阶
float a[MATRIX_SIZE][MATRIX_SIZE], b[MATRIX_SIZE][MATRIX_SIZE], c[MATRIX_SIZE][MATRIX_SIZE];
void Random_Number(float source[][MATRIX_SIZE]) { for(int i = 0; i < MATRIX_SIZE; i++) { for(int j = 0; j < MATRIX_SIZE; j++) { source[i][j] = float(rand() % 10) / 10; } } }
__global__ static void Matrix_Mul(const float* source1, const float* source2, float* result) { const int tid = threadIdx.x; const int bid = blockIdx.x; const int id = bid * blockDim.x + tid; const int row = id / MATRIX_SIZE; const int col = id % MATRIX_SIZE;
if(row < MATRIX_SIZE && col < MATRIX_SIZE) { float t = 0; for(int i = 0; i < MATRIX_SIZE; i++) { t += source1[row * MATRIX_SIZE + i] * source2[i * MATRIX_SIZE + col]; } result[row * MATRIX_SIZE + col] = t; } }
int main(int argc,char* argv[]) { InitCUDA();//初始化CUDA
float *ac, *bc, *cc; size_t lda, ldb, ldc;
srand(0);
Random_Number(a); Random_Number(b);
unsigned int timer = 0; CUT_SAFE_CALL( cutCreateTimer(&timer)); CUT_SAFE_CALL( cutStartTimer(timer));//define in cutil.h //到显存中申请空间,其中lda,ldb,ldc为显存中的行间距 cudaMallocPitch((void**)&ac, &lda, sizeof(float) * MATRIX_SIZE, MATRIX_SIZE); cudaMallocPitch((void**)&bc, &ldb, sizeof(float) * MATRIX_SIZE, MATRIX_SIZE); cudaMallocPitch((void**)&cc, &ldc, sizeof(float) * MATRIX_SIZE, MATRIX_SIZE); //复制内存元素到显存 cudaMemcpy2D(ac, lda, a, sizeof(float) * MATRIX_SIZE, sizeof(float) * MATRIX_SIZE, MATRIX_SIZE, cudaMemcpyHostToDevice); cudaMemcpy2D(bc, ldb, b, sizeof(float) * MATRIX_SIZE, sizeof(float) * MATRIX_SIZE, MATRIX_SIZE, cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);
int BLOCK_NUM = (MATRIX_SIZE + THREAD_NUM - 1) / THREAD_NUM;
Matrix_Mul<<
cutStopTimer(timer);
printf("Processing time: %f (ms)\n", cutGetTimerValue(timer));
for(int j = 0; j < MATRIX_SIZE; j++) { float temp = 0; for(int i = 0; i < MATRIX_SIZE; i++) { temp += a[0][i] * b[i][j]; }
printf ("CPU:c[0][%d]=%f\n", j, temp); printf ("GPU:c[0][%d]=%f\n", j, c[0][j]); }
system("PAUSE");
return 0; }
▲图1 没有使用共享存储器的矩阵相乘
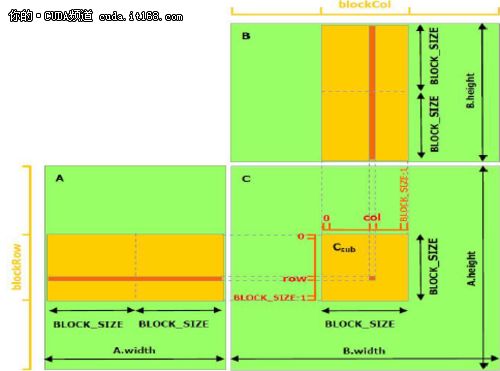
下面的例子代码利用了共享存储器实现矩阵相乘。本实现中,每个线程块负责计算一个小方阵Csub,Csub是C的一部分,而块内的每个线程计算Csub的一个元素。如图2所示。Csub等于两个长方形矩阵的乘积:A的子矩阵尺寸是(A.width,block_size),行索引与Csub相同,B的子矩阵的尺寸是(block_size,A.width),列索引与Csub相同。为了满足设备的资源,两个长方形的子矩阵分割为尺寸为block_size的方阵,Csub是这些方阵积的和。每次乘法的计算是这样的,首先从全局存储器中将二个对应的方阵载入共享存储器中,载入的方式是一个线程载入一个矩阵元素,然后一个线程计算乘积的一个元素。每个线程积累每次乘法的结果并写入寄存器中,结束后,再写入全局存储器。
采用这种将计算分块的方式,利用了快速的共享存储器,节约了许多全局存储器带宽,因为在全局存储器中,A只被读了(B.width/block_size)次同时B读了(A.height/block_size)次。
前面代码中的Matrix 类型增加了一个stride域,这样子矩阵能够用同样的类型有效表示。__device__函数(相关阅读的文章中提及)用于读写元素和从矩阵中建立子矩阵。
#define BLOCK_SIZE 16
// Matrices are stored in row-major order:
// M(row, col) = *(M.elements + row * M.stride + col)
typedef struct {
int width;
int height; int stride;
float* elements;
}
Matrix;
// Get a matrix element
__device__ float GetElement(const Matrix A, int row, int col)
{
return A.elements[row * A.stride + col];
}
// Set a matrix element
__device__ void SetElement(Matrix A, int row, int col, float value)
{
A.elements[row * A.stride + col] = value;
}
// Get the BLOCK_SIZExBLOCK_SIZE sub-matrix Asub of A that is
// located col sub-matrices to the right and row sub-matrices down
// from the upper-left corner of A
__device__ Matrix GetSubMatrix(Matrix A, int row, int col) {
Matrix Asub;
Asub.width = BLOCK_SIZE;
Asub.height = BLOCK_SIZE;
