Apollo项目代码迁移到Cyber RT框架(Apollo 3.5以上版本)的方法
严正声明:本文系作者davidhopper原创,未经许可,不得转载。
Apollo 3.5彻底摒弃ROS,改用自研的Cyber RT作为底层通讯与调度平台,实时性与灵活性更为突出。关于Apollo 3.5的构建方法,可参见我的一篇博客。关于Apollo 3.5各功能模块的启动过程解析,可参见我的另一篇博客。
本文阐述Apollo项目代码迁移到Cyber RT框架(Apollo 3.5以上版本)的方法。本文在Apollo官方文档:How to create and run a new component in Apollo Cyber RT及How to use Cyber commands的基础上撰写,但更为翔实具体。
一、功能模块代码的迁移
Apollo Cyber RT框架基于组件的概念构建、加载各功能模块。Localization、 Perception、Prediction、Planning、Control等功能模块均作为Apollo Cyber RT框架的一个组件而存在,基于Cyber RT提供的调度程序mainboard加载运行。
基于Apollo Cyber RT框架创建和发布新的功能模块组件,需执行以下五个基本步骤:
- 设置组件文件结构
- 实现组件类
- 提供构建文件
- 提供配置文件
- 启动组件
下面以Planning模块为例进行阐述。
1.1 设置组件文件结构
基于路径${APOLLO_HOME}/modules/planning(${APOLLO_HOME}表示Apollo项目的根目录,以我的机器为例,Docker外部为/home/davidhopper/code/apollo,Docker内部自不必说,全部为/apollo。为描述简单起见,下文全部以Docker内部的路径/apollo为准)设置如下组件文件结构:
- 头文件:
planning_component.h; - 实现文件:
planning_component.cc; - 构建文件:
BUILD; - DAG配置文件:
dag/planning.dag; - Launch配置文件:
launch/planning.launch。
1.2 实现组件类
执行以下步骤以实现组件类:
- 基于模板类
Component派生出规划模块的组件类PlanningComponent; - 在派生类
PlanningComponent中覆盖要虚函数Init()andProc()函数; - 使用宏
CYBER_REGISTER_COMPONENT(PlanningComponent)注册组件类PlanningComponent,以便Cyber RT能正确创建并加载该类对象(关于该宏的具体含义,参见我的博客Apollo 3.5各功能模块的启动过程解析)。
1.2.1 组件类PlanningComponent的声明
namespace apollo {
namespace planning {
class PlanningComponent final
: public cyber::Component<prediction::PredictionObstacles, canbus::Chassis,
localization::LocalizationEstimate> {
public:
PlanningComponent() = default;
~PlanningComponent() = default;
public:
bool Init() override;
bool Proc(const std::shared_ptr<prediction::PredictionObstacles>&
prediction_obstacles,
const std::shared_ptr<canbus::Chassis>& chassis,
const std::shared_ptr<localization::LocalizationEstimate>&
localization_estimate) override;
private:
void CheckRerouting();
bool CheckInput();
std::shared_ptr<cyber::Reader<perception::TrafficLightDetection>>
traffic_light_reader_;
std::shared_ptr<cyber::Reader<routing::RoutingResponse>> routing_reader_;
std::shared_ptr<cyber::Reader<planning::PadMessage>> pad_message_reader_;
std::shared_ptr<cyber::Reader<relative_map::MapMsg>> relative_map_reader_;
std::shared_ptr<cyber::Writer<ADCTrajectory>> planning_writer_;
std::shared_ptr<cyber::Writer<routing::RoutingRequest>> rerouting_writer_;
std::mutex mutex_;
perception::TrafficLightDetection traffic_light_;
routing::RoutingResponse routing_;
PadMessage pad_message_;
relative_map::MapMsg relative_map_;
LocalView local_view_;
std::unique_ptr<PlanningBase> planning_base_;
PlanningConfig config_;
};
CYBER_REGISTER_COMPONENT(PlanningComponent)
} // namespace planning
} // namespace apollo
注意到基类Component的定义为:
template <typename M0 = NullType, typename M1 = NullType,
typename M2 = NullType, typename M3 = NullType>
class Component : public ComponentBase {
// ...
};
可见,Component类最多接受4个模板参数,每个模板参数均表示一种输入的消息类型,这些消息在Proc函数中被周期性地接收并处理;而PlanningComponent继承的是该模板类接受3个参数的一个特化版本:
template <typename M0, typename M1, typename M2>
class Component<M0, M1, M2, NullType> : public ComponentBase {
// ...
};
即PlanningComponent继承自cyber::Component,3个消息参数分别为:prediction::PredictionObstacles、canbus::Chassis、localization::LocalizationEstimate,这些消息在Proc函数中被周期性地接收并处理。
1.2.2 组件类PlanningComponent的实现
PlanningComponent的实现主要包括两个覆盖的虚函数Init() and Proc()函数:
bool PlanningComponent::Init() {
if (FLAGS_open_space_planner_switchable) {
planning_base_ = std::unique_ptr<PlanningBase>(new OpenSpacePlanning());
} else {
planning_base_ = std::unique_ptr<PlanningBase>(new StdPlanning());
}
CHECK(apollo::common::util::GetProtoFromFile(FLAGS_planning_config_file,
&config_))
<< "failed to load planning config file " << FLAGS_planning_config_file;
planning_base_->Init(config_);
if (FLAGS_use_sim_time) {
Clock::SetMode(Clock::MOCK);
}
routing_reader_ = node_->CreateReader<RoutingResponse>(
FLAGS_routing_response_topic,
[this](const std::shared_ptr<RoutingResponse>& routing) {
AINFO << "Received routing data: run routing callback."
<< routing->header().DebugString();
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(mutex_);
routing_.CopyFrom(*routing);
});
traffic_light_reader_ = node_->CreateReader<TrafficLightDetection>(
FLAGS_traffic_light_detection_topic,
[this](const std::shared_ptr<TrafficLightDetection>& traffic_light) {
ADEBUG << "Received traffic light data: run traffic light callback.";
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(mutex_);
traffic_light_.CopyFrom(*traffic_light);
});
if (FLAGS_use_navigation_mode) {
pad_message_reader_ = node_->CreateReader<PadMessage>(
FLAGS_planning_pad_topic,
[this](const std::shared_ptr<PadMessage>& pad_message) {
ADEBUG << "Received pad data: run pad callback.";
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(mutex_);
pad_message_.CopyFrom(*pad_message);
});
relative_map_reader_ = node_->CreateReader<MapMsg>(
FLAGS_relative_map_topic,
[this](const std::shared_ptr<MapMsg>& map_message) {
ADEBUG << "Received relative map data: run relative map callback.";
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(mutex_);
relative_map_.CopyFrom(*map_message);
});
}
planning_writer_ =
node_->CreateWriter<ADCTrajectory>(FLAGS_planning_trajectory_topic);
rerouting_writer_ =
node_->CreateWriter<RoutingRequest>(FLAGS_routing_request_topic);
return true;
}
其中Init()函数用于创建实际规划类对象,创建除prediction::PredictionObstacles、canbus::Chassis、localization::LocalizationEstimate三类消息以外的其他消息处理回调函数,创建Planning模块的输出器:轨迹输出器planning_writer_和重新生成路由输出器rerouting_writer_。注意目前(2019年1月7日)版本并未创建导航模式规划器NaviPlanning。
bool PlanningComponent::Proc(
const std::shared_ptr<prediction::PredictionObstacles>&
prediction_obstacles,
const std::shared_ptr<canbus::Chassis>& chassis,
const std::shared_ptr<localization::LocalizationEstimate>&
localization_estimate) {
CHECK(prediction_obstacles != nullptr);
if (FLAGS_use_sim_time) {
Clock::SetNowInSeconds(localization_estimate->header().timestamp_sec());
}
// check and process possible rerouting request
CheckRerouting();
// process fused input data
local_view_.prediction_obstacles = prediction_obstacles;
local_view_.chassis = chassis;
local_view_.localization_estimate = localization_estimate;
{
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(mutex_);
if (!local_view_.routing ||
hdmap::PncMap::IsNewRouting(*local_view_.routing, routing_)) {
local_view_.routing =
std::make_shared<routing::RoutingResponse>(routing_);
local_view_.is_new_routing = true;
} else {
local_view_.is_new_routing = false;
}
}
{
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(mutex_);
local_view_.traffic_light =
std::make_shared<TrafficLightDetection>(traffic_light_);
}
if (!CheckInput()) {
AERROR << "Input check failed";
return false;
}
ADCTrajectory adc_trajectory_pb;
planning_base_->RunOnce(local_view_, &adc_trajectory_pb);
auto start_time = adc_trajectory_pb.header().timestamp_sec();
common::util::FillHeader(node_->Name(), &adc_trajectory_pb);
// modify trajecotry relative time due to the timestamp change in header
const double dt = start_time - adc_trajectory_pb.header().timestamp_sec();
for (auto& p : *adc_trajectory_pb.mutable_trajectory_point()) {
p.set_relative_time(p.relative_time() + dt);
}
planning_writer_->Write(std::make_shared<ADCTrajectory>(adc_trajectory_pb));
return true;
}
而Proc()函数周期性地接收prediction::PredictionObstacles、canbus::Chassis、localization::LocalizationEstimate三类消息,调用planning_base_->RunOnce()函数执行实际的路径与速度规划,并将规划结果adc_trajectory_pb借助函数planning_writer_->Write()将生成的规划轨迹输出给控制模块执行。
1.3 提供构建文件/apollo/modules/planning/BUILD
下面列出/apollo/modules/planning/BUILD文件中与Cyber RT相关的内容,可见基于planning_component_lib库最终生成了一个共享库文件libplanning_component.so,而该共享库通过Cyber RT调度程序mainboard动态加载运行:
load("//tools:cpplint.bzl", "cpplint")
package(default_visibility = ["//visibility:public"])
cc_library(
name = "planning_component_lib",
srcs = [
"planning_component.cc",
],
hdrs = [
"planning_component.h",
],
copts = [
"-DMODULE_NAME=\\\"planning\\\"",
],
deps = [
":planning_lib",
"//cyber",
"//modules/common/adapters:adapter_gflags",
"//modules/common/util:message_util",
"//modules/localization/proto:localization_proto",
"//modules/map/relative_map/proto:navigation_proto",
"//modules/perception/proto:perception_proto",
"//modules/planning/proto:planning_proto",
"//modules/prediction/proto:prediction_proto",
],
)
cc_binary(
name = "libplanning_component.so",
linkshared = True,
linkstatic = False,
deps = [":planning_component_lib"],
)
# ...
1.4 提供DAG配置文件: /apollo/dag/planning.dag
DAG配置文件是Cyber RT调度程序mainboard动态加载Planning模块的最终配置文件,加载命令一般为:
/apollo/bazel-bin/cyber/mainboard -d /apollo/modules/planning/dag/planning.dag
标准模式的DAG配置文件如下:
# Define all coms in DAG streaming.
module_config {
# 共享库文件路径
module_library : "/apollo/bazel-bin/modules/planning/libplanning_component.so"
components {
# 组件类名称,一定不能写错,否则mainboard无法动态创建PlanningComponent组件对象
class_name : "PlanningComponent"
config {
# 模块名
name: "planning"
# GFlag配置文件路径,注意路径一定写成绝对路径,否则可能无法找到配置文件,导致模块加载失败
flag_file_path: "/apollo/modules/planning/conf/planning.conf"
# PlanningComponent组件Proc()函数中使用的三个消息接收器
readers: [
{
channel: "/apollo/prediction"
},
{
channel: "/apollo/canbus/chassis"
qos_profile: {
depth : 15
}
pending_queue_size: 50
},
{
channel: "/apollo/localization/pose"
qos_profile: {
depth : 15
}
pending_queue_size: 50
}
]
}
}
}
1.5 提供Launch配置文件: /apollo/launch/planning.launch
Launch配置文件是Cyber RT提供的一个Python工具程序cyber_launch加载Planning模块所需的配置文件,启动命令如下所示(最终仍归结于mainboard加载):
cyber_launch start /apollo/launch/planning.launch
标准模式的Launch配置文件如下:
<cyber>
<module>
<name>planning</name>
<dag_conf>/apollo/modules/planning/dag/planning.dag</dag_conf>
<process_name>planning</process_name>
</module>
</cyber>
1.6 如何接收消息?
基于Cyber RT接收消息分两种情形,第一种是1.2.1节描述的在虚函数PlanningComponent::Proc()中处理指定的消息类型,这类消息是周期性触发,但最多只能接收4种(因为cyber::Component的模板参数最多只有4个),一般用于模块主要输入消息的接收。第二种是直接创建消息接收器,一般用于接收非周期性消息或模块的次要输入消息,示例代码如下,注意消息处理回调函数均以Lambda表达式的方式展现:
routing_reader_ = node_->CreateReader<RoutingResponse>(
FLAGS_routing_response_topic,
[this](const std::shared_ptr<RoutingResponse>& routing) {
AINFO << "Received routing data: run routing callback."
<< routing->header().DebugString();
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(mutex_);
routing_.CopyFrom(*routing);
});
traffic_light_reader_ = node_->CreateReader<TrafficLightDetection>(
FLAGS_traffic_light_detection_topic,
[this](const std::shared_ptr<TrafficLightDetection>& traffic_light) {
ADEBUG << "Received traffic light data: run traffic light callback.";
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(mutex_);
traffic_light_.CopyFrom(*traffic_light);
});
1.7 如何发布消息?
基于Cyber RT发布消息非常直观,首先创建发布器对象,然后填充消息,最后发布消息,示例代码如下:
// 1.创建发布器
planning_writer_ =
node_->CreateWriter<ADCTrajectory>(FLAGS_planning_trajectory_topic);
// 2.填充消息
ADCTrajectory adc_trajectory_pb;
planning_base_->RunOnce(local_view_, &adc_trajectory_pb);
auto start_time = adc_trajectory_pb.header().timestamp_sec();
common::util::FillHeader(node_->Name(), &adc_trajectory_pb);
// modify trajecotry relative time due to the timestamp change in header
const double dt = start_time - adc_trajectory_pb.header().timestamp_sec();
for (auto& p : *adc_trajectory_pb.mutable_trajectory_point()) {
p.set_relative_time(p.relative_time() + dt);
}
// 3.发布消息
planning_writer_->Write(std::make_shared<ADCTrajectory>(adc_trajectory_pb));
1.8 如何在main()函数中单独使用Cyber RT?
Cyber RT可以在main()函数中单独使用,示例代码如下,更多示例可查看Cyber examples:
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
google::ParseCommandLineFlags(&argc, &argv, true);
// Init the cyber framework
apollo::cyber::Init(argv[0]);
FLAGS_alsologtostderr = true;
NavigationInfo navigation_info;
// ...
std::shared_ptr<apollo::cyber::Node> node(
apollo::cyber::CreateNode("navigation_info"));
auto writer = node->CreateWriter<apollo::relative_map::NavigationInfo>(
FLAGS_navigation_topic);
// In theory, the message only needs to be sent once. Considering the problems
// such as the network delay, We send it several times to ensure that the data
// is sent successfully.
Rate rate(1.0);
constexpr int kTransNum = 3;
int trans_num = 0;
while (apollo::cyber::OK()) {
if (trans_num > kTransNum) {
break;
}
apollo::common::util::FillHeader(node->Name(), &navigation_info);
writer->Write(navigation_info);
ADEBUG << "Sending navigation info:" << navigation_info.DebugString();
rate.Sleep();
++trans_num;
}
return 0;
}
二、辅助工具的迁移
2.1 常用工具对比
Apollo 3.0以下版本提供了许多基于ROS的调试工具,Apollo 3.5的Cyber RT框架同样提供了类似功能,下面给出常用工具的对比表:
| ROS | Cyber | 备注 |
|---|---|---|
| rosbag | cyber_recorder | 处理数据文件 |
| rostopic | cyber_channel | 查看某个topic的信息 |
| scripts/diagnostics.sh | cyber_monitor | 查看诊断消息 |
| offline_lidar_visualizer_tool | cyber_visualizer | 激光点云及摄像头可视化工具,需要安装NVIDIA显卡驱动及CUDA |
2.2 常用命令迁移
| ROS | Cyber | 备注 |
|---|---|---|
| rosbag play example.bag | cyber_recorder play -f example.record | 播放一个包 |
| rosbag info example.bag | cyber_recorder info example.record | 查看一个包的信息 |
| rosbag record /apollo/canbus/chassis \ /apollo/canbus/chassis_detail | cyber_recorder record -c /apollo/canbus/chassis \ /apollo/canbus/chassis_detail | 录制多个topic |
| rosbag filter input.bag output.bag ‘topic != “/apollo/planning”’ | cyber_recorder split -f input_file.record -o ouput_file.record -k “/apollo/planning” | 滤除一个topic |
| rosbag filter csc.bag csc_no_plannig_and_relativemap.bag ‘topic != “/apollo/planning” and “/apollo/relative_map”’ | cyber_recorder split -f input_file.record -o ouput_file.record -k “/apollo/planning” -k “/apollo/relative_map”’ | 滤除多个topic |
| rostopic list | cyber_channel list | 列出所有活动的topic |
| rostopic info /apollo/planning | cyber_channel info /apollo/planning | 查看 /apollo/planning topic的概要信息 |
| rostopic echo /apollo/planning | cyber_channel echo /apollo/planning | 查看 /apollo/planning topic的内容 |
| rostopic hz /apollo/planning | cyber_channel hz /apollo/planning | 查看 /apollo/planning topic的发送频率 |
| rostopic bw /apollo/planning | cyber_channel bw /apollo/planning | 查看 /apollo/planning topic的带宽 |
| rostopic type /apollo/planning | cyber_channel type /apollo/planning | 查看 /apollo/planning topic的数据类型 |
示例:
cyber_recorder record -c /apollo/localization/pose /apollo/canbus/chassis /apollo/perception/obstacles /apollo/prediction /apollo/planning /apollo/control
三、GDB调试功能的迁移
3.1 调试启动命令
下面给出Apollo 3.0以下版本及Apollo 3.5以上版本的GDB调试启动命令:
### 方法1:直接启动模块调试
# Apollo 3.0以下版本GDB调试启动命令
gdb -q --args bazel-bin/modules/planning/planning --flagfile=/apollo/modules/planning/conf/planning.conf
# Apollo 3.5以上版本GDB调试启动命令
gdb -q --args bazel-bin/cyber/mainboard -d /apollo/modules/planning/dag/planning.dag
### 方法2:通过Dreamview启动相关模块,附加调试相关进程
# Apollo 3.0以下版本GDB调试启动命令
# 在Dreamview中启动Planning模块,然后使用ps aux | grep planning命令查找
# planning进程ID(PID),假设为35872,则使用attach模式附加到当前planning进程调试
sudo gdb -q bazel-bin/modules/planning/planning -p 35872
