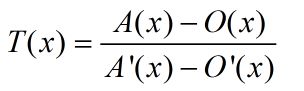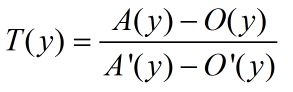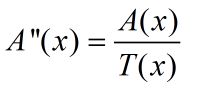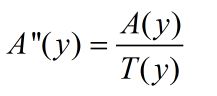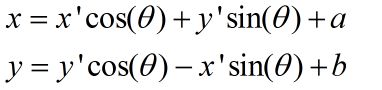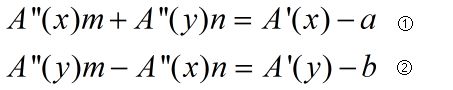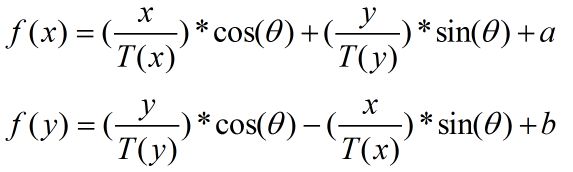不同平面直角坐标系之间的转换公式的推导及C#代码实现
本篇讨论的主题是在平面坐标系中如何将一个坐标系(目标坐标系,以下简称目标系)中的所有点投射到另一个坐标系(基坐标系)中。平面坐标系之间的转化一般有三步操作:1、平移;2、旋转;3、拉伸。
在转化的过程中需要的几个已知条件分别是:1、目标系的一个已知点(特征点A)对应于基坐标系中的点(特征点A’)。2、目标系的原点(O)对应于基坐标系中的原点(O')。3、基座标系的原点(O‘’)。
一、坐标系拉伸
①、计算两坐标系X和Y轴分别对应的拉伸比例:
②、将A点按缩放比例映射到基坐标系中(A''):
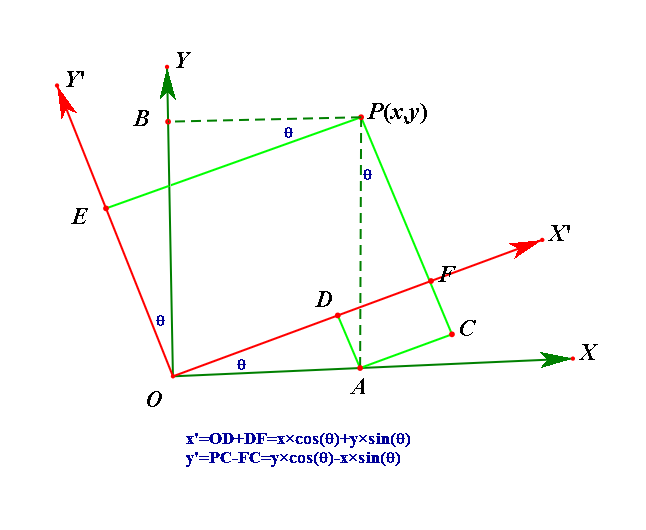
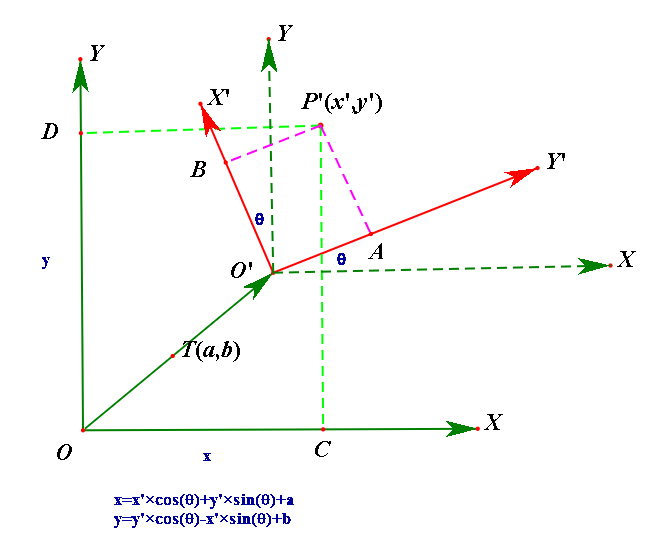
二、坐标系旋转和平移
①:坐标系旋转
②坐标系平移加旋转
③得出公式
根据坐标系旋转和平移的规则,可以得出公式
我们的目标是求出θ。
设m = cos(θ),n=sin(θ),根据已知量可得出公式:
得出方程组的增广矩阵,根据高斯消除元法即可求得m,n:
再根据反三角函数求得θ,此时θ、a、b、T(坐标系倍数)的值都已经得到。
故任意目标系坐标(x、y)可通过公式映射到基坐标系(f(x)、f(y)):
C#代码:
public class CoorPoint
{
public double x { get; set; }
public double y { get; set; }
public CoorPoint()
{ }
public CoorPoint(double x, double y)
{
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
public CoorPoint(CoorPoint pt)
{
this.x = pt.x;
this.y = pt.y;
}
public static CoorPoint operator +(CoorPoint src, CoorPoint tar)
{
CoorPoint result = new CoorPoint(src);
result.x += tar.x;
result.y += tar.y;
return result;
}
public static CoorPoint operator -(CoorPoint src, CoorPoint tar)
{
CoorPoint result = new CoorPoint(src);
result.x -= tar.x;
result.y -= tar.y;
return result;
}
public static CoorPoint operator /(CoorPoint src, CoorPoint tar)
{
CoorPoint result = new CoorPoint(src);
result.x /= tar.x;
result.y /= tar.y;
return result;
}
public static CoorPoint operator *(CoorPoint src, CoorPoint tar)
{
CoorPoint result = new CoorPoint(src);
result.x *= tar.x;
result.y *= tar.y;
return result;
}
}
class CoordinateSystemChg
{
///
/// 基坐标系:特征点(A')
///
public CoorPoint baseCoor_basePoint { get; set; }
///
/// 基坐标系:原点(O)
///
