Linux多线程学习(五)条件变量
一、条件变量
条件变量是线程的一种同步机制,条件变量与互斥量一起使用,适用于多个线程之间存在某种依赖关系,只有满足某种条件时,某个线程才可以使用的情景。
1、条件变量的创建
linux下用pthread_cond_t类型的变量表示条件变量,创建方式如下:
pthread_cond_t cond;
2、条件变量的初始化,条件变量在使用前必须初始化,有两种初始化方式:
(1)静态初始化
pthread_cond_t cond = PTHREAD_COND_INITIALIZER;
(2)动态初始化,初始化函数如下:
int pthread_cond_init(pthread_cond_t *restrict cond,
const pthread_condattr_t *restrict attr);
参数:
cond:是一个需要初始化的pthread_cond_t类型的指针;
attr:是初始化cond为attr属性的条件变量,若要以默认属性初始化cond,则传入NULL;
函数调用成功,返回0,否则返回一个非0的错误码。
3、条件变量的销毁
int pthread_cond_destroy(pthread_cond_t *cond);
函数调用成功返回0,否则返回非0的错误码。
4、条件变量的使用
条件变量一般与条件测试、互斥量、条件等待函数、条件通知函数一起使用;
4.1 条件测试:执行线程对某个条件进行测试,如果条件不满足,则调用条件等待函数;
比如: if( var < 500) 、while( !flag );
4.2 条件等待函数有两个:
1)条件不满足,一直等待
int pthread_cond_wait(pthread_cond_t *restrict cond,
pthread_mutex_t *restrict mutex);
mutex为互斥量指针;这个互斥量会在调用条件等待,调用线程加入条件变量等待队列后,被释放。
2)超时等待,超时后返回
int pthread_cond_timedwait(pthread_cond_t *restrict cond,
pthread_mutex_t *restrict mutex, const struct timespec *restrict abstime);
其中变量abstime是timespec_t类型的指针,timespec_t定义如下:
typedef struct timespec
{
time_t tv_sec; //秒
long tv_nsec; //纳秒
};
4.3条件通知函数
当另一个线程修改了某参数可能使得条件变量所关联的条件变成真时,它应该通知一个
或者多个等待在条件变量等待队列中的线程。条件通知函数有两个:
int pthread_cond_broadcast(pthread_cond_t *cond);
int pthread_cond_signal(pthread_cond_t *cond);
前者用来唤醒所有条件等待队列中的线程,后者用来唤醒一个条件变量等待队列中的线程。
二、编程练习
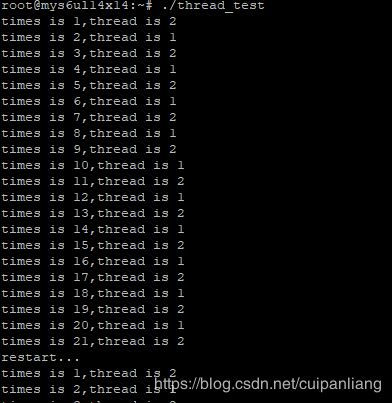
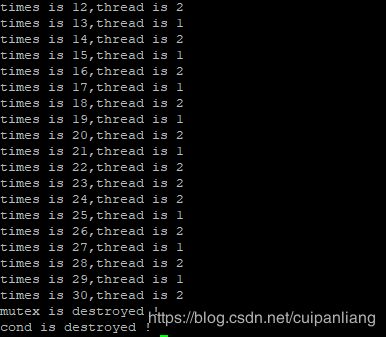
1、条件等待使用没有超时参数的函数,一个线程使变量 i 自增,另一个线程判断 i 小于20则等待,当大于20时,使 i 清零,清零2次后退出两个线程,并销毁互斥锁和条件变量。
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
//条件变量实验
int i = 0;
int j = 0; //用来控制i清0的次数
pthread_t thread1,thread2,thread3;
//静态初始化
pthread_mutex_t lock = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;
pthread_cond_t cond = PTHREAD_COND_INITIALIZER;
void *pthread_func(void * pra)
{
int para = (int)pra;
while( i < 30 )
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&lock);
i++;
printf("times is %d,thread is %d\r\n",i,para);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&lock);
if(i > 20)
{
j++;
pthread_cond_signal(&cond);
}
usleep(100);
}
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
void *pthread3_func(void * pra)
{
restart:
//使用互斥量保护临界
pthread_mutex_lock(&lock);
if( i<20 )
{
pthread_cond_wait(&cond,&lock);
}
i = 0;
printf("restart...\r\n");
//退出临界区
pthread_mutex_unlock(&lock);
//运行两遍后,退出线程销毁条件变量和互斥量
if( j < 2 )
{
goto restart;
}
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
