小波降噪详解
“小波”就是小的波形。所谓“小”是指它具有衰减性,而称之为“波”则是指它的波动性,其振幅正负相间的震荡形式。
小波在整个时间范围的幅度平均值是0,具有有限的持续时间和突变的频率和振幅,可以是不规则,也可以是不对称。
小波变换是时间(空间)频率的局部化分析,它通过伸缩平移运算对信号(函数)逐步进行多尺度细化,最终达到高频处时间细分,低频处频率细分,能自动适应时频信号分析的要求,从而可聚焦到信号的任意细节。
傅里叶变换不具有局部性,而小波变换不但具有局部性,而且尺度参数a可以改变频谱结构和窗口的形状,起到“变焦”的作用,因此小波分析可达到多分辨率分析的效果。
参考资料:
http://blog.csdn.net/jbb0523/article/details/42028587
小波公式
对于任意实数对(a,b),其中参数a必须为非零实数,称如下形式的函数:
为由小波母函数ψ(x)生成的依赖于参数(a,b)的连续小波函数,简称小波。小波母函数ψ(x)只有在原点的附近才会有明显偏离水平轴的波动,在远离原点的地方函数值将迅速衰减为零。所以对于任意参数(a,b),小波函数ψa,b(x)在x=b附近存在明显的波动,远离x=b的地方迅速衰减到零(因为b是时移量,母小波是以原点为中心,时移就以b为中心了,如果有尺度变换的话再考虑进去就可以了)。
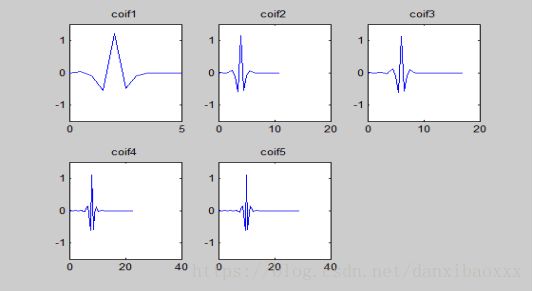
小波形状
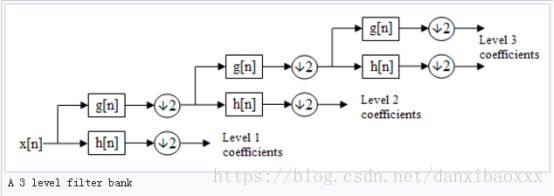
多尺度一维离散小波分解
the first step is
The length of each filter is equal to 2N. If n = length(s), the signals F and G are of length n + 2N −1 and the coefficients cA1 and cD1 are of length floor(n−12)+N.
The next step splits the approximation coefficients cA1 in two parts using the same scheme, replacing s by cA1, and producing cA2 andcD2, and so on.
The tree is known as a filter bank.
参考资料:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Discrete_wavelet_transform
小波去噪过程
去噪步骤
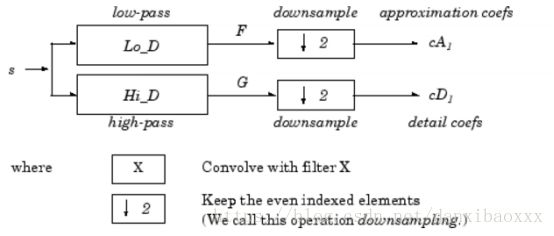
对原始信号进行小波分解,得到各细节分量(高频)与近似分量(低频)
对细节分量进行阈值处理
用处理后的各分量进行小波重构,得到去噪后的信号
去噪过程详解
依据MATLAB函数介绍整个去噪过程
函数原型
XD = wden(X,TPTR,SORH,SCAL,N,'wname')
[XD,CXD,LXD] = wden(...)
函数功能
wden is a one-dimensional de-noising function.
wden performs an automatic de-noising process of a one-dimensional signal using wavelets.
wden returns a de-noised version XD of input signal X obtained by thresholding the wavelet coefficients.
参考资料
https://cn.mathworks.com/help/wavelet/ref/wden.html?searchHighlight=wden&s_tid=doc_srchtitle
1. 选择合适的小波,分解尺度
小波coif2,分解尺度N=4
2. 选择合适的计算阈值方法
TPTR = 'rigrsure', adaptive threshold selection using principle of Stein's Unbiased Risk Estimate.
1)无偏似然估计原则(rigrsure): 是一种基于Stein无偏似然估计的自适应阈值选择。对于给定的阈值T,得到它的似然估计,再讲似然T最小化,就得到了所选的阈值,这是一种软件阈值估计。
TPTR = 'heursure', heuristic variant of the first option.
2)启发式阈值原则(heursure): 是无偏似然估计和固定阈值估计原则的折中。如果信噪比很小,按无偏似然估计原则处理的信号噪声较大,在这种情况下,就采用固定阈值形式。
TPTR = 'sqtwolog', threshold is sqrt(2*log(length(X))).
3)固定阈值原则(sqtwlolg): 固定阈值T的计算公式![]()
TPTR = 'minimaxi', minimax thresholding.
4)极值阈值原则(minimax): 采用极大极小原理选择阈值,它产生一个最小均方误差的极值,而不是没有误差。统计学上,这种极值原理用来设计估计器。因为被消噪的信号可以看作与未知回归函数的估计器相似,这种极值估计器可在给定的函数中实现最大均方误差最小化。
参考资料
https://cn.mathworks.com/help/wavelet/ref/thselect.html
3. 阈值处理方法
SORH ('s' or 'h') is for soft or hard thresholding
![]()
![]()
硬阈值方法能够保留更多尖峰特征,软阈值方法使重建信号比较光滑。
参考资料
https://cn.mathworks.com/help/wavelet/ref/wthresh.html
4. 对细节信号做阈值处理
SCAL defines multiplicative threshold rescaling:
'one' for no rescaling
'sln' for rescaling using a single estimation of level noise based on first-level coefficients
'mln' for rescaling done using level-dependent estimation of level noise
Wnoisest returns estimates of the detail coefficients' standard deviation for levels
The estimator used is Median Absolute Deviation / 0.6745, well suited for zero mean Gaussian white noise in the de-noising one-dimensional model.
参考资料
https://cn.mathworks.com/help/wavelet/ref/wnoisest.html?searchHighlight=wnoisest&s_tid=doc_srchtitle