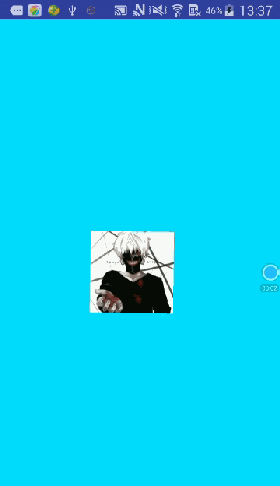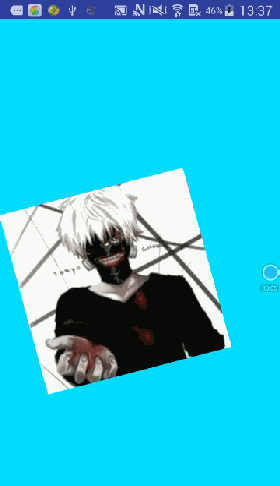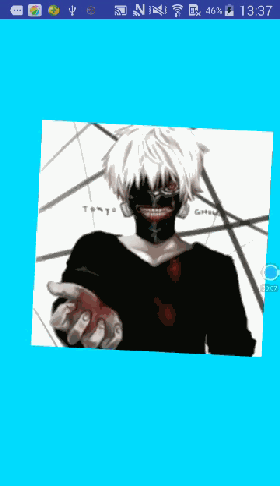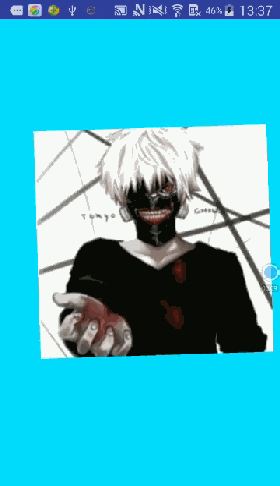
先来看看要实现的效果图
在讲解中,需要大家提前了解一些关于图片绘制的原理的相关知识。
关于实现的流程
1、自定义View
2、获得操作图片的Bitmap
3、复写View的onTouchEvent()方法中的ACTION_DOWN,ACTION_POINTER_DOWN,ACTION_MOVE,ACTION_POINTER_UP以及ACTION_UP事件。
4、定义相应图片变化的Matrix矩阵,通过手势操作的变化来设置相应的Matrix。
5、完成最终的Matrix设置时,通过invalidate()方法重新绘制页面。
那么接下来我们根据以上流程一步一步实现代码。
代码演示
/**
* 作者:ZhouYou
* 日期:2016/8/23.
*/
public class TouchImageView extends View {
// 绘制图片的边框
private Paint paintEdge;
// 绘制图片的矩阵
private Matrix matrix = new Matrix();
// 手指按下时图片的矩阵
private Matrix downMatrix = new Matrix();
// 手指移动时图片的矩阵
private Matrix moveMatrix = new Matrix();
// 资源图片的位图
private Bitmap srcImage;
// 多点触屏时的中心点
private PointF midPoint = new PointF();
// 触控模式
private int mode;
private static final int NONE = 0; // 无模式
private static final int TRANS = 1; // 拖拽模式
private static final int ZOOM = 2; // 缩放模式
// 是否超过边界
private boolean withinBorder;
public TouchImageView(Context context) {
this(context, null);
}
public TouchImageView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
this(context, attrs, 0);
}
public TouchImageView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
init();
}
private void init() {
paintEdge = new Paint();
paintEdge.setColor(Color.BLACK);
paintEdge.setAlpha(170);
paintEdge.setAntiAlias(true);
}
@Override
protected void onSizeChanged(int w, int h, int oldw, int oldh) {
super.onSizeChanged(w, h, oldw, oldh);
srcImage = BitmapFactory.decodeResource(getResources(), R.mipmap.ic_avatar_1);
}
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
super.onDraw(canvas);
float[] points = getBitmapPoints(srcImage, matrix);
float x1 = points[0];
float y1 = points[1];
float x2 = points[2];
float y2 = points[3];
float x3 = points[4];
float y3 = points[5];
float x4 = points[6];
float y4 = points[7];
// 画边框
canvas.drawLine(x1, y1, x2, y2, paintEdge);
canvas.drawLine(x2, y2, x4, y4, paintEdge);
canvas.drawLine(x4, y4, x3, y3, paintEdge);
canvas.drawLine(x3, y3, x1, y1, paintEdge);
// 画图片
canvas.drawBitmap(srcImage, matrix, null);
}
// 手指按下屏幕的X坐标
private float downX;
// 手指按下屏幕的Y坐标
private float downY;
// 手指之间的初始距离
private float oldDistance;
// 手指之间的初始角度
private float oldRotation;
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
int action = MotionEventCompat.getActionMasked(event);
switch (action) {
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN:
mode = TRANS;
downX = event.getX();
downY = event.getY();
downMatrix.set(matrix);
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_POINTER_DOWN: // 多点触控
mode = ZOOM;
oldDistance = getSpaceDistance(event);
oldRotation = getSpaceRotation(event);
downMatrix.set(matrix);
midPoint = getMidPoint(event);
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE:
// 缩放
if (mode == ZOOM) {
moveMatrix.set(downMatrix);
float deltaRotation = getSpaceRotation(event) - oldRotation;
float scale = getSpaceDistance(event) / oldDistance;
moveMatrix.postScale(scale, scale, midPoint.x, midPoint.y);
moveMatrix.postRotate(deltaRotation, midPoint.x, midPoint.y);