Asub.stride = A.stride;
Asub.elements = &A.elements[A.stride * BLOCK_SIZE * row + BLOCK_SIZE * col];
return Asub;
}
// Thread block size #define BLOCK_SIZE 16
// Forward declaration of the matrix multiplication kernel
__global__ void MatMulKernel(const Matrix, const Matrix, Matrix);
// Matrix multiplication - Host code
// Matrix dimensions are assumed to be multiples of BLOCK_SIZE
void MatMul(const Matrix A, const Matrix B, Matrix C)
{
// Load A and B to device memory
Matrix d_A;
d_A.width = d_A.stride = A.width;
d_A.height = A.height;
size_t size = A.width * A.height * sizeof(float);
cudaMalloc((void**)&d_A.elements, size);
cudaMemcpy(d_A.elements, A.elements, size, cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);
Matrix d_B;
d_B.width = d_B.stride = B.width;
d_B.height = B.height;
size = B.width * B.height * sizeof(float);
cudaMalloc((void**)&d_B.elements, size);
cudaMemcpy(d_B.elements, B.elements, size,cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);
// Allocate C in device memory
Matrix d_C;
d_C.width = d_C.stride = C.width;
d_C.height = C.height;
size = C.width * C.height * sizeof(float);
cudaMalloc((void**)&d_C.elements, size);
// Invoke kernel
dim3 dimBlock(BLOCK_SIZE, BLOCK_SIZE);
dim3 dimGrid(B.width / dimBlock.x, A.height / dimBlock.y);
MatMulKernel<<>>(d_A, d_B, d_C);
// Read C from device memory
cudaMemcpy(C.elements, d_C.elements, size, cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost);
// Free device memory
cudaFree(d_A.elements);
cudaFree(d_B.elements);
cudaFree(d_C.elements);
}
// Matrix multiplication kernel called by MatMul()
__global__ void MatMulKernel(Matrix A, Matrix B, Matrix C) {
// Block row and column
int blockRow = blockIdx.y;
int blockCol = blockIdx.x;
// Each thread block computes one sub-matrix Csub of C
Matrix Csub = GetSubMatrix(C, blockRow, blockCol);
// Each thread computes one element of Csub
// by accumulating results into Cvalue
float Cvalue = 0;
// Thread row and column within Csub
int row = threadIdx.y;
int col = threadIdx.x;
// Loop over all the sub-matrices of A and B that are
// required to compute Csub
// Multiply each pair of sub-matrices together
// and accumulate the results
for (int m = 0; m < (A.width / BLOCK_SIZE); ++m)
{
// Get sub-matrix Asub of A
Matrix Asub = GetSubMatrix(A, blockRow, m);
// Get sub-matrix Bsub of B
Matrix Bsub = GetSubMatrix(B, m, blockCol);
// Shared memory used to store Asub and Bsub respectively
__shared__ float As[BLOCK_SIZE][BLOCK_SIZE];
__shared__ float Bs[BLOCK_SIZE][BLOCK_SIZE];
// Load Asub and Bsub from device memory to shared memory
// Each thread loads one element of each sub-matrix
As[row][col] = GetElement(Asub, row, col);
Bs[row][col] = GetElement(Bsub, row, col);
// Synchronize to make sure the sub-matrices are loaded
// before starting the computation
__syncthreads();
// Multiply Asub and Bsub together
for (int e = 0; e < BLOCK_SIZE; ++e)
Cvalue += As[row][e] * Bs[e][col];
// Synchronize to make sure that the preceding
// computation is done before loading two new
// sub-matrices of A and B in the next iteration
__syncthreads(); }
// Write Csub to device memory
// Each thread writes one element
SetElement(Csub, row, col, Cvalue);
}
▲图2 使用共享存储器的矩阵相乘
http://cuda.it168.com/a2011/1207/1285/000001285186.shtml