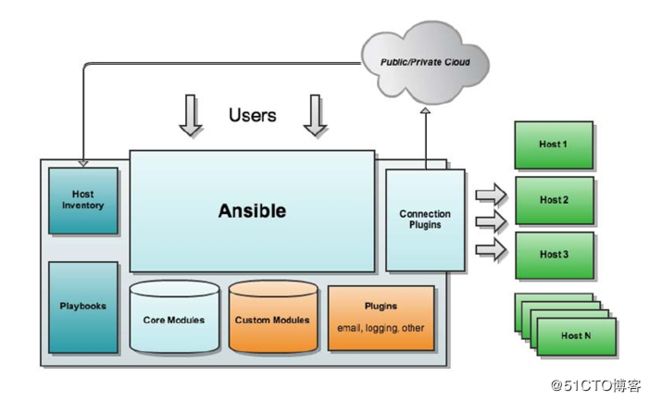
ansible基础与部分模块应用
1. ansible特性:
- ansible糅合了众多老牌运维工具的优点,基本上pubbet和saltstack能实现的功能全部能实现。
- 部署简单:不需要在被管控主机上安装任何客户端,操作客户端时直接运行命令。
- 基于python语言实现,有Paramiko, PyYAML和Jinja2三个关键模块。
- 模块化:调用特定模块完成特定任务。可使用任意语言开发模块,且支持自定义模块。
- 使用yaml语言定制剧本playbook。
- 基于SSH作
2. ansible的模块
- connection plugins:连接插件,通过ssh方式
- host inventory:主机清单,要管理的主机
- playbooks:剧本,yaml格式的配置文件
- core modules:核心模块
- custom modules:自定义模块
- plugins:插件
- email:发送邮件。
- loggings:记录日志
3. 安装
ansible放置位置:
- 外网主机:可通过×××连接为内网主机进行管理
- 内网主机:直接管理
ansible的安装:
配置好epel源,直接通过yum安装
~]# yum -y install ansibleansible的配置文件:/etc/ansible/ansible.cfg
ansible的主机清单:/etc/ansible/hosts
ansible的主程序:ansible、ansible-playbos、ansible-doc
4. ansible命令的使用:
[root@nfs ~]# ansible -h
Usage: ansible [options]
Options:
-a MODULE_ARGS, --args=MODULE_ARGS
module arguments
-C, --check don't make any changes; instead, try to predict some
of the changes that may occur
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-m MODULE_NAME, --module-name=MODULE_NAME
module name to execute (default=command)
--syntax-check perform a syntax check on the playbook, but do not
execute it
-f FORKS, --forks=FORKS
specify number of parallel processes to use
(default=5)
-u REMOTE_USER, --user=REMOTE_USER
connect as this user (default=None)
-c CONNECTION, --connection=CONNECTION
connection type to use (default=smart)
5. 定义主机列表:
示例1. 通过直接指定主机名或IP地址定义主机列表。
# Ex 1: Ungrouped hosts, specify before any group headers.
## green.example.com
## blue.example.com
## 192.168.100.1
## 192.168.100.10示例2. 先定义组名,再在组下填入主机名或IP地址
# Ex 2: A collection of hosts belonging to the 'webservers' group
## [webservers]
## alpha.example.org
## beta.example.org
## 192.168.1.100
## 192.168.1.110
# If you have multiple hosts following a pattern you can specify
# them like this:
# 如果有多个连续主机,也可用如下方法指定主机。
## www[001:006].example.com示例3.
# Ex 3: A collection of database servers in the 'dbservers' group
## [dbservers]
##
## db01.intranet.mydomain.net
## db02.intranet.mydomain.net
## 10.25.1.56
## 10.25.1.57
# Here's another example of host ranges, this time there are no
# leading 0s:
## db-[99:101]-node.example.com
## 以上写法可扩展为如下主机:
## db-99-nod.example.com
## db-100-nod.example.com
## db-101-nod.example.com定义主机列表示例:
[root@nfs ~]# tail -2 /etc/ansible/hosts
np[1:2].lxk.com
nfs.lxk.com获取主机列表:
[root@nfs ~]# ansible all --list-hosts
hosts (3):
np1.lxk.com
np2.lxk.com
nfs.lxk.com6. ansible的常用模块:
获取模块帮助信息:
[root@nfs ~]# ansible-doc --help
Usage: ansible-doc [-l|-F|-s] [options] [plugin]
plugin documentation tool
Options:
-a, --all **For internal testing only** Show documentation for
all plugins. #内测使用
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-l, --list List available plugins 显示可用插件
-s, --snippet Show playbook snippet for specified plugin(s)
## 显示指定插件用法获取模块列表:
~]# ansible-doc -l6.1 ping模块:探测远程主机
[root@nfs ~]# ansible-doc -s ping
- name: Try to connect to host, verify a usable python and return `pong' on success
# 尝试连接主机,若目标主机可用,就回应一个'pong'
ping:
data: # Data to return for the `ping' return value. If this parameter is set to `crash', the module will cause an exception.示例1:向所有可控主机发起ping操作
[root@nfs ~]# ansible all -m ping
np2.lxk.com | SUCCESS => {
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}
nfs.lxk.com | SUCCESS => {
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}
np1.lxk.com | SUCCESS => {
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}示例2:data自定义回显内容为abc
[root@nfs ~]# ansible all -m ping -a data='abc'
np1.lxk.com | SUCCESS => {
"changed": false,
"ping": "abc"
}
np2.lxk.com | SUCCESS => {
"changed": false,
"ping": "abc"
}
nfs.lxk.com | SUCCESS => {
"changed": false,
"ping": "abc"
}*示例3:data为crash时,显示结果为false
[root@nfs ~]# ansible all -m ping -a data='crash'
np1.lxk.com | FAILED! => {
"changed": false,
"module_stderr": "Shared connection to np1.lxk.com closed.\r\n",
"module_stdout": "Traceback (most recent call last):\r\n File \"/tmp/ansible_2DLaM3/ansible_module_ping.py\", line 84, in \r\n main()\r\n File \"/tmp/ansible_2DLaM3/ansible_module_ping.py\", line 74, in main\r\n raise Exception(\"boom\")\r\nException: boom\r\n",
"msg": "MODULE FAILURE",
"rc": 1
}
nfs.lxk.com | FAILED! => {
"changed": false,
"module_stderr": "Shared connection to nfs.lxk.com closed.\r\n",
"module_stdout": "Traceback (most recent call last):\r\n File \"/tmp/ansible_imV6B2/ansible_module_ping.py\", line 84, in \r\n main()\r\n File \"/tmp/ansible_imV6B2/ansible_module_ping.py\", line 74, in main\r\n raise Exception(\"boom\")\r\nException: boom\r\n",
"msg": "MODULE FAILURE",
"rc": 1
}
np2.lxk.com | FAILED! => {
"changed": false,
"module_stderr": "Shared connection to np2.lxk.com closed.\r\n",
"module_stdout": "Traceback (most recent call last):\r\n File \"/tmp/ansible_iocg2P/ansible_module_ping.py\", line 84, in \r\n main()\r\n File \"/tmp/ansible_iocg2P/ansible_module_ping.py\", line 74, in main\r\n raise Exception(\"boom\")\r\nException: boom\r\n",
"msg": "MODULE FAILURE",
"rc": 1
} 6.2 command模块:在远程主机上运行命令
模块用法:
对于command来说,要使用哪个命令,使用-a选项,直接给出命令本身即可。
例1:创建临时文件
[root@nfs ~]# ansible all -m command -a "mktemp /tmp/abc.XXXX"
nfs.lxk.com | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
/tmp/abc.Xyz7
np2.lxk.com | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
/tmp/abc.lwqo
np1.lxk.com | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
/tmp/abc.jjHW例2:创建用户
[root@nfs ~]# ansible all -m command -a "useradd user1" # 第一次创建成功
nfs.lxk.com | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
np1.lxk.com | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