withinBorder = getMatrixBorderCheck(srcImage, event.getX(), event.getY());
if (withinBorder) {
matrix.set(moveMatrix);
invalidate();
}
}
// 平移
else if (mode == TRANS) {
moveMatrix.set(downMatrix);
moveMatrix.postTranslate(event.getX() - downX, event.getY() - downY);
withinBorder = getMatrixBorderCheck(srcImage, event.getX(), event.getY());
if (withinBorder) {
matrix.set(moveMatrix);
invalidate();
}
}
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_POINTER_UP:
case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP:
mode = NONE;
break;
default:
break;
}
return true;
}
/**
* 获取手指的旋转角度
*
* @param event
* @return
*/
private float getSpaceRotation(MotionEvent event) {
double deltaX = event.getX(0) - event.getX(1);
double deltaY = event.getY(0) - event.getY(1);
double radians = Math.atan2(deltaY, deltaX);
return (float) Math.toDegrees(radians);
}
/**
* 获取手指间的距离
*
* @param event
* @return
*/
private float getSpaceDistance(MotionEvent event) {
float x = event.getX(0) - event.getX(1);
float y = event.getY(0) - event.getY(1);
return (float) Math.sqrt(x * x + y * y);
}
/**
* 获取手势中心点
*
* @param event
*/
private PointF getMidPoint(MotionEvent event) {
PointF point = new PointF();
float x = event.getX(0) + event.getX(1);
float y = event.getY(0) + event.getY(1);
point.set(x / 2, y / 2);
return point;
}
/**
* 将matrix的点映射成坐标点
*
* @return
*/
protected float[] getBitmapPoints(Bitmap bitmap, Matrix matrix) {
float[] dst = new float[8];
float[] src = new float[]{
0, 0,
bitmap.getWidth(), 0,
0, bitmap.getHeight(),
bitmap.getWidth(), bitmap.getHeight()
};
matrix.mapPoints(dst, src);
return dst;
}
/**
* 检查边界
*
* @param x
* @param y
* @return true - 在边界内 | false - 超出边界
*/
private boolean getMatrixBorderCheck(Bitmap bitmap, float x, float y) {
if (bitmap == null) return false;
float[] points = getBitmapPoints(bitmap, moveMatrix);
float x1 = points[0];
float y1 = points[1];
float x2 = points[2];
float y2 = points[3];
float x3 = points[4];
float y3 = points[5];
float x4 = points[6];
float y4 = points[7];
float edge = (float) Math.sqrt(Math.pow(x1 - x2, 2) + Math.pow(y1 - y2, 2));
if ((2 + Math.sqrt(2)) * edge >= Math.sqrt(Math.pow(x - x1, 2) + Math.pow(y - y1, 2))
+ Math.sqrt(Math.pow(x - x2, 2) + Math.pow(y - y2, 2))
+ Math.sqrt(Math.pow(x - x3, 2) + Math.pow(y - y3, 2))
+ Math.sqrt(Math.pow(x - x4, 2) + Math.pow(y - y4, 2))) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
我已经在代码中针对可能遇到的问题做了详细的注释。
1. Matrix
// 绘制图片的矩阵 private Matrix matrix = new Matrix(); // 手指按下时图片的矩阵 private Matrix downMatrix = new Matrix(); // 手指移动时图片的矩阵 private Matrix moveMatrix = new Matrix();
首先我定义了三个Matrix变量,目的在于通过不同手势的操控图片的Matrix最终由绘制图片的Matrix所接收,因此需要在不同的操作中使用不同的Matrix进行图形变换的数据传递,从而在渲染页面的时候将最终的Matrix再传递回绘图的Matrix。
2. PointF
// 多点触屏时的中心点 private PointF midPoint = new PointF();
因为如果是针对图片的旋转和放大操作,需要通过两个手指进行控制,因此我们需要知道在多个手指触摸屏幕时的中心点坐标。
3. 触控模式
// 触控模式 private int mode; private static final int NONE = 0; // 无模式 private static final int TRANS = 1; // 拖拽模式 private static final int ZOOM = 2; // 缩放模式
在onTouchEvent()事件中,会根据不同的事件变换触控的模式,从而进行不同图片变换的操作。
