golang 调度学习-综述
综述
本文将会描述golang调度的大致方式,并介绍后文中将会用到的一些数据结构,及实现原理
注:
这本是给自己学习用的笔记,其中包含一些网上大牛的资料节选片段,也忘了出处,求海涵。大佬不愿意可以联系删除谢谢。
主要参考:《go语言学习笔记》
线程模型
一般多线程会有以下几种线程模型:
- 线程模型内核级线程模型(KSE(Kernel Scheduling Entity))
关键点: 完全靠操作系统调度
每一个用户线程绑定一个实际的内核线程,而线程的调度则完全交付给操作系统内核去做,应用程序对线程的创建、终止以及同步都基于内核提供的系统调用来完成。这个模型能够利用机器上的所有核心的优势,但是上下文切换非常慢,因为它不得不陷入OS(trap through the OS) - 用户级线程模型
关键点: 完全靠自己调度
用户线程与内核线程KSE是多对一(N : 1)的映射模型,多个用户线程的一般从属于单个进程的调度是由用户自己的线程库来完成,线程的创建、销毁以及多线程之间的协调等操作都是由用户自己的线程库来负责而无须借助系统调用来实现。操作系统只知道用户进程而对其中的线程是无感知的,内核的所有调度都是基于用户进程。这个模型可以很快的进行上下文切换,但是不能利用多核系统(multi-core systems)的优势 - 两级(混合型)线程模型
关键点: 自身调度与系统调度协同工作
用户线程与内核KSE是多对多(N : M)的映射模型。首先,区别于用户级线程模型,两级线程模型中的一个进程可以与多个内核线程KSE关联,于是进程内的多个线程可以绑定不同的KSE,这点和内核级线程模型相似;
其次,又区别于内核级线程模型,它的进程里的所有线程并不与KSE一一绑定,而是可以动态绑定不同KSE, 当某个KSE因为其绑定的线程的阻塞操作被内核调度出CPU时,其关联的进程中其余用户线程可以重新与其他KSE绑定运行
Go采用方案:采用两级(混合型)线程模型,通过M:N的调度器去获取这两个世界的全部优势,在任意数目的OS线程上调用任意数目的goroutines。
- 优点:可以快速进行上下文切换,并且还能利用你系统上所有的核心的优势;可以方便实现STW(stop the world, gc扫描和标记阶段)机制。
- 缺点:增加了调度器的复杂性。
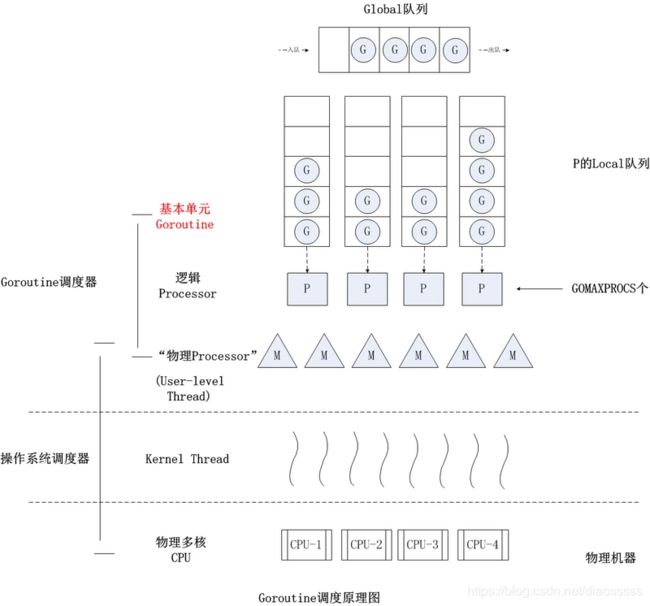
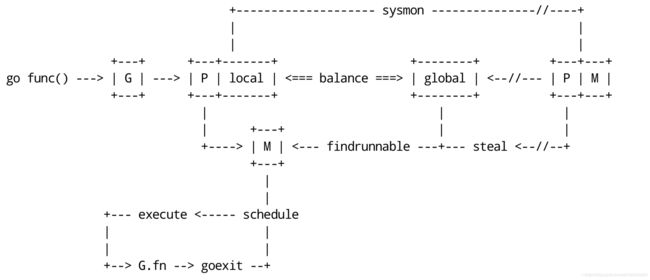
golang G-P-M 模型
结合两个图我们可以分析出几个结论:
- 我们通过 go func()来创建一个goroutine;
- 有两个存储goroutine的队列,一个是局部调度器P的local queue(当p绑定的时候m的时候,可以无锁分配内存和无锁访问任务队列)、一个是全局调度器数据模型schedt的global queue。新创建的goroutine会先保存在local queue,如果local queue已经满了就会保存在全局的global queue;
- goroutine只能运行在M中,一个M必须持有一个P,M与P是1:1的关系。M会从P的local queue弹出一个Runable状态的goroutine来执行,如果P的local queue为空,就会执行work stealing;
- 一个M调度goroutine执行的过程是一个loop;
- 当M执行某一个goroutine时候如果发生了syscall或则其余阻塞操作,M会阻塞,如果当前有一些G在执行,runtime会把这个线程M从P中摘除(detach),然后再创建一个新的操作系统的线程(如果有空闲的线程可用就复用空闲线程)来服务于这个P;
- 当系统调用结束时候,这个goroutine会尝试获取一个空闲的P执行,并放入到这个P的local queue。如果获取不到P,那么这个线程M会park它自己(休眠), 加入到空闲线程中,然后这个goroutine会被放入schedt的global queue。
GPM简介(具体结构见下文数据结构):
-
M(Machine)
OS线程抽象,代表着真正执行计算的资源, 每一个goroutine实际上就是在M中执行,M的数量目前最多10000个。
M与P绑定,调度循环的执行G并发任务。M通过修改寄存器,将执行栈指向G自带的栈内存,并在此空间内分配堆栈帧,执行任务函数。中途切换时,将寄存器值保存回G的空间即可维持状态,任何M都可以恢复。线程只负责执行,不保存状态,这是并发任务跨线程调度,实现多路复用的根本所在 -
P(Processor)
分配程序执行的上下文环境, 数量<=内核数量, 即同时能够并行执行的G的数量,相对于G而言, P的角色相当于CPU,每个工作线程必须绑定一个p才能正常运行,否则只能休眠,等待空闲的p,然后被唤醒。
p为线程提供了执行资源,如对象分配内存,本地任务队列等。线程独享p资源,可以无锁操作。G程序代码中的每一次使用关键字go执行函数其实都生成了一个G,并将之加入到本地的G队列中, 之后M会生成G执行的上下文也就是绑定P来执行函数。
p控制了程序的并行度,如果还有一个p,那么同时只能执行一个任务,可以通过GOMAXPROCS设置p的个数 -
G(Goroutine)
维护者goroutine需要的栈、程序计数器以及它所在的M等信息。基本上进程的一切都在g上运行。g并非执行体,它仅仅保存并发任务状态,为人物提供所需要的栈空间。g创建成功后放在p的本地队列或者全局队列,等待调度
基本数据结构
下文介绍调度其中会使用到的部分基本数据结构,源码中的数据结构在runtime包中的runtime2.go中
stack
stack 描述了Go执行堆栈。堆栈的边界正好是 [lo,hi),两边都没有隐式数据结构。