np2.lxk.com | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
[root@nfs ~]# ansible all -m command -a "useradd user1" #第二次创建相同用户失败
nfs.lxk.com | FAILED | rc=9 >>
useradd: user 'user1' already existsnon-zero return code
np1.lxk.com | FAILED | rc=9 >>
useradd: user 'user1' already existsnon-zero return code
np2.lxk.com | FAILED | rc=9 >>
useradd: user 'user1' already existsnon-zero return code用加条件判断创建用户失败,因||是直接发给目标主机内核运行,不是经由shell运行,而||是shell的内置命令。
[root@nfs ~]# ansible all -m command -a "id user1 || useradd user1"
nfs.lxk.com | FAILED | rc=1 >>
id: extra operand ‘||’
Try 'id --help' for more information.non-zero return code
np1.lxk.com | FAILED | rc=1 >>
id: extra operand ‘||’
Try 'id --help' for more information.non-zero return code
np2.lxk.com | FAILED | rc=1 >>
id: extra operand ‘||’
Try 'id --help' for more information.non-zero return code
6.3 shell模块:在节点中执行命令
与command模块很相似,所不同处是它是在shell下运行的。还可使用executable切换至指定node下运行命令。
例:加条件判断创建用户
[root@nfs ~]# ansible all -m shell -a "id user1 || useradd user1"
np2.lxk.com | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
uid=1001(user1) gid=1001(user1) groups=1001(user1)
nfs.lxk.com | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
uid=1000(user1) gid=1000(user1) groups=1000(user1)
np1.lxk.com | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
uid=1000(user1) gid=1000(user1) groups=1000(user1)
6.4 group模块:添加或删除组
group模块用法:
[root@nfs ~]# ansible-doc -s group
- name: Add or remove groups
group:
gid: # Optional `GID' to set for the group.是否使用自定义的id号
name: # (required) Name of the group to manage. 要管理的组名,必须要定义的。
state: # Whether the group should be present or not on the remote host. 状态信息,决定是删除还是添加。创建:present,删除:absent
system: # If `yes', indicates that the group created is a system group. 是否创建系统用户示例:创建一个系统组
[root@nfs ~]# ansible np1.lxk.com -m group -a 'name=mygrp gid=200 system=yes'
np1.lxk.com | SUCCESS => {
"changed": true, #变更:成功
"gid": 200, #自定义组ID:200
"name": "mygrp", #组名:mygrp
"state": "present", #状态:添加
"system": true #是否为系统用户:是
}示例:删除组
[root@nfs ~]# ansible np1.lxk.com -m group -a 'name=mygrp state=absent'
np1.lxk.com | SUCCESS => {
"changed": true,
"name": "mygrp",
"state": "absent"
}上面命令重复执行时,changed状态为false。
[root@nfs ~]# ansible np1.lxk.com -m group -a 'name=mygrp state=absent'
np1.lxk.com | SUCCESS => {
"changed": false,
"name": "mygrp",
"state": "absent"
}6.5 user模块:管理用户帐户
模块内置命令一堆,请自行查看,基本见名知意。
示例:创建一个用户,名字为tom,用户ID为2000,组名为mygrp,shell类型为/bin/bash,状态为添加。
[root@nfs ~]# ansible np1.lxk.com -m user -a 'name=tom state=present uid=2000 groups=mygrp shell=/bin/bash'
np1.lxk.com | SUCCESS => {
"changed": true,
"comment": "",
"create_home": true,
"group": 2000,
"groups": "mygrp",
"home": "/home/tom",
"name": "tom",
"shell": "/bin/bash",
"state": "present",
"system": false,
"uid": 2000
}示例:修改tom用户的ID为2020,shell类型为/bin/tcsh
[root@nfs ~]# ansible np1.lxk.com -m user -a 'name=tom state=present uid=2020 groups=mygrp shell=/bin/tcsh'
np1.lxk.com | SUCCESS => {
"append": false,
"changed": true,
"comment": "",
"group": 2000,
"groups": "mygrp",
"home": "/home/tom",
"move_home": false,
"name": "tom",
"shell": "/bin/tcsh",
"state": "present",
"uid": 2020
}6.6 copy模块
用法:
[root@nfs ~]# ansible-doc -s copy
- name: Copies files to remote locations #复制一个或多个文件至远程主机
copy:
dest: # (required) Remote absolute path where the file should be copied to. If `src' is a directory, this must be a directory too. If `dest' is a nonexistent path and if either `dest' ends with "/" or `src' is a directory, `dest' is created. If `src' and `dest' are files, the parent directory of `dest' isn't created: the task fails if it doesn't already exist.
#复制指定文件至目标远程需要是绝对路径。如果src是目录,dest也必须是目录。如果dest是一个不存在的路径,并且dest不以/结尾或者src是个目录,dest会自动创建。如果src和dest都是多个文件,dest的父目录没创建,复制就会失败。
src: # Local path to a file to copy to the remote server; can be absolute or relative. If path is a directory, it is copied recursively. In this case, if path ends with "/", only inside contents of that directory are copied to destination. Otherwise, if it does not end with "/", the directory itself with all contents is copied. This behavior is similar to Rsync.