4. onTouchEvent()
首先,我们是自定义的View,因此如果要对该事件进行消费的话,需要将返回值设置为true。
(1)ACTION_DOWN - 该事件是单点触屏的事件,也就是说如果一个手指按下屏幕的时候就会回调这个事件。那么我们在该事件中就将触控模式设置为拖拽模式(TRANS),记录下按下屏幕的xy坐标,并在这个事件中将绘图的Matrix复制给按下屏幕的Matrix。
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN: mode = TRANS; downX = event.getX(); downY = event.getY(); downMatrix.set(matrix); break;
(2)ACTION_POINTER_DOWN - 这个事件发生在超过一个手指触摸屏幕的时候。我们在这个事件中即可针对多点触屏的操作进行初始化设置。在该事件中,我们将触控模式重新设置为(ZOOM),初始化两指之间触摸屏幕的距离以及两指之间的旋转角度,初始化两指之间的中心点坐标。最后把绘图的Matrix复制给按下屏幕的Matrix。
case MotionEvent.ACTION_POINTER_DOWN: // 多点触控
mode = ZOOM;
oldDistance = getSpaceDistance(event);
oldRotation = getSpaceRotation(event);
midPoint = getMidPoint(event);
downMatrix.set(matrix);
break;
(3)ACTION_MOVE - 到了移动的事件中,根据之前的触控模式进行判断。首先,将按下事件的Matrix复制给移动事件的Matrix。如果是(ZOOM)模式,我们将会根据事件获得手指旋转角度的差值,以及手指之间距离的差值。根据这两个差值,以及在ACTION_DOWN事件中获得的中点坐标,我们即可设置MOVE事件的缩放和旋转。(TRANS)模式也是如此。最后通过获取图片变换的边界值来判断是否进行绘图渲染。
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE:
// 缩放
if (mode == ZOOM) {
moveMatrix.set(downMatrix);
float deltaRotation = getSpaceRotation(event) - oldRotation;
float scale = getSpaceDistance(event) / oldDistance;
moveMatrix.postScale(scale, scale, midPoint.x, midPoint.y);
moveMatrix.postRotate(deltaRotation, midPoint.x, midPoint.y);
withinBorder = getMatrixBorderCheck(srcImage, event.getX(), event.getY());
if (withinBorder) {
matrix.set(moveMatrix);
invalidate();
}
}
// 平移
else if (mode == TRANS) {
moveMatrix.set(downMatrix);
moveMatrix.postTranslate(event.getX() - downX, event.getY() - downY);
withinBorder = getMatrixBorderCheck(srcImage, event.getX(), event.getY());
if (withinBorder) {
matrix.set(moveMatrix);
invalidate();
}
}
break;
(4)ACTION_POINTER_UP和ACTION_UP - 在这两个事件中,重新将触屏的模式设置会NONE。
5. 边界判断
以下即为边界判断的逻辑是针对正方形的图片来说的。首先通过原图片相对自己四个坐标映射成为Matrix对应屏幕的点坐标。通过得到4个点的坐标,我们即可根据手指触摸图片时的坐标与图片的4个点坐标进行关联。
边界判断的逻辑是手指触摸图片的点到4个顶点的距离之和如果小于(2+根号2倍)的斜边长度,即视为不超过边界。
/**
* 将matrix的点映射成坐标点
*
* @return
*/
protected float[] getBitmapPoints(Bitmap bitmap, Matrix matrix) {
float[] dst = new float[8];
float[] src = new float[]{
0, 0,
bitmap.getWidth(), 0,
0, bitmap.getHeight(),
bitmap.getWidth(), bitmap.getHeight()
};
matrix.mapPoints(dst, src);
return dst;
}
/**
* 检查边界
*
* @param x
* @param y
* @return true - 在边界内 | false - 超出边界
*/
private boolean getMatrixBorderCheck(Bitmap bitmap, float x, float y) {
if (bitmap == null) return false;
float[] points = getBitmapPoints(bitmap, moveMatrix);
float x1 = points[0];
float y1 = points[1];
float x2 = points[2];
float y2 = points[3];
float x3 = points[4];
float y3 = points[5];
float x4 = points[6];
float y4 = points[7];
float edge = (float) Math.sqrt(Math.pow(x1 - x2, 2) + Math.pow(y1 - y2, 2));
if ((2 + Math.sqrt(2)) * edge >= Math.sqrt(Math.pow(x - x1, 2) + Math.pow(y - y1, 2))
+ Math.sqrt(Math.pow(x - x2, 2) + Math.pow(y - y2, 2))
+ Math.sqrt(Math.pow(x - x3, 2) + Math.pow(y - y3, 2))
+ Math.sqrt(Math.pow(x - x4, 2) + Math.pow(y - y4, 2))) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
总结
好了,本文的内容到这就结束了,完成了以上的步骤,即可完成针对图片在屏幕上的放大、平移和旋转的操作。是不是还是很简单的。有兴趣的可以自己动手操作起来,希望这篇文章对大家的学习和工作能有所帮助,如果有疑问可以留言交流,谢谢大家对脚本之家的支持。