基于对抗生成网络的图像去模糊
论文参考: Deep Generative Filter for motion deblurring 论文解读
完整工程代码下载: https://download.csdn.net/download/dcrmg/10620482
1. 图像大小 256×256 。
训练时候把清晰图像和模糊图像合成在一张图上,左侧是清晰图像,右侧是模糊图像。
2. 根据训练和测试图片生成 HDF5格式 文件
HDF(Hierarchical Data Format)可以存储不同类型的图像和数码数据的文件格式,并且可以在不同类型的机器上传输,支持并行I / O。
标准图片格式到HDF5格式的转换函数:
# according the image path to read the image and covert it
# to the given size, then slice it, finally return the full and blur images
def format_image(image_path, size):
image = Image.open(image_path)
# slice image into full and blur images
image_full = image.crop((0, 0, image.size[0] / 2, image.size[1]))
# Note the full image in left, the blur image in right
image_blur = image.crop((image.size[0] / 2, 0, image.size[0], image.size[1]))
# image_full.show()
# image_blur.show()
image_full = image_full.resize((size, size), Image.ANTIALIAS)
image_blur = image_blur.resize((size, size), Image.ANTIALIAS)
# return the numpy arrays
return np.array(image_full), np.array(image_blur)
# convert images to hdf5 data
def build_hdf5(jpeg_dir, size=256):
# put data in HDF5
hdf5_file = os.path.join('data', 'data.h5')
with h5py.File(hdf5_file, 'w') as f:
for data_type in tqdm(['train', 'test'], desc='create HDF5 dataset from images'):
data_path = jpeg_dir + '/%s/*.jpg' % data_type
images_path = gb.glob(data_path)
# print(images_path)
data_full = []
data_blur = []
for image_path in images_path:
image_full, image_blur = format_image(image_path, size)
data_full.append(image_full)
data_blur.append(image_blur)
# print(len(data_full))
# print(len(data_blur))
f.create_dataset('%s_data_full' % data_type, data=data_full)
f.create_dataset('%s_data_blur' % data_type, data=data_blur)3. 生成器网络
keras实现的生成器网络:
def generator_model():
# Input Image, Note the shape is variable
inputs = Input(shape=(None, None, 3))
# The Head
h = Convolution2D(filters=4 * channel_rate, kernel_size=(3, 3), padding='same')(inputs)
# The Dense Field
d_1 = dense_block(inputs=h)
x = concatenate([h, d_1])
# the paper used dilated convolution at every even numbered layer within the dense field
d_2 = dense_block(inputs=x, dilation_factor=(1, 1))
x = concatenate([x, d_2])
d_3 = dense_block(inputs=x)
x = concatenate([x, d_3])
d_4 = dense_block(inputs=x, dilation_factor=(2, 2))
x = concatenate([x, d_4])
d_5 = dense_block(inputs=x)
x = concatenate([x, d_5])
d_6 = dense_block(inputs=x, dilation_factor=(3, 3))
x = concatenate([x, d_6])
d_7 = dense_block(inputs=x)
x = concatenate([x, d_7])
d_8 = dense_block(inputs=x, dilation_factor=(2, 2))
x = concatenate([x, d_8])
d_9 = dense_block(inputs=x)
x = concatenate([x, d_9])
d_10 = dense_block(inputs=x, dilation_factor=(1, 1))
# The Tail
x = LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2)(d_10)
x = Convolution2D(filters=4 * channel_rate, kernel_size=(1, 1), padding='same')(x)
x = BatchNormalization()(x)
# The Global Skip Connection
x = concatenate([h, x])
x = Convolution2D(filters=channel_rate, kernel_size=(3, 3), padding='same')(x)
# PReLU can't be used, because it is connected with the input shape
# x = PReLU()(x)
x = LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2)(x)
# Output Image
outputs = Convolution2D(filters=3, kernel_size=(3, 3), padding='same', activation='tanh')(x)
model = Model(inputs=inputs, outputs=outputs, name='Generator')
return model
其中用到了10次密集连接模块dense_block:
# Dense Block
def dense_block(inputs, dilation_factor=None):
x = LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2)(inputs)
x = Convolution2D(filters=4 * channel_rate, kernel_size=(1, 1), padding='same')(x)
x = BatchNormalization()(x)
x = LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2)(x)
# the 3 × 3 convolutions along the dense field are alternated between ‘spatial’ convolution
# and ‘dilated’ convolution with linearly increasing dilation factor
if dilation_factor is not None:
x = Convolution2D(filters=channel_rate, kernel_size=(3, 3), padding='same',
dilation_rate=dilation_factor)(x)
else:
x = Convolution2D(filters=channel_rate, kernel_size=(3, 3), padding='same')(x)
x = BatchNormalization()(x)
# add Gaussian noise
x = Dropout(rate=0.5)(x)
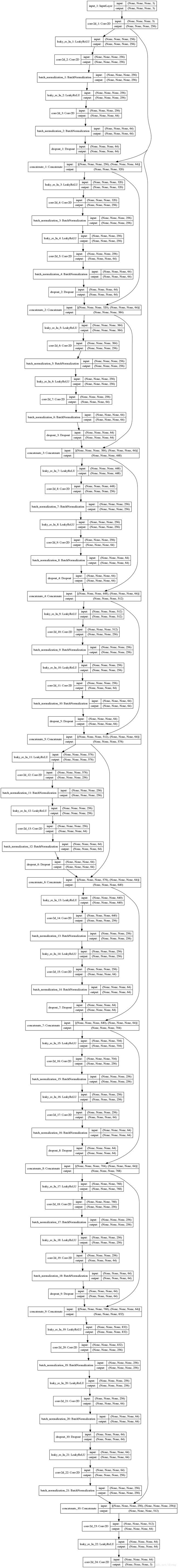
return x网络结构解析:
- 1. 参数包含300万个可训练参数,和近7000个固定参数。
- 2. 输入是彩色图像,第一层卷积核大小是3×3,个数是256个;
- 3. 输入经过一个卷积之后连续接了10个密集连接模块,并且每一个密集连接模块的输出跟下一个密集连接模块的输出组合在一起,作为第三个密集连接模块的输入。密集连接模块的结构图:

每个密集连接模块包含2个Leaky ReLU函数,2个Batch normalization批规范化操作,1个1×1卷积和1个3×3卷积,最后是一个Dropout层。
- 4. 连续加了10个密集连接模块之后的输出经过LR,1×1卷积,BN之后跟第一个密集连接模块的输入一起组合成512个特征图(结构图可见一条线直接拉下来连接到最后),再经过卷积+LR+卷积之后生成一个3个特征图的输出(跟输入维度一致),没有全连接层。
4. 判别器网络
keras实现的判别器网络:
def discriminator_model():
# PatchGAN
inputs = Input(shape=patch_shape)
x = Convolution2D(filters=channel_rate, kernel_size=(3, 3), strides=(2, 2), padding="same")(inputs)
x = BatchNormalization()(x)
x = LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2)(x)
x = Convolution2D(filters=2 * channel_rate, kernel_size=(3, 3), strides=(2, 2), padding="same")(x)
x = BatchNormalization()(x)
x = LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2)(x)
x = Convolution2D(filters=4 * channel_rate, kernel_size=(3, 3), strides=(2, 2), padding="same")(x)
x = BatchNormalization()(x)
x = LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2)(x)