#本地需要复制到远程主机的文件的路径。可以是绝对路径,也可以是相对路径。如果路径是个目录,则递归复制。如果路径以/结尾,只复制目录下的文件至目标路径。如果不以/结尾,则会把目录以及其下的内容都复制至目标主机。这种行为类似于rsync。
content: # When used instead of `src', sets the contents of a file directly to the specified value. For anything advanced or with formatting also look at the template module.
#如果不使用src而使用content,把文件内容直接指定为content所指定的内容。然后剩下的懒得翻译了。
owner: # Name of the user that should own the file/directory, as would be fed to `chown'.
mode: # Mode the file or directory should be.
group: # Name of the group that should own the file/directory, as would be fed to `chown'.示例1:通过content指定文件内容并复制至目标主机(若不带\n,不会自动换行)
[root@nfs ~]# ansible np2.lxk.com -m copy -a 'dest=/tmp/textfile.txt content="hello,brother!\n"'
np2.lxk.com | SUCCESS => {
"changed": true,
"checksum": "8634ff795ad950aa9c762c45cc8b07137248002a",
"dest": "/tmp/textfile.txt",
"gid": 0,
"group": "root",
"md5sum": "2252b10979e37d2884855832666fd811",
"mode": "0644",
"owner": "root",
"size": 15,
"src": "~None/.ansible/tmp/ansible-tmp-1528471338.21-89043902941123/source", #ansible会把给定的源生成一个临时源当做源文件复制至目标位置。
"state": "file",
"uid": 0
}目标主机查看文件内容:
[root@np2 ~]# cat /tmp/textfile.txt
hello,brother!示例2:复制本地/etc/fstab至np1.lxk.com的/tmp目录下,改名为fstab.txt,属主改为user2,权限0600.(user2需先创建)
[root@nfs ~]# np1.lxk.com all -m copy -a 'src=/etc/fstab dest=/tmp/fstab.txt owner=user2 mode=0600'
np1.lxk.com | SUCCESS => {
"changed": true,
"checksum": "e634b64dbf499a1c2f14ade1dc9fc0d932b93093",
"dest": "/tmp/fstab.txt",
"gid": 0,
"group": "root",
"md5sum": "5aee64ae648da49b3b16e2b9ea70d279",
"mode": "0600",
"owner": "user2",
"size": 595,
"src": "~None/.ansible/tmp/ansible-tmp-1528518314.71-128514426299583/source",
"state": "file",
"uid": 1024
}查看目标主机上的文件:
[root@np1 ~]# ll /tmp
total 4
-rw------- 1 user2 root 595 Jun 9 12:25 fstab.txt6.7 fetch模块
[root@nfs ~]# ansible-doc -s fetch
- name: Fetches a file from remote nodes #从远程主机取来文件
fetch:
dest: # (required) A directory to save the file into. For example, if the `dest' directory is `/backup' a `src' file named `/etc/profile' on host `host.example.com', would be saved into `/backup/host.example.com/etc/profile'
#(必须项)要保存文件的目录。如指定的目录为/backup,远程主机host.example.com上的/etc/profile文件会保存在本地/backup/host.example.com/etc/profile
src: # (required) The file on the remote system to fetch. This `must' be a file, not a directory. Recursive fetching may be supported in a later release.