int main(void)
{
int res;
int para1 = 1;
int para2 = 2;
res = pthread_create(&thread1,NULL,pthread_func,(void*)para1);
if(res)
{
printf("thread1 create fail\r\n");
exit(-1);
}
res = pthread_create(&thread2,NULL,pthread_func,(void*)para2);
if(res)
{
printf("thread2 create fail\r\n");
exit(-1);
}
res = pthread_create(&thread3,NULL,pthread3_func,NULL);
if(res)
{
printf("thread3 create fail\r\n");
exit(-1);
}
//等待线程1,线程2运行结束后,销毁互斥量
pthread_join(thread1, NULL);
pthread_join(thread2, NULL);
pthread_join(thread3, NULL);
res = pthread_mutex_destroy(&lock);
if(!res)
{
printf("mutex is destroyed !\r\n");
}
res = pthread_cond_destroy(&cond);
if(!res)
{
printf("cond is destroyed !\r\n");
}
return 0;
}
运行结果:
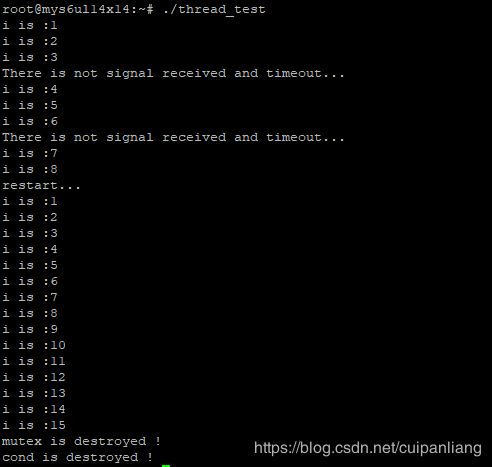
2.条件等待函数使用带超时参数的函数
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
//条件变量实验----超时等待
int i = 0;
pthread_t thread1,thread3;
//静态初始化
pthread_mutex_t lock = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;
pthread_cond_t cond = PTHREAD_COND_INITIALIZER;
void *pthread_func(void * pra)
{
while( i < 15 )
{
i++;
if(i > 7)
{
pthread_cond_signal(&cond);
}
printf("i is :%d\r\n",i);
sleep(1);
}
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
void *pthread3_func(void * pra)
{
struct timeval nowTime;
struct timespec timeout;
int res ;
restart:
//使用互斥量保护临界
pthread_mutex_lock(&lock);
gettimeofday(&nowTime,NULL);
timeout.tv_sec = nowTime.tv_sec+3; //超时时间 = 当前时间+3s
timeout.tv_nsec = nowTime.tv_usec*1000;
if(i < 15)
res = pthread_cond_timedwait(&cond,&lock,&timeout);
if(res == ETIMEDOUT ) //时间到,但未接收到条件通知信号
{
printf("There is not signal received and timeout...\r\n");
pthread_mutex_unlock(&lock);
goto restart;
}
else if(res == 0 ) //未超时,并收到了条件通知信号
{
//i复位后退出该线程
i = 0;
printf("restart...\r\n");
}
//退出临界区
pthread_mutex_unlock(&lock);
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
int main(void)
{
int res;
int para1 = 1;
res = pthread_create(&thread1,NULL,pthread_func,(void*)para1);
if(res)
{
printf("thread1 create fail\r\n");
exit(-1);
}
res = pthread_create(&thread3,NULL,pthread3_func,NULL);
if(res)
{
printf("thread3 create fail\r\n");
exit(-1);
}
//等待线程1,线程2运行结束后,销毁互斥量
pthread_join(thread1, NULL);
res = pthread_mutex_destroy(&lock);
if(!res)
{
printf("mutex is destroyed !\r\n");
}
pthread_join(thread3, NULL);
res = pthread_cond_destroy(&cond);
if(!res)
{
printf("cond is destroyed !\r\n");
}
return 0;
} 运行结果: