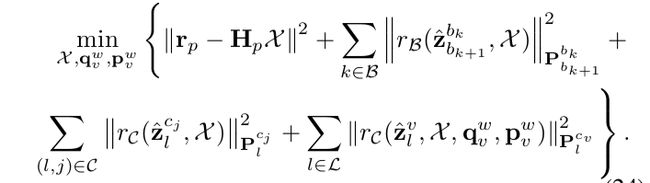vins mono 刚开始学习 一
简介
VINS-Mono 是香港科技大学开源的一个VIO,我简单的测试了,发现效果不错。做个简单的笔记,详细的内容等我毕设搞完再弄。
代码主要分为前端(feature tracker),后端(sliding window, loop closure),还加了初始化(visual-imu aligment)
Feature tracker
这部分代码在feature_tracker包下面,主要是接收图像topic,使用KLT光流算法跟踪特征点,同时保持每一帧图像有最少的(100-300)个特征点。
根据配置文件中的freq,确定每隔多久的时候,把检测到的特征点打包成/feature_tracker/featuretopic 发出去,
要是没有达到发送的时间,这幅图像的feature就作为下一时刻的
KLT追踪的特征点,就是不是每一副图像都要处理的,那样计算时间大了,而且数据感觉冗余,帧与帧之间图像的差距不会那么明显。
这里的freq配置文件建议至少设置10,为了保证好的前端。
void img_callback(const sensor_msgs::ImageConstPtr &img_msg)
{
for (int i = 0; i < NUM_OF_CAM; i++)
{
ROS_DEBUG("processing camera %d", i);
if (i != 1 || !STEREO_TRACK)
//调用FeatureTracker的readImage
trackerData[i].readImage(ptr->image.rowRange(ROW * i, ROW * (i + 1)));
}
for (unsigned int i = 0;; i++)
{
bool completed = false;
for (int j = 0; j < NUM_OF_CAM; j++)
if (j != 1 || !STEREO_TRACK)
//更新feature的ID
completed |= trackerData[j].updateID(i);
if (!completed)
break;
}
//发布特征点topic
if (round(1.0 * pub_count / (img_msg->header.stamp.toSec() - first_image_time)) <= FREQ)
{
sensor_msgs::PointCloudPtr feature_points(new sensor_msgs::PointCloud);
//特征点的id,图像的(u,v)坐标
sensor_msgs::ChannelFloat32 id_of_point;
sensor_msgs::ChannelFloat32 u_of_point;
sensor_msgs::ChannelFloat32 v_of_point;
pub_img.publish(feature_points);
}
if (SHOW_TRACK)
{
//根据特征点被追踪的次数,显示他的颜色,越红表示这个特征点看到的越久,一幅图像要是大部分特征点是蓝色,前端tracker效果很差了,估计要挂了
double len = std::min(1.0, 1.0 * trackerData[i].track_cnt[j] / WINDOW_SIZE);
cv::circle(tmp_img, trackerData[i].cur_pts[j], 2, cv::Scalar(255 * (1 - len), 0, 255 * len), 2);
}
}void FeatureTracker::readImage(const cv::Mat &_img)
{
//直方图均匀化
//if image is too dark or light, trun on equalize to find enough features
if (EQUALIZE)
{
cv::Ptr clahe = cv::createCLAHE(3.0, cv::Size(8, 8));
TicToc t_c;
clahe->apply(_img, img);
ROS_DEBUG("CLAHE costs: %fms", t_c.toc());
}
if (cur_pts.size() > 0)
{
TicToc t_o;
vector<uchar> status;
vector<float> err;
//根据上一时刻的cur_img,cur_pts,寻找当前时刻的forw_pts,
cv::calcOpticalFlowPyrLK(cur_img, forw_img, cur_pts, forw_pts, status, err, cv::Size(21, 21), 3);
}
if (img_cnt == 0)
{
//根据fundamentalMatrix中的ransac去除一些outlier
rejectWithF();
//跟新特征点track的次数
for (auto &n : track_cnt)
n++;
//为下面的goodFeaturesToTrack保证相邻的特征点之间要相隔30个像素,设置mask image
setMask();
int n_max_cnt = MAX_CNT - static_cast<int>(forw_pts.size());
if (n_max_cnt > 0)
{
//保证每个image有足够的特征点,不够就新提取
cv::goodFeaturesToTrack(forw_img, n_pts, MAX_CNT - forw_pts.size(), 0.1, MIN_DIST, mask);
}
}
} Slide Window
主要是对imu的数据进行预积分,vision重投影误差的构造,loop-closure的检测,slide-window的维护 ,marginzation prior的维护,东西比较多。
loop-closure的检测是使用视觉词带的,这里的特征不是feature-tracker的,那样子太少了。是通过订阅IMAGE_TOPIC,传递到闭环检测部分,重新检测的,这个我还没有认真看(做了很多限制,为了搜索的速度,词带不会很大,做了很多限制,从论文上看优化的方程只是加了几个vision重投影的限制,速度不会太慢)。
是只有4个自由度的优化,roll, pitch由于重力对齐的原因是可观测的,就不去优化。
最主要的还是下面这个最小二乘法方程构建,主要的代码我列出来。
void Estimator::processIMU(double dt, const Vector3d &linear_acceleration, const Vector3d &angular_velocity)
{
if (frame_count != 0)
{
pre_integrations[frame_count]->push_back(dt, linear_acceleration, angular_velocity);
//调用imu的预积分,propagation ,计算对应的雅可比矩阵
//if(solver_flag != NON_LINEAR)
tmp_pre_integration->push_back(dt, linear_acceleration, angular_velocity);
dt_buf[frame_count].push_back(dt);
linear_acceleration_buf[frame_count].push_back(linear_acceleration);
angular_velocity_buf[frame_count].push_back(angular_velocity);
//提供imu计算的当前位置,速度,作为优化的初值
int j = frame_count;
Vector3d un_acc_0 = Rs[j] * (acc_0 - Bas[j]) - g;
Vector3d un_gyr = 0.5 * (gyr_0 + angular_velocity) - Bgs[j];
Rs[j] *= Utility::deltaQ(un_gyr * dt).toRotationMatrix();
Vector3d un_acc_1 = Rs[j] * (linear_acceleration - Bas[j]) - g;
Vector3d un_acc = 0.5 * (un_acc_0 + un_acc_1);
Ps[j] += dt * Vs[j] + 0.5 * dt * dt * un_acc;
Vs[j] += dt * un_acc;
}
}
void Estimator::processImage(const map<int, vectorint, Vector3d>>> &image, const std_msgs::Header &header)
{
//根据视差判断是不是关键帧,
if (f_manager.addFeatureCheckParallax(frame_count, image))
marginalization_flag = MARGIN_OLD;
else
marginalization_flag = MARGIN_SECOND_NEW;
ImageFrame imageframe(image, header.stamp.toSec());
imageframe.pre_integration = tmp_pre_integration;
all_image_frame.insert(make_pair(header.stamp.toSec(), imageframe));
tmp_pre_integration = new IntegrationBase{acc_0, gyr_0, Bas[frame_count], Bgs[frame_count]};
//参数要是设置imu-camera的外参数未知,也可以帮你求解的
if(ESTIMATE_EXTRINSIC == 2)
{
}
//初始化的流程
if (solver_flag == INITIAL)
{
if (frame_count == WINDOW_SIZE)
{
bool result = false;
if( ESTIMATE_EXTRINSIC != 2 && (header.stamp.toSec() - initial_timestamp) > 0.1)
{
//构造sfm,优化imu偏差,加速度g,尺度的确定
result = initialStructure();
initial_timestamp = header.stamp.toSec();
}
if(result)
{
solver_flag = NON_LINEAR;
solveOdometry();
slideWindow();
f_manager.removeFailures();
ROS_INFO("Initialization finish!");
last_R = Rs[WINDOW_SIZE];
last_P = Ps[WINDOW_SIZE];
last_R0 = Rs[0];
last_P0 = Ps[0];
}
else
slideWindow();
}
//先凑够window-size的数量的Frame
else
frame_count++;
}
else
{
solveOdometry();
//失败的检测
if (failureDetection())
{
clearState();
setParameter();
return;
}
slideWindow();
f_manager.removeFailures();
// prepare output of VINS
key_poses.clear();
for (int i = 0; i <= WINDOW_SIZE; i++)
key_poses.push_back(Ps[i]);
last_R = Rs[WINDOW_SIZE];
last_P = Ps[WINDOW_SIZE];
last_R0 = Rs[0];
last_P0 = Ps[0];
}
} void Estimator::slideWindow()
{
//WINDOW_SIZE中的参数的之间调整,同时FeatureManager进行管理feature,有些点要删除掉,有些点的深度要在下一frame表示(start frame已经删除了)
Headers[frame_count - 1] = Headers[frame_count];
Ps[frame_count - 1] = Ps[frame_count];
Vs[frame_count - 1] = Vs[frame_count];
Rs[frame_count - 1] = Rs[frame_count];
Bas[frame_count - 1] = Bas[frame_count];
Bgs[frame_count - 1] = Bgs[frame_count];
delete pre_integrations[WINDOW_SIZE];
pre_integrations[WINDOW_SIZE] = new IntegrationBase{acc_0, gyr_0, Bas[WINDOW_SIZE], Bgs[WINDOW_SIZE]};
//清楚数据,给下一副图像提供空间
dt_buf[WINDOW_SIZE].clear();
linear_acceleration_buf[WINDOW_SIZE].clear();
angular_velocity_buf[WINDOW_SIZE].clear();
}
void Estimator::solveOdometry()
{
if (frame_count < WINDOW_SIZE)
return;
if (solver_flag == NON_LINEAR)
{
//三角化点
f_manager.triangulate(Ps, tic, ric);
ROS_DEBUG("triangulation costs %f", t_tri.toc());
optimization();
}
}void Estimator::optimization()
{
//添加frame的state,(p,v,q,b_a,b_g),就是ceres要优化的参数
for (int i = 0; i < WINDOW_SIZE + 1; i++)
{
ceres::LocalParameterization *local_parameterization = new PoseLocalParameterization();
problem.AddParameterBlock(para_Pose[i], SIZE_POSE, local_parameterization);
problem.AddParameterBlock(para_SpeedBias[i], SIZE_SPEEDBIAS);
}
//添加camera-imu的外参数
for (int i = 0; i < NUM_OF_CAM; i++)
{
ceres::LocalParameterization *local_parameterization = new PoseLocalParameterization();
problem.AddParameterBlock(para_Ex_Pose[i], SIZE_POSE, local_parameterization);
}
//为ceres参数赋予初值
vector2double();
//添加margination residual, 先验知识
//他的Evaluate函数看好,固定了线性化的点,First Jacobian Estimate
if (last_marginalization_info)
{
// construct new marginlization_factor
MarginalizationFactor *marginalization_factor = new MarginalizationFactor(last_marginalization_info);
problem.AddResidualBlock(marginalization_factor, NULL,
last_marginalization_parameter_blocks);
}
//添加imu的residual
for (int i = 0; i < WINDOW_SIZE; i++)
{
int j = i + 1;
if (pre_integrations[j]->sum_dt > 10.0)
continue;
IMUFactor* imu_factor = new IMUFactor(pre_integrations[j]);
problem.AddResidualBlock(imu_factor, NULL, para_Pose[i], para_SpeedBias[i], para_Pose[j], para_SpeedBias[j]);
}
//添加vision的residual
for (auto &it_per_id : f_manager.feature)
{
for (auto &it_per_frame : it_per_id.feature_per_frame)
{
imu_j++;
if (imu_i == imu_j)
{
continue;
}
Vector3d pts_j = it_per_frame.point;
ProjectionFactor *f = new ProjectionFactor(pts_i, pts_j);
problem.AddResidualBlock(f, loss_function, para_Pose[imu_i], para_Pose[imu_j], para_Ex_Pose[0], para_Feature[feature_index]);
f_m_cnt++;
}
}
//添加闭环的参数和residual
if(LOOP_CLOSURE)
{
ceres::LocalParameterization *local_parameterization = new PoseLocalParameterization();
problem.AddParameterBlock(front_pose.loop_pose, SIZE_POSE, local_parameterization);
if(front_pose.features_ids[retrive_feature_index] == it_per_id.feature_id)
{
Vector3d pts_j = Vector3d(front_pose.measurements[retrive_feature_index].x, front_pose.measurements[retrive_feature_index].y, 1.0);
Vector3d pts_i = it_per_id.feature_per_frame[0].point;
ProjectionFactor *f = new ProjectionFactor(pts_i, pts_j);
problem.AddResidualBlock(f, loss_function, para_Pose[start], front_pose.loop_pose, para_Ex_Pose[0], para_Feature[feature_index]);
retrive_feature_index++;
loop_factor_cnt++;
}
}
//设置了优化的最长时间,保证实时性
if (marginalization_flag == MARGIN_OLD)
options.max_solver_time_in_seconds = SOLVER_TIME * 4.0 / 5.0;
else
options.max_solver_time_in_seconds = SOLVER_TIME;
// 求解
ceres::Solve(options, &problem, &summary);
// http://blog.csdn.net/heyijia0327/article/details/53707261#comments
// http://blog.csdn.net/heyijia0327/article/details/52822104
if (marginalization_flag == MARGIN_OLD)
{
//如果当前帧是关键帧的,把oldest的frame所有的信息margination,作为下一时刻的先验知识,参考上面的两个网址,大神的解释很明白
}
else{
//如果当前帧不是关键帧的,把second newest的frame所有的视觉信息丢弃掉,imu信息不丢弃,记住不是做margination,是为了保持矩阵的稀疏性
}
}后续
imu的参数很重要,还有就是硬件同步,global shutter的摄像头很重要。我要是动作快的话,效果就不行了。但人家的视频感觉效果很不错。
这个还要继续弄硬件和代码原理,代码中最小二乘法优化中的FOCAL_LENGTH感觉要根据自己的摄像头设置,还没有具体看,视觉信息矩阵的设置还没有看。
工程中具体的情况还是要自己解决,