# # Apollo 3.5以上版本GDB调试启动命令
# 在Dreamview中启动Planning模块,然后使用ps aux | grep mainboard命令查找
# 带有“mainboard -d /apollo/modules/planning/dag/planning.dag”描述字符的mainboard进程ID(PID),
# 假设为35872,则使用attach模式附加到mainboard进程调试
sudo gdb -q bazel-bin/cyber/mainboard -p 35872
值得指出的是,因为Apollo 3.5以上版本通过动态创建的方式启动Planning模块,因此在使用GDB设置断点时,按下TAB键不会有提示,可以借助VSCode提供的Copy Relative Path功能撰写正确的源代码文件路径,如下图所示:

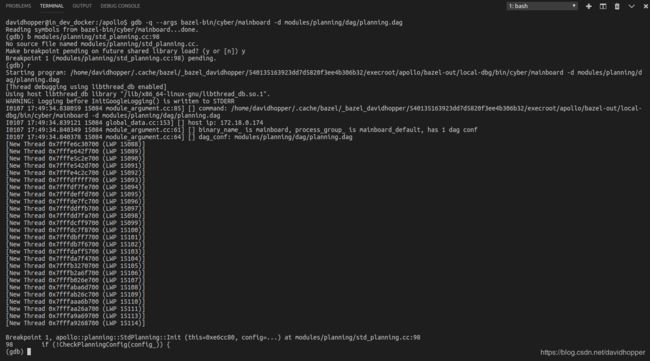
3.2 调试示例
3.3 特殊情况处理
3.3.1 人工发送prediction::PredictionObstacles消息
为提高消息处理的实时性和灵活性,Apollo 3.5的Planning模块不再基于定时器触发更新,而是基于三个输入消息的改变而动态更新,这三个输入消息分别为:prediction::PredictionObstacles、canbus::Chassis、localization::LocalizationEstimate。也就是说,只有上述三个消息同时存在时,Planning模块的消息处理函数PlanningComponent::Proc()才会被调用,而具体的某一类规划算法(例如OnLanePlanning)才会真正工作。
若某条消息因为特殊原因不能及时发送,解决办法就是人工生成假消息。例如,若不能收到prediction::PredictionObstacles消息,则可在在Docker内部通过如下命令生成假prediction::PredictionObstacles消息:
cyber_launch start /apollo/modules/tools/prediction/fake_prediction/fake_prediction.launch
该假消息的具体生成代码见/apollo/modules/tools/prediction/fake_prediction,其他假消息的生成可参照该示例撰写。
3.3.2 人工发送perception::TrafficLightDetection消息
调试规划算法时,需要动态改变红绿灯的信号状态,可以通过如下命令人工发送perception::TrafficLightDetection消息来实现:
cyber_launch start /apollo/modules/tools/manual_traffic_light/manual_traffic_light.launch
程序启动后,按c键和回车键,可以动态切换红绿灯状态。
四、ROS bag数据包的迁移
如果之前使用ROS录制了很多bag数据包,当然不能轻易浪费这些资源。所幸Cyber RT充分考虑到该问题,已为我们提供了转换工具rosbag_to_record,下面将一个Apollo 2.5 demo bag转换为Cyber RT支持的record格式数据包:
rosbag_to_record demo_2.5.bag demo.record
关于该转换工具的更多描述,请参见Apollo帮助文档。
五、ROS读写.bag文件功能的迁移
如下所示,ROS提供了直接从.bag文件读取、分析数据的功能:
rosbag::Bag bag;
try {
bag.open(bag_filename); // BagMode is Read by default
} catch (const rosbag::BagException& e) {
AERROR << "Can't open the input bag file: " << bag_filename;
AERROR << "The reason is: " << e.what();
return false;
}
std::vector<std::string> topics = {"/apollo/navi_generator/collector"};
rosbag::View view(bag, rosbag::TopicQuery(topics));
for (const auto& message : view) {
auto msg = message.instantiate<TrajectoryCollectorMsg>();
if (msg != nullptr) {
*min_speed_limit = msg->min_speed_limit();
*max_speed_limit = msg->max_speed_limit();
}
}
bag.close();
Cyber RT也提供了类似功能,只不过ROS操作的是.bag文件,而Cyber RT操作的是.record文件,示例代码如下:
RecordReader reader(readfile);
RecordMessage message;
uint64_t msg_count = reader.GetMessageNumber(CHANNEL_NAME_1);
AINFO << "MSGTYPE: " << reader.GetMessageType(CHANNEL_NAME_1);
AINFO << "MSGDESC: " << reader.GetProtoDesc(CHANNEL_NAME_1);
// read all message
uint64_t i = 0;
uint64_t valid = 0;
for (i = 0; i < msg_count; ++i) {
if (reader.ReadMessage(&message)) {
AINFO << "msg[" << i << "]-> "
<< "channel name: " << message.channel_name
<< "; content: " << message.content << "; msg time: " << message.time;
valid++;
} else {
AERROR << "read msg[" << i << "] failed";
}
}
AINFO << "static msg=================";
AINFO << "MSG validmsg:totalcount: " << valid << ":" << msg_count;
上述代码位于/apollo/cyber/examples/record.cc文件中,其他接口可通过/apollo/cyber/record目录下的record_reader.h和record_viewer.h文件查询。