#远程主机需要fetch的文件,必须是文件,不能是目录。以后可能会支持目录。示例1:从远程主机np1.lxk.com上复制/etc/fstab至本地/tmp目录下
[root@nfs ~]# ansible np1.lxk.com -m fetch -a 'src=/etc/fstab dest=/tmp/'
np1.lxk.com | SUCCESS => {
"changed": true,
"checksum": "e634b64dbf499a1c2f14ade1dc9fc0d932b93093",
"dest": "/tmp/np1.lxk.com/etc/fstab",
"md5sum": "5aee64ae648da49b3b16e2b9ea70d279",
"remote_checksum": "e634b64dbf499a1c2f14ade1dc9fc0d932b93093",
"remote_md5sum": null
}示例2:从所有可控的远程主机上复制/etc/fstab至本地/tmp目录下
[root@nfs ~]# ansible all -m fetch -a 'src=/etc/fstab dest=/tmp/'
np1.lxk.com | SUCCESS => {
"changed": false,
"checksum": "e634b64dbf499a1c2f14ade1dc9fc0d932b93093",
"dest": "/tmp/np1.lxk.com/etc/fstab",
"file": "/etc/fstab",
"md5sum": "5aee64ae648da49b3b16e2b9ea70d279"
}
np2.lxk.com | SUCCESS => {
"changed": true,
"checksum": "e634b64dbf499a1c2f14ade1dc9fc0d932b93093",
"dest": "/tmp/np2.lxk.com/etc/fstab",
"md5sum": "5aee64ae648da49b3b16e2b9ea70d279",
"remote_checksum": "e634b64dbf499a1c2f14ade1dc9fc0d932b93093",
"remote_md5sum": null
}
nfs.lxk.com | SUCCESS => {
"changed": true,
"checksum": "e634b64dbf499a1c2f14ade1dc9fc0d932b93093",
"dest": "/tmp/nfs.lxk.com/etc/fstab",
"md5sum": "5aee64ae648da49b3b16e2b9ea70d279",
"remote_checksum": "e634b64dbf499a1c2f14ade1dc9fc0d932b93093",
"remote_md5sum": null
}查看本地目录:
[root@nfs ~]# tree /tmp
/tmp
├── issue.txt
├── nfs.lxk.com
│ └── etc
│ └── fstab
├── np1.lxk.com
│ └── etc
│ └── fstab
└── np2.lxk.com
└── etc
└── fstab
6 directories, 4 files6.8 file模块:修改文件的属性信息
[root@nfs ~]# ansible-doc -s file
- name: Sets attributes of files
file:
force: # force the creation of the symlinks in two cases: the source file does not exist (but will appear later); the destination exists and is a file (so, we need to unlink the "path" file and create symlink to the "src" file in place of it). #在两种情况下强制创建链接:源文件不存在(随后会出现)或目标存在且是文件(将会取消path指定的文件并创建链接)
group: # Name of the group that should own the file/directory, as would be fed to `chown'. #改变文件的属组
mode: # Mode the file or directory should be. For those used to `/usr/bin/chmod' remember that modes are actually octal numbers (like `0644' or `01777'). #改变文件或目录的权限
owner: # Name of the user that should own the file/directory, as would be fed to `chown'. #改变文件的属主
path: # (required) path to the file being managed. Aliases: `dest', `name' #必须项。要修改的文件的路径
recurse: # recursively set the specified file attributes (applies only to directories) #递归地设置文件属性
src: # path of the file to link to (applies only to `state=link' and `state=hard'). Will accept absolute, relative and nonexisting paths. Relative paths are not expanded.
#要链接到的文件路径(只适用于“state=link”和“state=hard”)。将接受绝对路径、相对路径和不存在路径。相对路径没有展开。
state: # If `directory', all intermediate subdirectories will be created if they do not exist. Since Ansible 1.7 they will be created with the supplied permissions. If `file', the file will NOT be created if it does not exist; see the `touch' value or the [copy] or [template] module if you want that behavior. If `link', the symbolic link will be created or changed. Use `hard' for hardlinks. If `absent', directories will be recursively deleted, and files or symlinks will be unlinked. Note that `absent' will not cause `file' to fail if the `path' does not exist as the state did not change. If `touch' (new in 1.4), an empty file will be created if the `path' does not exist, while an existing file or directory will receive updated file access and modification times (similar to the way `touch` works from the command line).