public CoorPoint baseCoor_originPoint { get; set; }
///
/// 现实坐标系:特征点(A)
///
public CoorPoint realistic_basePoint { get; set; }
///
/// 现实坐标系对应基坐标系拉伸后的点(A'')
///
public CoorPoint realistic_basePointAfterZoom { get; set; }
///
/// 现实坐标系:原点(O)
///
public CoorPoint realistic_originPoint { get; set; }
///
/// 现实坐标系对应基坐标系:原点(O')
///
public CoorPoint realistic_originAsBaseCoorPoint { get; set; } //定义原点时 已经统一缩放比例
//第一步的结果
//位移量:a(x轴),b(y轴)
double a = 0;
double b = 0;
//坐标系倍数
CoorPoint coorTimes;
//坐标系夹角
double offsetAngle;
//第一步:得到坐标系之间的角度θ
///
/// 计算出两坐标系的X,Y比例
///
public void GetSale()
{
coorTimes = (realistic_basePoint - realistic_originPoint) / (baseCoor_basePoint - realistic_originAsBaseCoorPoint);
if (coorTimes.x < 0)
coorTimes.x = -coorTimes.x;
if (coorTimes.y < 0)
coorTimes.y = -coorTimes.y;
}
///
/// ①按比例缩放(实际坐标系的基点),使之与基坐标系统一
///
public void DoZoom()
{
realistic_basePointAfterZoom = realistic_basePoint / coorTimes;
}
///
/// ②得到偏移角,入参实际坐标系原点坐标在基坐标系上的坐标
///
public void GetOffsetAngle()
{
double[] x = new double[2];
a = (realistic_originAsBaseCoorPoint.x - baseCoor_originPoint.x);
b = (realistic_originAsBaseCoorPoint.y - baseCoor_originPoint.y);
double[,] g = {
{ realistic_basePointAfterZoom.x, realistic_basePointAfterZoom.y, (baseCoor_basePoint.x - a) },
{ realistic_basePointAfterZoom.y, -realistic_basePointAfterZoom.x, (baseCoor_basePoint.y - b) }
};
GaussianElimination(g, x);
// x[0]:θ角的余弦值;x[1]:θ角的正弦值
offsetAngle = Math.Acos(x[0]);
Console.WriteLine(x[0] + ":" + Math.Acos(x[0]));
Console.WriteLine(x[1] + ":" + Math.Asin(x[1]));
}
//第二步:根据θ角求出在基坐标系中点的映射
///
/// 将实际坐标系中的点转换到基坐标系中的点
///
///
///
public void GetCoordinateBaseSystem(CoorPoint src, out CoorPoint rlt)
{
double db1 = Math.Cos(offsetAngle);
double db2 = Math.Sin(offsetAngle);
rlt = new CoorPoint();
rlt.x = ((src.x / coorTimes.x) * Math.Cos(offsetAngle) + (src.y / coorTimes.y) * Math.Sin(offsetAngle) + a);
