上一篇搭建了一个简单的cnn网络用来识别手写数字。
基于tensorflow搭建一个简单的CNN模型(code)
这次我们将要搭建一个较复杂的卷积神经网络结构去对CIFAR-10进行训练和识别。
1. load 一些必要的库和 start a graph session:
import os
import sys
import tarfile
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
from six.moves import urllib
sess = tf. Session()
2. 定义一些模型参数
batch_size = 128
output_every = 50
generations = 20000
eval_every = 500
image_height = 32
image_width = 32
crop_height = 24
crop_width = 24
num_channels = 3
num_targets = 10
data_dir = 'temp'
extract_folder = 'cifar-10-batches-bin'
3. 定义训练学习率等几个参数
learning_rate = 0.1
lr_decay = 0.9
num_gens_to_wait = 250
4. 现在我们建立可以读取二进制 CIFAR-10图片的参数
image_vec_length = image_height * image_width * num_channels
record_length = 1 + image_vec_length
5. 建立数据的路径及下载CIFAR-10数据集图片
data_dir = 'temp'
if not os.path.exists(data_dir):
os.makedirs(data_dir)
cifar10_url = 'http://www.cs.toronto.edu/~kriz/cifar-10-binary.tar.gz'
data_file = os.path.join(data_dir, 'cifar-10-binary.tar.gz')
if not os.path.isfile(data_file):
# Download file
filepath, _ = urllib.request.urlretrieve(cifar10_url, data_file, progress)
# Extract file
tarfile.open(filepath, 'r:gz').extractall(data_dir)
6. 建立函数读取随机扭曲的图片
def read_cifar_files(filename_queue, distort_images = True):
reader = tf.FixedLengthRecordReader(record_bytes=record_length)
key, record_string = reader.read(filename_queue)
record_bytes = tf.decode_raw(record_string, tf.uint8)
# Extract label
image_label = tf.cast(tf.slice(record_bytes, [0], [1]),
tf.int32)
# Extract image
image_extracted = tf.reshape(tf.slice(record_bytes, [1],
[image_vec_length]), [num_channels, image_height, image_width])
# Reshape image
image_uint8image = tf.transpose(image_extracted, [1, 2, 0])
reshaped_image = tf.cast(image_uint8image, tf.float32)
# Randomly Crop image
final_image = tf.image.resize_image_with_crop_or_pad(reshaped_
image, crop_width, crop_height)
if distort_images:
# Randomly flip the image horizontally, change the brightness and contrast
final_image = tf.image.random_flip_left_right(final_image)
final_image = tf.image.random_brightness(final_image,max_delta=63)
final_image = tf.image.random_contrast(final_
image,lower=0.2, upper=1.8)
# Normalize whitening
注意## For anyone else who has this problem, per_image_whitening was replaced by per_image_standardization
# final_image = tf.image.per_image_whitening(final_image)
final_image = tf.image.per_image_standardization(final_image)
return(final_image, image_label)
## by per_image_standardization in v0.12
## For anyone else who has this problem, per_image_whitening was replaced
## by per_image_standardization in v0.12
final_image = tf.image.per_image_standardization(final_image)
7. 定义一个函数传入数据
def input_pipeline(batch_size, train_logical=True):
if train_logical:
files = [os.path.join(data_dir, extract_folder, 'data_
batch_{}.bin'.format(i)) for i in range(1,6)]
else:
files = [os.path.join(data_dir, extract_folder, 'test_batch.bin')]
filename_queue = tf.train.string_input_producer(files)
image, label = read_cifar_files(filename_queue)
min_after_dequeue = 1000
capacity = min_after_dequeue + 3 * batch_size
example_batch, label_batch = tf.train.shuffle_batch([image,
label], batch_size, capacity, min_after_dequeue)
return(example_batch, label_batch)
8. 定义模型
# Define the model architecture, this will return logits from images
def cifar_cnn_model(input_images, batch_size, train_logical=True):
def truncated_normal_var(name, shape, dtype):
return(tf.get_variable(name=name, shape=shape, dtype=dtype, initializer=tf.truncated_normal_initializer(stddev=0.05)))
def zero_var(name, shape, dtype):
return(tf.get_variable(name=name, shape=shape, dtype=dtype, initializer=tf.constant_initializer(0.0)))
# First Convolutional Layer
with tf.variable_scope('conv1') as scope:
# Conv_kernel is 5x5 for all 3 colors and we will create 64 features
conv1_kernel = truncated_normal_var(name='conv_kernel1', shape=[5, 5, 3, 64], dtype=tf.float32)
# We convolve across the image with a stride size of 1
conv1 = tf.nn.conv2d(input_images, conv1_kernel, [1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
# Initialize and add the bias term
conv1_bias = zero_var(name='conv_bias1', shape=[64], dtype=tf.float32)
conv1_add_bias = tf.nn.bias_add(conv1, conv1_bias)
# ReLU element wise
relu_conv1 = tf.nn.relu(conv1_add_bias)
# Max Pooling
pool1 = tf.nn.max_pool(relu_conv1, ksize=[1, 3, 3, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 1],padding='SAME', name='pool_layer1')
# Local Response Normalization (parameters from paper)
# paper: http://papers.nips.cc/paper/4824-imagenet-classification-with-deep-convolutional-neural-networks
norm1 = tf.nn.lrn(pool1, depth_radius=5, bias=2.0, alpha=1e-3, beta=0.75, name='norm1')
# Second Convolutional Layer
with tf.variable_scope('conv2') as scope:
# Conv kernel is 5x5, across all prior 64 features and we create 64 more features
conv2_kernel = truncated_normal_var(name='conv_kernel2', shape=[5, 5, 64, 64], dtype=tf.float32)
# Convolve filter across prior output with stride size of 1
conv2 = tf.nn.conv2d(norm1, conv2_kernel, [1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
# Initialize and add the bias
conv2_bias = zero_var(name='conv_bias2', shape=[64], dtype=tf.float32)
conv2_add_bias = tf.nn.bias_add(conv2, conv2_bias)
# ReLU element wise
relu_conv2 = tf.nn.relu(conv2_add_bias)
# Max Pooling
pool2 = tf.nn.max_pool(relu_conv2, ksize=[1, 3, 3, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding='SAME', name='pool_layer2')
# Local Response Normalization (parameters from paper)
norm2 = tf.nn.lrn(pool2, depth_radius=5, bias=2.0, alpha=1e-3, beta=0.75, name='norm2')
# Reshape output into a single matrix for multiplication for the fully connected layers
reshaped_output = tf.reshape(norm2, [batch_size, -1])
reshaped_dim = reshaped_output.get_shape()[1].value
# First Fully Connected Layer
with tf.variable_scope('full1') as scope:
# Fully connected layer will have 384 outputs.
full_weight1 = truncated_normal_var(name='full_mult1', shape=[reshaped_dim, 384], dtype=tf.float32)
full_bias1 = zero_var(name='full_bias1', shape=[384], dtype=tf.float32)
full_layer1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.add(tf.matmul(reshaped_output, full_weight1), full_bias1))
# Second Fully Connected Layer
with tf.variable_scope('full2') as scope:
# Second fully connected layer has 192 outputs.
full_weight2 = truncated_normal_var(name='full_mult2', shape=[384, 192], dtype=tf.float32)
full_bias2 = zero_var(name='full_bias2', shape=[192], dtype=tf.float32)
full_layer2 = tf.nn.relu(tf.add(tf.matmul(full_layer1, full_weight2), full_bias2))
# Final Fully Connected Layer -> 10 categories for output (num_targets)
with tf.variable_scope('full3') as scope:
# Final fully connected layer has 10 (num_targets) outputs.
full_weight3 = truncated_normal_var(name='full_mult3', shape=[192, num_targets], dtype=tf.float32)
full_bias3 = zero_var(name='full_bias3', shape=[num_targets], dtype=tf.float32)
final_output = tf.add(tf.matmul(full_layer2, full_weight3), full_bias3)
return(final_output)
9. 定义loss函数
def cifar_loss(logits, targets):
# Get rid of extra dimensions and cast targets into integers
targets = tf.squeeze(tf.cast(targets, tf.int32))
# Calculate cross entropy from logits and targets
cross_entropy = tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=logits, labels=targets)
# Take the average loss across batch size
cross_entropy_mean = tf.reduce_mean(cross_entropy)
return(cross_entropy_mean)
10.定义训练,其中学习率将要以指数下降。
def train_step(loss_value, generation_num):
# Our learning rate is an exponential decay (stepped down)
model_learning_rate = tf.train.exponential_decay(learning_rate, generation_num, num_gens_to_wait, lr_decay, staircase=True)
# Create optimizer
my_optimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(model_learning_rate)
# Initialize train step
train_step = my_optimizer.minimize(loss_value)
return(train_step)
11. 计算准确率
def accuracy_of_batch(logits, targets):
# Make sure targets are integers and drop extra dimensions
targets = tf.squeeze(tf.cast(targets, tf.int32))
# Get predicted values by finding which logit is the greatest
batch_predictions = tf.cast(tf.argmax(logits, 1), tf.int32)
# Check if they are equal across the batch
predicted_correctly = tf.equal(batch_predictions, targets)
# Average the 1's and 0's (True's and False's) across the batch size
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(predicted_correctly, tf.float32))
return(accuracy)
12.输入图片
images, targets = input_pipeline(batch_size, train_logical=True)
test_images, test_targets = input_pipeline(batch_size, train_logical=False)
13. 声明训练模型和测试时模型用同样的变量
with tf.variable_scope('model_definition') as scope:
# Declare the training network model
model_output = cifar_cnn_model(images, batch_size)
# Use same variables within scope
scope.reuse_variables()
# Declare test model output
test_output = cifar_cnn_model(test_images, batch_size)
14.初始化loss和测试精度函数
loss = cifar_loss(model_output, targets)
accuracy = accuracy_of_batch(test_output, test_targets)
generation_num = tf.Variable(0, trainable=False)
train_op = train_step(loss, generation_num)
15. 初始化网络的所有变量
# Initialize Variables
print('Initializing the Variables.')
init = tf.initialize_all_variables()
sess.run(init)
# Initialize queue (This queue will feed into the model, so no placeholders necessary)
tf.train.start_queue_runners(sess=sess)
16. 迭代训练,保存loss和测试accuracy
# Train CIFAR Model
print('Starting Training')
train_loss = []
test_accuracy = []
for i in range(generations):
_, loss_value = sess.run([train_op, loss])
if (i+1) % output_every == 0:
train_loss.append(loss_value)
output = 'Generation {}: Loss = {:.5f}'.format((i+1), loss_value)
print(output)
if (i+1) % eval_every == 0:
[temp_accuracy] = sess.run([accuracy])
test_accuracy.append(temp_accuracy)
acc_output = ' --- Test Accuracy = {:.2f}%.'.format(100.*temp_accuracy)
print(acc_output)
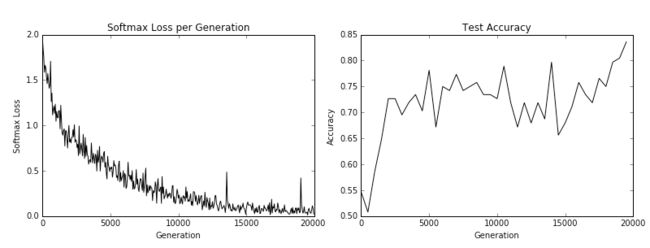
17.使用 matplotlib 讲loss和测试accuracy图像输出来
# Print loss and accuracy
# Matlotlib code to plot the loss and accuracies
eval_indices = range(0, generations, eval_every)
output_indices = range(0, generations, output_every)
# Plot loss over time
plt.plot(output_indices, train_loss, 'k-')
plt.title('Softmax Loss per Generation')
plt.xlabel('Generation')
plt.ylabel('Softmax Loss')
plt.show()
# Plot accuracy over time
plt.plot(eval_indices, test_accuracy, 'k-')
plt.title('Test Accuracy')
plt.xlabel('Generation')
plt.ylabel('Accuracy')
plt.show()