如果是目录,父目录不存在时会自动创建。
如果是文件,文件不存在时不会创建。
如果是链接,将会创建或者改变。
如果是absent,目录将会被递归删除,文件或链接会被取消链接。
如果是touch,不存在的文件将会被创建。目录将会更改访问时间和改变时间。示例1:修改np1.lxk.com主机/tmp/fstab.txt的属主为mygrp,权限为660
[root@nfs ~]# ansible np1.lxk.com -m file -a 'path=/tmp/fstab.txt group=mygrp mode=0660'
np1.lxk.com | SUCCESS => {
"changed": true,
"gid": 200,
"group": "mygrp",
"mode": "0660",
"owner": "user2",
"path": "/tmp/fstab.txt",
"size": 595,
"state": "file",
"uid": 1024
}查看目标主机文件属性:
[root@np1 ~]# ll -d /tmp/fstab.txt
-rw-rw---- 1 user2 mygrp 595 Jun 9 12:25 /tmp/fstab.txt示例2:为np1.lxk.com主机的/tmp/fstab.txt创建软链接/tmp/fstab.link
[root@nfs ~]# ansible np1.lxk.com -m file -a 'path=/tmp/fstab.link src=/tmp/fstab.txt state=link'
np1.lxk.com | SUCCESS => {
"changed": true,
"dest": "/tmp/fstab.link",
"gid": 0,
"group": "root",
"mode": "0777",
"owner": "root",
"size": 14,
"src": "/tmp/fstab.txt",
"state": "link",
"uid": 0
}示例3:在np1.lxk.com的/tmp目录下创建目录file.dir,权限为770
[root@nfs ~]# ansible np1.lxk.com -m file -a 'path=/tmp/file.dir mode=0770 state=directory'
np1.lxk.com | SUCCESS => {
"changed": true,
"gid": 0,
"group": "root",
"mode": "0770",
"owner": "root",
"path": "/tmp/file.dir",
"size": 4096,
"state": "directory",
"uid": 0
}6.9 get_url模块:下载文件
示例:下载一个文件至np1.lxk.com的/tmp目录下
[root@nfs ~]# ansible np1.lxk.com -m get_url -a 'dest=/tmp/ url=https://mirrors.aliyun.com/centos/7.5.1804/paas/x86_64/openshift-origin36/jq-devel-1.5-1.el7.x86_64.rpm'
np1.lxk.com | SUCCESS => {
"changed": true,
"checksum_dest": null,
"checksum_src": "c566cb3df854f4551da1ab7f642e96889b77439c",
"dest": "/tmp/jq-devel-1.5-1.el7.x86_64.rpm",
"gid": 0,
"group": "root",
"md5sum": "43f5092eadb4855fb780e67244d997df",
"mode": "0644",
"msg": "OK (6472 bytes)",
"owner": "root",
"size": 6472,
"src": "/tmp/tmpwix52V",
"state": "file",
"status_code": 200,
"uid": 0,
"url": "https://mirrors.aliyun.com/centos/7.5.1804/paas/x86_64/openshift-origin36/jq-devel-1.5-1.el7.x86_64.rpm"
}查看目标主机/tmp下的文件:
[root@np1 ~]# ls /tmp
file.dir fstab.link fstab.txt jq-devel-1.5-1.el7.x86_64.rpm6.10 cron模块:创建周期性计划任务
示例1:创建一个时间同步的任务,每5分钟运行一次。
[root@nfs ~]# ansible np1.lxk.com -m cron -a "minute=*/5 job='/usr/sbin/ntpdate 192.168.200.254 &> /dev/null' name=timesync"
np1.lxk.com | SUCCESS => {
"changed": true,
"envs": [],
"jobs": [
"timesync"
]
}目标主机上查看任务:
[root@np1 ~]# crontab -l
#Ansible: timesync #注明是由ansible生成的,标识名为timesync
*/5 * * * * /usr/sbin/ntpdate 192.168.200.254 &> /dev/null示例2:删除刚才创建的计划任务
ansible删除计划任务是根据name所定义的名字来标识的。
[root@nfs ~]# ansible np1.lxk.com -m cron -a "state=absent name=timesync"
np1.lxk.com | SUCCESS => {
"changed": true,
"envs": [],
"jobs": []
}查看目标主机计划任务列表为空。
6.11 yum模块:用yum包管理器管理软件
[root@nfs ~]# ansible-doc -s yum
- name: Manages packages with the `yum' package manager
yum:
conf_file: # The remote yum configuration file to use for the transaction.
#指明当前事务使用哪个repo文件
state: # Whether to install (`present' or `installed', `latest'), or remove (`absent' or `removed') a package.
#安装选项:presetn、installed、latest
#卸载选项:absent、removed
name: # (required) A package name , or package specifier with version, like `name-1.0'.
#必须项。指定软件名
skip_broken: # Resolve depsolve problems by removing packages that are causing problems from the transaction.