rlt.y = ((src.y / coorTimes.y) * Math.Cos(offsetAngle) - (src.x / coorTimes.x) * Math.Sin(offsetAngle) + b);
}
///
/// 将基坐标系中的点转换到实际坐标系中的点
///
///
///
public void GetCoordinateRealisticSystem(CoorPoint src, out CoorPoint rlt)
{
double[] x = new double[2];
double[,] g = {
{ Math.Cos(offsetAngle), Math.Sin(offsetAngle),(src.x - a)*coorTimes.x },
{ -Math.Sin(offsetAngle), Math.Cos(offsetAngle),(src.y - b)*coorTimes.y }
};
GaussianElimination(g, x);
rlt = new CoorPoint();
rlt.x = x[0];
rlt.y = x[1];
}
#region 数学方法
//简单的高斯消元法;
//输入要求解的扩展矩阵g[m,n];和存放结果的数组x[n];
//返回值为计算结果数组x[n];
public static double[] GaussianElimination(double[,] g, double[] x)
{
int m = g.GetLength(0);//获得扩展矩阵的行(方程个数);
int n = g.GetLength(1);//获得扩展矩阵的列(未知数个数+1);
//========================================================
//消元过程;
for (int i = 1; i < m; i++)
{
for (int j = i; j < m; j++)
{
for (int k = n - 1; k > i - 2; k--)
{
g[j, k] = g[j, k] - (g[j, i - 1] / g[i - 1, i - 1]) * (g[i - 1, k]);
}
}
}
//回代过程;
//第一步:翻转;
//换行;
double tem;
for (int i = 0; i < m / 2; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
tem = g[i, j];
g[i, j] = g[m - i - 1, j];
g[m - i - 1, j] = tem;
}
//倒序
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < n / 2; j++)
{
tem = g[i, j];
g[i, j] = g[i, n - 2 - j];
g[i, n - 2 - j] = tem;
}
//第二步:消元;
for (int i = 1; i < m; i++)
{
for (int j = i; j < m; j++)
{
for (int k = n - 1; k > i - 2; k--)
{
g[j, k] = g[j, k] - (g[j, i - 1] / g[i - 1, i - 1]) * (g[i - 1, k]);
}
}
}
//第三步:翻回;
//重新换行;
for (int i = 0; i < m / 2; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
tem = g[i, j];
g[i, j] = g[m - i - 1, j];
g[m - i - 1, j] = tem;
}
//重新倒序;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < n / 2; j++)
{
tem = g[i, j];
g[i, j] = g[i, n - 2 - j];
g[i, n - 2 - j] = tem;
}
//取结果(这里是正序结果哦);
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
x[i] = g[i, n - 1] / g[i, i];
return x;//返回计算结果;
}
#endregion
}