强化学习之Q-learning algorithm学习总结
目录
文章纲要
介绍Q-table
Q-learning algorithm: learning the Action Value Function
Step 1: Q-value初始化
Step 2: Episode循环,直到学习停止
Step 3: 选择action
Step 4-5: 估计
总结
两天学习Q-learning算法,先看了莫烦的视频,大概了解了算法的流程,但仍然有很多不懂的地方。
网上又看到这篇文章,讲得更通俗易懂点,在此翻译总结一下,以便自己记住。原文章链接: https://medium.freecodecamp.org/diving-deeper-into-reinforcement-learning-with-q-learning-c18d0db58efe
文章纲要
- 什么是Q-Learning
- 怎么用Numpy实现
介绍Q-table
Each Q-table score("Q" for the "quality" of the action)will be the maximum expected future reward that I'll get if I take the action at that state with the best policy given.
那么怎样计算Q table中的每个元素的值呢? 我们将采用Q learning 算法来学习Q-table的每个值。
Q-learning algorithm: learning the Action Value Function
Action Value Function(或“Q-function”)有两个输入:“state”和“action”。其返回在该state下选择该action的expected future reward:
我们可以把这个Q function看做是一个读者,在Q-table中搜索对应所查state和action的行、列,然后返回相一致那格的Q value。这就是“expected future reward”。
在explore环境之前,一般将Q-table设置为一样的固定值(通常设为0)。随着我们explore,通过迭代更新Q(s,a),Q-table中的估计值会越来越好,更新方法采用贝尔曼方程(Bellman Equation)。
Q-learning算法的过程:
前4步都好理解,主要在于对第5步更新Q-value方法的理解。
Step 1: Q-value初始化
创建一个m列(m = 可采取的actions数量)、n行(n = states的数量)的Q-table。
Step 2: Episode循环,直到学习停止
重复step3到step5,直到达到我们设定的最大episodes。
Step 3: 选择action
在当前state s下,根据Q-value估计值,选择action。
采用epsilon greedy strategy:定义一个exploration rate “epsilon”,代表explore(随机选取action)的概率。在开始的时候将其设置为1,因为刚开始对Q-table的values一无所知。之后慢慢减少epsilon的值,如下图。
Step 4-5: 估计
采用贝尔曼方程(the Bellman equation)更新Q(s,a)。
用语言描述就是:
New Q value = Current Q value + lr * [Reward + discount_rate * (highest Q value between possible actions from the new state s’ ) — Current Q value ]
通过一个例子来看看具体更新过程:
比如下面的小老鼠,第一步可以往下或者往右,因为此时epsilon设置很大,所以随机选择,比如向右:
移动后获得一块cheese(+1), 现在可以用它来更新Q-value了。如上所说,采用贝尔曼方程(the Bellman equation)来更新Q(s,a):
-
首先,计算Q的变化值
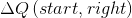 ;
; -
其次,将
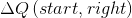 乘以learning rate,加到初始的Q value上。
乘以learning rate,加到初始的Q value上。
对learning rate(α)的理解:该网络放弃之前的value而采用新的value的快速程度。如果learning rate = 1,那么新的估计值就直接用作新的Q-value(如果α=1,那么![]() )。
)。
总结
- Q-learning是一个value-based强化学习算法,用来通过q function查找最优的action-selection policy。
- 目标:使value function Q(expected future reward given a state and action)最大化。
- Function Q(state, action) → 返回在该state采取该action时的expected future reward。(对未来面临同样情况(state,action)时可能获得的reward的估计)
- 该function可以用Q-learning方法进行估计,Q-learning是用贝尔曼方程的方法对Q(s,a)迭代更新。
最重要的是自己实现代码,尝试改善已有的代码,如增加epochs、改改learning rate、采用更复杂的环境(如Frozen-lake with 8x8 tiles)。
