数据结构之哈夫曼树
一.什么是哈夫曼树
基本概念
节点之间的路径:一个结点到另一个结点,所经过节点的结点序列。
结点之间的路径长度:结点之间路径上的分支数(边),如汽车到下一站的路径长度为1。
树的路径长度:从根结点到每个叶子结点的路径长度之和。
带权路径: 路径上加上的实际意义 。如汽车到下一站的距离我们叫做权值
树的带权路经长度: 每个叶子结点到根的路径长度*权值 之和,记作WPL。还是汽车的例子,汽车到达天津有2条路 可以走。第一条路经过3个站,每个站相距13km。第二条有2个站,每个站相距18km。那么有距离的路我们叫做带权路径。根结点为天津的树,那么第一条路带权路径为 3*13 = 39,第二条为2*18。树的带权路径WPL 3*13+2*18.
哈夫曼树: 重点来了,什么是哈夫曼树呢。二叉树是n个结点的结合,它的度(所有孩子个数的最大值)小于等于2。n个结点构成一个二叉树有许多方法。使二叉树的带权路径最小的树 ,我们叫做哈夫曼树。
二.哈夫曼树有什么用
介绍了这么多概念,不知道它有什么用,让初学者感觉数据结构没什么劲。哈夫曼树主要用在数据的压缩如JPEG格式图片,在通信中我们可以先对发送的数据进行哈夫曼编码压缩数据提高传输速度。查询优化 在工作中我们我们身边放许多工具,由于空间限制我们不能把所有工具放在我们最容易拿到的地方,所有我们把使用频率最高的工具放在最容易的位置。同样的道理在查询的时候我们把查询频率最高的数据建立索引,这些都是使用了哈夫曼算法的思想。
三.怎么构造哈夫曼树
给定权值为12 3 6 8 2 如果构造其哈夫曼树
1.给定n个权值{w1,w2,w3…..,wn}构成 n棵二叉树的集合F={T1,T2,T3…..Tn}, 其中每棵树只有权值为Wi的根节点。
构成的二叉树为

2.在F中选取权值最小的两棵树作为 左子树和右子树 构成新的二叉树根的权值为两棵树之和
3.将前两棵树从F删除 加入新树
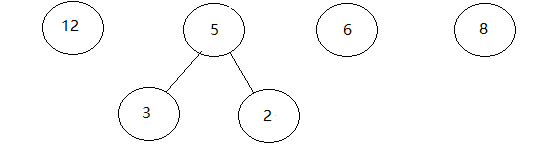
4.重复2和3直到只剩一棵树
三.代码实现哈夫曼树
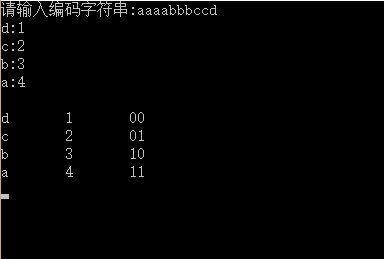
程序功能输入一串字符,统计字符个数,并把字符个数作为权值构造一棵哈夫曼树,求出字符的编码
程序效果图
1.代码
//头文件
//为了学习 我使用链表来实现
//从树种找出权值最小的两个树 我先对树排序 取最小的两棵
//新的树先和最后一棵树 比较 找到合适位置进行插入 也就是插入排序
#include 0].weight) {
break;
}
tree[j + 1] = tree[j];
}
if (j == len + (i / 2)) {
tree[tree[0].lchirld].parent = j + 1;
tree[tree[0].rchirld].parent = j + 1;
tree[j+1] = tree[0];
}
else
{
tree[tree[0].lchirld].parent = j ;
tree[tree[0].rchirld].parent = j ;
tree[j] = tree[0];
}
}
tree[2 * len - 1].parent = 0;
//初始化栈
Stack1 s;
InitStack1(&s);
//从霍夫曼树中队字符编码
for (i = 1; i <= len; i++) {
//查找到根的路径
printf("\n%c %d ", tree[i].ch,tree[i].weight);
Push1(i, &s);
int parent = tree[i].parent,child;
while (parent != 0) {
Push1(parent, &s);
parent = tree[parent].parent;
}
parent = Pull1(&s);
while (!IsEmptyStack1(&s)){
child = Pull1(&s);
if (child == tree[parent].lchirld) {
printf("0");
}
else {
printf("1");
}
parent = child;
}
}
printf("\n");
return tree;
}
//清除哈夫曼树的内存
void ClearHuffman(HuffmanTree tree) {
free(tree);
}
//打印哈夫曼树
void DispHuffman(HuffmanTree tree,int n) {
int i = 0;
for (i = 1; i < 2 * n;i++) {
printf("i:%d w:%d c:%c l:%d r:%d p:%d\n", i, tree[i].weight, tree[i].ch, tree[i].lchirld, tree[i].rchirld, tree[i].parent);
}
}
//测试函数
void testHafuman(){
printf("请输入编码字符串:");
char buf[1024];
scanf("%s", buf);
CharNode * p = CountChar(buf);
CharNode * a = SortCharTable(p);
DispCharTable(a);
HuffmanTree tree = HuffManEncodeing(a);
ClearCharTable(a);
ClearHuffman(tree);
}