#跳过错误信息
update_only: # When using latest, only update installed packages. Do not install packages. Has an effect only if state is `latest'
#只升级,如果软件包未安装则不安装。示例1:安装或者查看nginx软件是否已安装
[root@nfs ~]# ansible all -m yum -a "name=nginx state=installed"
nfs.lxk.com | SUCCESS => {
"changed": false,
"msg": "",
"rc": 0,
"results": [
"1:nginx-1.12.2-2.el7.x86_64 providing nginx is already installed"
]
}
np1.lxk.com | SUCCESS => {
"changed": false,
"msg": "",
"rc": 0,
"results": [
"1:nginx-1.12.2-2.el7.x86_64 providing nginx is already installed"
]
}
np2.lxk.com | SUCCESS => {
"changed": false,
"msg": "",
"rc": 0,
"results": [
"1:nginx-1.12.2-2.el7.x86_64 providing nginx is already installed"
]
}示例2:卸载nginx
[root@nfs ~]# ansible all -m yum -a "name=nginx state=absent"
nfs.lxk.com | SUCCESS => {
"changed": true,
"msg": "",
"rc": 0,
…………
太长,不贴了。在命令返回中可以看到Erasing字样,
…………示例3:使用np1.lxk.com主机的/etc/yum.repos.d/repobak/base.repo安装httpd软件
[root@nfs ~]# ansible np1.lxk.com -m yum -a "name=httpd state=installed conf_file=/etc/yum.repos.d/repobak/base.repo"
np1.lxk.com | SUCCESS => {
"changed": true,
"msg": "",
"rc": 0,
"results": [
"Resolving Dependencies\n--> Running transaction check\n---> Package httpd.x86_64 0:2.4.6-80.el7.centos will be installed\n--> Finished Dependency Resolution\n\nDependencies Resolved\n\n================================================================================\n Package Arch Version Repository Size\n================================================================================\nInstalling:\n httpd x86_64 2.4.6-80.el7.centos base 2.7 M\n\nTransaction Summary\n================================================================================\nInstall 1 Package\n\nTotal download size: 2.7 M\nInstalled size: 9.4 M\nDownloading packages:\nRunning transaction check\nRunning transaction test\nTransaction test succeeded\nRunning transaction\n Installing : httpd-2.4.6-80.el7.centos.x86_64 1/1 \n Verifying : httpd-2.4.6-80.el7.centos.x86_64 1/1 \n\nInstalled:\n httpd.x86_64 0:2.4.6-80.el7.centos \n\nComplete!\n"
]
}
实际显示效果就是这样。有点丑。但是安装成功了。示例4:更新缓存并安装httpd
[root@nfs ~]# ansible np2.lxk.com -m yum -a "name=httpd state=installed update_cache=yes"
np2.lxk.com | SUCCESS => {
"changed": false,
"msg": "",
"rc": 0,
"results": [
"httpd-2.4.6-80.el7.centos.x86_64 providing httpd is already installed"
]
}6.12 hostname模块:管理主机名,通常一次只能设置一个。
[root@nfs ~]# ansible-doc -s hostname
- name: Manage hostname
hostname:
name: # (required) Name of the host示例:
[root@nfs ~]# ansible np1.lxk.com -m hostname -a "name=np1"
np1.lxk.com | SUCCESS => {
"ansible_facts": {
"ansible_domain": "lxk.com",
"ansible_fqdn": "np1.lxk.com",
"ansible_hostname": "np1",
"ansible_nodename": "np1"
},
"changed": true,
"name": "np1"
}6.12 git模块
[root@nfs ~]# ansible-doc -s git
- name: Deploy software (or files) from git checkouts
git:
clone: # If `no', do not clone the repository if it does not exist locally
dest: # (required) The path of where the repository should be checked out. This parameter is required, unless `clone' is set to `no'.
repo: # (required) git, SSH, or HTTP(S) protocol address of the git repository
version: # What version of the repository to check out.
#指定要clone的版本,如果不指,默认为最新版本。示例: 下载kubernetes至/tmp/kubernetes/
[root@nfs ~]# ansible np1.lxk.com -m git -a 'repo="https://github.com/kubernetes/kubernetes.git" dest=/tmp/kubernetes'
#下载需要等待查看目标主机下载情况:
[root@np1 ~]# tree -a /tmp/kubernetes
/tmp/kubernetes
└── .git
├── branches
├── config
├── description
├── HEAD
├── hooks
│ ├── applypatch-msg.sample
│ ├── commit-msg.sample
│ ├── post-update.sample
│ ├── pre-applypatch.sample
│ ├── pre-commit.sample
│ ├── prepare-commit-msg.sample
│ ├── pre-push.sample
│ ├── pre-rebase.sample
│ └── update.sample
├── info
│ └── exclude
├── objects
│ ├── info
│ └── pack
└── refs
├── heads
└── tags
10 directories, 13 files
[root@np1 ~]# du -sh /tmp/kubernetes
100K /tmp/kubernetes
#可看到目录已创建,因下载速度慢,文件还是这么小。6.13 pip模块:Manages Python library dependencies
[root@nfs ~]# ansible-doc -s pip
- name: Manages Python library dependencies
pip:
name: # The name of a Python library to install or the url of the remote package. As of 2.2 you can supply a list of names.
