数据结构学习笔记(四) 图之邻接矩阵实现广度优先遍历
以下是用邻接矩阵存储表示,实现图的广度优先遍历的实例。
用于遍历的无向图如下:
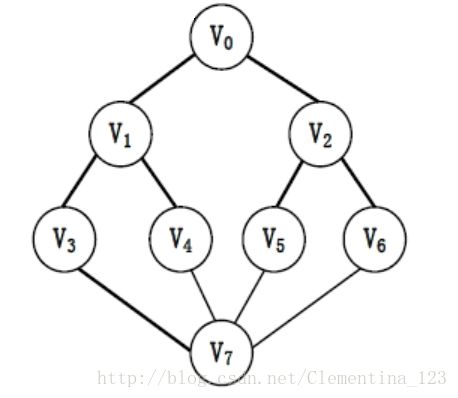
//v0-v7依次为字符0-7
#includereturn;
}
QU.Q[QU.rear]=x;
QU.rear=(QU.rear+1)%MaxSize;
}
//出队
void DeQueue(SeqQueue &QU,datatype &x)
{
//参数检查
if(QU.rear==QU.front)
{
cout<<"underflow!"<return;
}
x=QU.Q[QU.front];
QU.front=(QU.front+1)%MaxSize;
}
//判断队是否为空,为空则返回1,不为空则返回0
int QueueEmpty(SeqQueue &QU)
{
if(QU.rear==QU.front)
return 1;
return 0;
}
//构造邻接矩阵
void create(AMGraph &G)
{
G.n=8;
char x[8]={'0','1','2','3','4','5','6','7'};
for(int i=0;i<8;i++)
G.vex[i]=x[i];
for(int i=0;i<8;i++)
mark[i]=0;
int c[8][8]={{0,1,1},{1,0,0,1,1},{1,0,0,0,1,1},{0,1,0,0,0,0,0,1},{0,1,0,0,0,0,0,1},
{0,0,1,0,0,0,0,1},{0,0,1,0,0,0,0,1},{0,0,0,1,1,1,1}};
for(int i=0;i<8;i++)
for(int j=0;j<8;j++)
G.edge[i][j]=c[i][j];
}
//图的广度优先遍历
void BFS(AMGraph &G,int i)
{
int j;
int k;
SeqQueue QU;
ClearQueue(QU);
mark[i]=1;
EnQueue(QU,i);
while(!QueueEmpty(QU))
{
DeQueue(QU,k);
cout<<(char)G.vex[k]<while(G.edge[i][j]==1)
{
if(mark[j]==0)
{
mark[j]=1;
EnQueue(QU,j);
}
j++;
}
}
}
//广度优先遍历图的算法
void BFS_Component(AMGraph &G)
{
int i;
for(i=0;iif(mark[i]==0)
BFS(G,i);
}
//测试函数
int main()
{
create(G);
BFS_Component(G);
return 0;
}