spring-data-cassandra的简单使用
点评:一篇很有实操意义的文档
引自
之前写了JAVA操作cassandra驱动包,现在来看看spring-data对cassandra的支持。这里是spring-data-cassandra的官方文档:http://docs.spring.io/spring-data/cassandra/docs/1.5.0.M1/reference/html/
这个目录下还有api、版本日志等:http://docs.spring.io/spring-data/cassandra/docs/1.5.0.M1/
引入jar包
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.datagroupId>
<artifactId>spring-data-cassandraartifactId>
<version>1.5.0.M1version>
dependency>
定义域模型(实体类)
不存在复合主键的情况:
package com.my.domin.pojo;
import org.springframework.data.cassandra.mapping.Column;
import org.springframework.data.cassandra.mapping.PrimaryKey;
import org.springframework.data.cassandra.mapping.Table;
@Table
public class Person
{
// 主键
@PrimaryKey
private String id;
// 列名 与数据库列名一致时可不加
@Column(value = "name")
private String name;
private int age;
// 支持构造函数
public Person(String id, String name, int age)
{
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getId()
{
return id;
}
public void setId(String id)
{
this.id = id;
}
public String getName()
{
return name;
}
public void setName(String name)
{
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge()
{
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age)
{
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString()
{
return "Person [id=" + id + ", name=" + name + ", age=" + age + "]";
}
}
对应的CQL建表语句
CREATE TABLE mydb.person (
id text PRIMARY KEY,
age int,
name text
)
可以看出和JPA的注解很类似,不同的是cassandra主键用的是@PrimaryKey,而且允许使用构造函数。
如果存在复合主键,则要先映射一个主键的实体类,再映射一个包含这个主键的实体类
package com.my.domin.pojo;
import org.springframework.cassandra.core.Ordering;
import org.springframework.cassandra.core.PrimaryKeyType;
import org.springframework.data.cassandra.mapping.PrimaryKeyClass;
import org.springframework.data.cassandra.mapping.PrimaryKeyColumn;
@PrimaryKeyClass
public class Person2Key
{
// 分区键
@PrimaryKeyColumn(name = "id", ordinal = 0, type = PrimaryKeyType.PARTITIONED)
private String id;
// 集群键
@PrimaryKeyColumn(name = "name", ordinal = 1, type = PrimaryKeyType.CLUSTERED, ordering = Ordering.DESCENDING)
private String name;
public String getId()
{
return id;
}
public void setId(String id)
{
this.id = id;
}
public String getName()
{
return name;
}
public void setName(String name)
{
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString()
{
return "Person2Key [id=" + id + ", name=" + name + "]";
}
}
package com.my.domin.pojo;
import org.springframework.data.cassandra.mapping.PrimaryKey;
import org.springframework.data.cassandra.mapping.Table;
@Table(value = "person2")
public class Person2
{
@PrimaryKey
private Person2Key pKey;
private int age;
public Person2Key getpKey()
{
return pKey;
}
public void setpKey(Person2Key pKey)
{
this.pKey = pKey;
}
public int getAge()
{
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age)
{
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString()
{
return "Person2 [pKey=" + pKey + ", age=" + age + "]";
}
}
对应的CQL建表语句
CREATE TABLE mydb.person2 (
id text,
name text,
age int,
PRIMARY KEY (id, name)
) WITH CLUSTERING ORDER BY (name DESC)
其中的WITH CLUSTERING ORDER BY (name DESC) 对应主键类里的ordering = Ordering.DESCENDING,按照name降序存储,只有集群键才能在建表时设置降序存储。
其实还有更加复杂的复合分区键、复合集群键组合成的主键,看懂了上面应该就能举一反三了,而且用的不多,这里就不写了。
定义spring-data接口
package com.my.repository;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.data.cassandra.repository.Query;
import org.springframework.data.repository.CrudRepository;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import com.my.domin.pojo.Person2;
@Repository
public interface PersonRepository extends CrudRepository<Person2, String>
{
@Query("select * from Person2 where id= ?1 and name= ?2")
List<Person2> findByIdAndName(String id, String name);
}
我们可以看看继承的CrudRepository这个仓库接口类
/*
* Copyright 2008-2011 the original author or authors.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package org.springframework.data.repository;
import java.io.Serializable;
/**
* Interface for generic CRUD operations on a repository for a specific type.
*
* @author Oliver Gierke
* @author Eberhard Wolff
*/
@NoRepositoryBean
public interface CrudRepository<T, ID extends Serializable> extends Repository<T, ID> {
/**
* Saves a given entity. Use the returned instance for further operations as the save operation might have changed the
* entity instance completely.
*
* @param entity
* @return the saved entity
*/
<S extends T> S save(S entity);
/**
* Saves all given entities.
*
* @param entities
* @return the saved entities
* @throws IllegalArgumentException in case the given entity is {@literal null}.
*/
<S extends T> Iterable<S> save(Iterable<S> entities);
/**
* Retrieves an entity by its id.
*
* @param id must not be {@literal null}.
* @return the entity with the given id or {@literal null} if none found
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code id} is {@literal null}
*/
T findOne(ID id);
/**
* Returns whether an entity with the given id exists.
*
* @param id must not be {@literal null}.
* @return true if an entity with the given id exists, {@literal false} otherwise
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code id} is {@literal null}
*/
boolean exists(ID id);
/**
* Returns all instances of the type.
*
* @return all entities
*/
Iterable<T> findAll();
/**
* Returns all instances of the type with the given IDs.
*
* @param ids
* @return
*/
Iterable<T> findAll(Iterable<ID> ids);
/**
* Returns the number of entities available.
*
* @return the number of entities
*/
long count();
/**
* Deletes the entity with the given id.
*
* @param id must not be {@literal null}.
* @throws IllegalArgumentException in case the given {@code id} is {@literal null}
*/
void delete(ID id);
/**
* Deletes a given entity.
*
* @param entity
* @throws IllegalArgumentException in case the given entity is {@literal null}.
*/
void delete(T entity);
/**
* Deletes the given entities.
*
* @param entities
* @throws IllegalArgumentException in case the given {@link Iterable} is {@literal null}.
*/
void delete(Iterable<? extends T> entities);
/**
* Deletes all entities managed by the repository.
*/
void deleteAll();
}
这里面实现了一组CURD方法,如果要写一些条件查询的话可以参考
@Query("select * from Person where id= ?1 and name= ?2 ALLOW FILTERING")
List<Person> findByIdAndName(String id, String name);
这里要注意的是cassandra支持的查询是有限制的,可以参考这篇文章http://zhaoyanblog.com/archives/265.html 。3.0之后的版本改善了许多(如上面的查询3.0以下的版本是不支持的,name为非主键字段),一个是支持了非主键的条件查询,一个是降低了集群键的查询限制条件,这里最好自己在cql中测试一下。
spring-data-cassandra文档里还提到一个分页的仓库接口类PagingAndSortingRepository,这个继承自CrudRepository,而且提供了2个分页方法。但是经过测试是不能用的。。至少我没有测试通过,不知道是没有实现(比较倾向于这个,cassandra分页的确比较麻烦),还是自己没有正确使用。
application.xml配置文件
看名字就知道spring-data-cassandra是和spring一起使用的,下面的配置只是最最基本的,更多的配置选项可以参考 https://my.oschina.net/u/2392555/blog/469893 这篇文章。
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:cassandra="http://www.springframework.org/schema/data/cassandra"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/data/cassandra
http://www.springframework.org/schema/data/cassandra/spring-cassandra-1.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/data/cassandra/spring-cql.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/data/cassandra/spring-cql-1.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.0.xsd
">
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:cassandra.properties" />
<context:component-scan base-package="com.my" />
<tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="transactionManager" />
<cassandra:cluster contact-points="${cassandra_contactpoints}" port="${cassandra_port}" username="${cassandra_username}" password="${cassandra_password}" />
<cassandra:session keyspace-name="${cassandra_keyspace}" />
<cassandra:mapping />
<cassandra:converter />
<cassandra:template id="cqlTemplate" />
<cassandra:repositories base-package="com.my.repository" />
beans>
这个配置文件都有注释,没什么可讲的,唯一要注意的是
其中cassandra.properties文件配置
#cassandra数据库连接
#节点ip
cassandra_contactpoints=192.168.3.89
#端口
cassandra_port=9042
#当前操作键空间
cassandra_keyspace=mydb
#登录用户名
cassandra_username=cassandra
#登录密码
cassandra_password=cassandra
使用测试
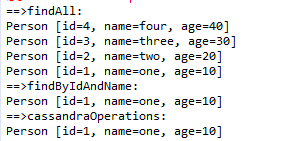
cassandra数据库person表中数据如下:

测试方法:
package com.my.serviceImpl;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.data.cassandra.core.CassandraOperations;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import com.datastax.driver.core.querybuilder.QueryBuilder;
import com.datastax.driver.core.querybuilder.Select;
import com.my.domin.pojo.Person;
import com.my.repository.PersonRepository;
import com.my.service.PersonService;
@Service
public class PersonServiceImpl implements PersonService
{
@Autowired
private PersonRepository personRepository;
@Autowired
private CassandraOperations cassandraOperations;
@Override
public void test()
{
//通过Repository查询
Iterable<Person> iterable = personRepository.findAll();
Iterator<Person> it = iterable.iterator();
System.out.println("==>findAll:");
while (it.hasNext())
{
Person p = it.next();
System.out.println(p.toString());
}
//通过Repository 自定义查询查询
List<Person> list = personRepository.findByIdAndName("1", "one");
System.out.println("==>findByIdAndName:");
for (Person person : list)
{
System.out.println(person.toString());
}
//通过cassandraOperations查询
Select select = QueryBuilder.select().from("person");
select.where(QueryBuilder.eq("id", "1"));
Person person = cassandraOperations.selectOne(select, Person.class);
System.out.println("==>cassandraOperations:");
System.out.println(person.toString());
}
}
这里面包含2种使用方法,一个是使用自己定义的仓库接口类,另一个是spring-data-cassandra提供的CassandraOperations类。CassandraOperations使用方式很多,上面只是列举了一种,其他具体应用官方文档都有说明。
到这里就告一段落了,官方文档还有很多内容,等有时间再去慢慢看了。