x = Convolution2D(filters=4 * channel_rate, kernel_size=(3, 3), strides=(2, 2), padding="same")(x)
x = BatchNormalization()(x)
x = LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2)(x)
x = Flatten()(x)
outputs = Dense(units=1, activation='sigmoid')(x)
model = Model(inputs=inputs, outputs=outputs, name='PatchGAN')
# model.summary()
# discriminator
inputs = Input(shape=image_shape)
list_row_idx = [(i * channel_rate, (i + 1) * channel_rate) for i in
range(int(image_shape[0] / patch_shape[0]))]
list_col_idx = [(i * channel_rate, (i + 1) * channel_rate) for i in
range(int(image_shape[1] / patch_shape[1]))]
list_patch = []
for row_idx in list_row_idx:
for col_idx in list_col_idx:
x_patch = Lambda(lambda z: z[:, row_idx[0]:row_idx[1], col_idx[0]:col_idx[1], :])(inputs)
list_patch.append(x_patch)
x = [model(patch) for patch in list_patch]
outputs = Average()(x)
model = Model(inputs=inputs, outputs=outputs, name='Discriminator')
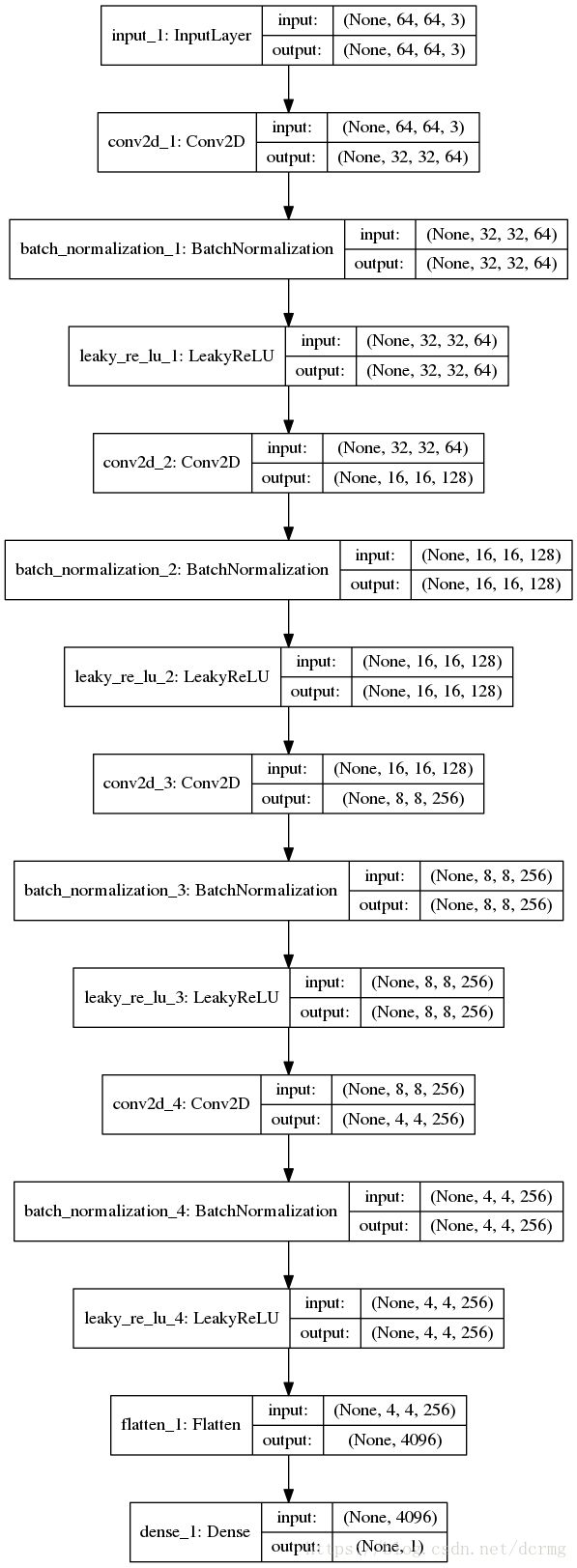
return model- 1. 参数包含96万个可训练参数,1400个固定参数。
- 2. 输入是大小是256×256的彩色图像。
- 3. 判别器网络的第二层并列包含16个卷积模块,每个模块都会把图像压缩到64×64大小。这16个模块的输出又会分别作为PatchGAN模块的输入, 得到16个输入。
PatchGAN模块输入是大小64×64的彩色图像,主要包含4个卷积,4个BN层,4个Leaky reLU层,倒数第二层是一个Flatten层,用来将输入拉伸成一维的,维度是4096,常用在从卷积层到全连接层的过渡。
最后一层是一个全连接层,输出是一维的,即对输入图像是真实图像的判定值,范围是[0,1]。这里是使用keras中的Dense函数实现。
- 4. 网络的最后是把16个模块的输出进行平均,得到最后的图像是否是真实图像的判定值,范围[0,1]
5. 生成器和判别器构成的整体GAN结构
整体上的GAN结构输入是256×256×3,经过生成器之后,再把生成的图像输入给判别器,得到预判值。结构如下: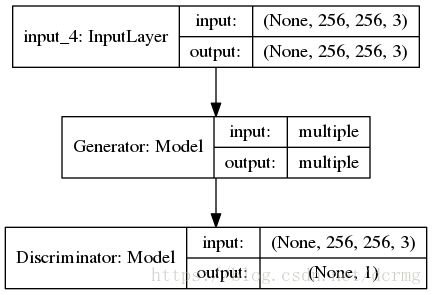
6. 生成器G的损失函数
keras实现的生成器损失函数:
def l1_loss(y_true, y_pred):
return K.mean(K.abs(y_pred - y_true))
def perceptual_loss(y_true, y_pred):
vgg = VGG16(include_top=False, weights='imagenet', input_shape=image_shape)
loss_model = Model(inputs=vgg.input, outputs=vgg.get_layer('block3_conv3').output)
# let the loss model can't be trained
loss_model.trainable = False
# loss_model.summary()
return K.mean(K.square(loss_model(y_true) - loss_model(y_pred)))
def generator_loss(y_true, y_pred,K_1=145, K_2=170):
return K_1 * perceptual_loss(y_true, y_pred) + K_2 * l1_loss(y_true, y_pred)包含两部分,通过K_1和K_2参数调整两者的比例。
第一部分是感知损失,使用的是VGG16网络的前三个卷积层组成的网络(网络参数固定使用预训练好的VGG参数,不可训练),求真实图像和生成图像在这个网络上的两个输出的均方误差损失。取K_1为145。
第二部分是L1损失,求的是真实图像和生成图像的平均绝对值误差损失。取K_2为170。
7. 判别器D的损失函数
判别器D的损失函数使用对数损失函数(logarithmic loss)
8. 整体GAN结构的损失函数
keras实现的整体GAN损失函数:
def adversarial_loss(y_true, y_pred):
return -K.log(y_pred)自然对数损失。
9.训练流程
- 1. 按batch_size大小获得训练清晰图片和模糊图片
- 2. 使用模糊图片+生成器网络生成目标清晰图片
- 3. 根据真实清晰图片和生成的清晰图片求判别器的损失,之后固定判别器,使判别器参数不能更新
- 4. 分别求GAN整体网络loss和生成器loss
- 5. 设判别器trainable=True,使判别器可以训练
10. 训练效果示意
以下展示的是第1轮、第4轮、第10轮的训练效果(并排的3张图,第一张是清晰图,第二张是模糊图,第三张是生成的去模糊图):