#指定名称,也可以以URL指定。2.2版本后支持名称列表。
state: # The state of module The 'forcereinstall' option is only available in Ansible 2.1 and above.
#同yum的state
version: # The version number to install of the Python library specified in the `name' parameter.
#指定要安装的版本6.14 npm模块:Manage node.js packages with npm
[root@nfs ~]# ansible-doc -s npm
- name: Manage node.js packages with npm
npm:
name: # The name of a node.js library to install
#要安装的node.js名称
path: # The base path where to install the node.js libraries
#指明安装源地址
state: # The state of the node.js library
version: # The version to be installed6.15 service模块:管理服务
[root@nfs ~]# ansible-doc -s service
- name: Manage services
service:
arguments: # Additional arguments provided on the command line
enabled: # Whether the service should start on boot. *At least one of state and enabled are required.*
#设置服务是否开机自启
name: # (required) Name of the service.
#必须项。服务的名称
pattern: # If the service does not respond to the status command, name a substring to look for as would be found in the output of the `ps' command as a stand- in for a status result. If the string is found, the service will be assumed to be running.
runlevel: # For OpenRC init scripts (ex: Gentoo) only. The runlevel that this service belongs to.
#运行级别
sleep: # If the service is being `restarted' then sleep this many seconds between the stop and start command. This helps to workaround badly behaving init scripts that exit immediately after signaling a process to stop.
#如果服务是重启,这个选项设置服务关闭后睡眠多长时间再重新开启服务。
state: # `started'/`stopped' are idempotent actions that will not run commands unless necessary. `restarted' will always bounce the service. `reloaded' will always reload. *At least one of state and enabled are required.* Note that reloaded will start the service if it is not already started, even if your chosen init system wouldn't normally.
#started:开启服务
#stoped:关闭服务
#restarted:重启服务
#reloaded:重载服务
#reloaded时,如果服务未启动会启动它。示例:启动httpd服务,并设置开机自启
[root@nfs ~]# ansible all -m service -a "name=httpd state=started enabled=yes"
nfs.lxk.com | SUCCESS => {
"changed": true,
"enabled": true,
"name": "httpd",
"state": "started",
"status": {
"ActiveEnterTimestampMonotonic": "0",
"ActiveExitTimestampMonotonic": "0",
"ActiveState": "inactive",
"After": "remote-fs.target basic.target network.target nss-lookup.target tmp.mount system.slice -.mount systemd-journald.socket",
"AllowIsolate": "no",
"AmbientCapabilities": "0",
…………
太长,不复制了
…………查看所有节点服务状态:
[root@nfs ~]# ansible all -m shell -a "ss -tnlp | grep 80"
np1.lxk.com | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
LISTEN 0 128 127.0.0.1:6379 *:* users:(("redis-server",pid=8077,fd=4))
LISTEN 0 128 :::80 :::* users:(("httpd",pid=14265,fd=4),("httpd",pid=14264,fd=4),("httpd",pid=14263,fd=4),("httpd",pid=14262,fd=4),("httpd",pid=14261,fd=4),("httpd",pid=14260,fd=4))
np2.lxk.com | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
LISTEN 0 128 :::80 :::* users:(("httpd",pid=14845,fd=4),("httpd",pid=14844,fd=4),("httpd",pid=14842,fd=4),("httpd",pid=14841,fd=4),("httpd",pid=14840,fd=4),("httpd",pid=14838,fd=4))
nfs.lxk.com | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
LISTEN 0 128 :::80 :::* users:(("httpd",pid=6953,fd=4),("httpd",pid=6952,fd=4),("httpd",pid=6951,fd=4),("httpd",pid=6950,fd=4),("httpd",pid=6949,fd=4),("httpd",pid=6948,fd=4))
[root@nfs ~]# ansible all -m shell -a "systemctl is-enabled httpd"
np2.lxk.com | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
enabled
np1.lxk.com | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
enabled
nfs.lxk.com | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
enabled
#所有节点httpd服务都是开机自启