type stack struct {
lo uintptr
hi uintptr
}
gobuf
g 的运行现场,创建时初始化,用来保存g当前的运行状况,g被抢占是会保存当前现场,下次调度的时候从这里恢复
type gobuf struct {
sp uintptr // sp 寄存器
pc uintptr // pc 寄存器
g guintptr // g 指针
ctxt unsafe.Pointer // 这个似乎是用来辅助 gc 的
ret sys.Uintreg
lr uintptr // 这是在 arm 上用的寄存器,不用关心
bp uintptr // 开启 GOEXPERIMENT=framepointer,才会有这个
}
g
type g struct {
stack stack // 简单数据结构,lo 和 hi 成员描述了栈的下界和上界内存地址,详细见上方stack结构
// 在函数的栈增长 prologue 中用 sp 寄存器和 stackguard0 来做比较
// 如果 sp 比 stackguard0 小(因为栈向低地址方向增长),那么就触发栈拷贝和调度
// 正常情况下 stackguard0 = stack.lo + StackGuard
// 不过 stackguard0 在需要进行调度时,会被修改为 StackPreempt
// 以触发抢占s
stackguard0 uintptr
// stackguard1 是在 C 栈增长 prologue 作对比的对象
// 在 g0 和 gsignal 栈上,其值为 stack.lo+StackGuard
// 在其它的栈上这个值是 ~0(按 0 取反)以触发 morestack 调用(并 crash)
stackguard1 uintptr
_panic *_panic // innermost panic - offset known to liblink
_defer *_defer // innermost defer
m *m // 当前的g绑定的m
sched gobuf // goroutine切换时,用于保存g的上下文
syscallsp uintptr // if status==Gsyscall, syscallsp = sched.sp to use during gc
syscallpc uintptr // if status==Gsyscall, syscallpc = sched.pc to use during gc
stktopsp uintptr // expected sp at top of stack, to check in traceback
param unsafe.Pointer // 用于传递参数,睡眠时其他goroutine可以设置param,唤醒时该goroutine可以获取
atomicstatus uint32
stackLock uint32 // sigprof/scang lock; TODO: fold in to atomicstatus
goid int64 // 唯一的goroutine的ID
waitsince int64// g被阻塞的大体时间
waitreason string // if status==Gwaiting
schedlink guintptr
preempt bool // 抢占标记,这个为 true 时,stackguard0 是等于 stackpreempt 的
paniconfault bool // panic (instead of crash) on unexpected fault address
preemptscan bool // preempted g does scan for gc
gcscandone bool // g has scanned stack; protected by _Gscan bit in status
gcscanvalid bool // false at start of gc cycle, true if G has not run since last scan; TODO: remove?
throwsplit bool // must not split stack
raceignore int8 // ignore race detection events
sysblocktraced bool // StartTrace has emitted EvGoInSyscall about this goroutine
sysexitticks int64 // cputicks when syscall has returned (for tracing)
traceseq uint64 // trace event sequencer
tracelastp puintptr // last P emitted an event for this goroutine
lockedm muintptr// 如果调用了 LockOsThread,那么这个 g 会绑定到某个 m 上,只会在这个m上执行
sig uint32
writebuf []byte
sigcode0 uintptr
sigcode1 uintptr
sigpc uintptr
gopc uintptr //创建该 goroutine 的语句的指令地址, 调用者的 PC/IP
startpc uintptr // goroutine 函数的指令地址
racectx uintptr
waiting *sudog // sudog structures this g is waiting on (that have a valid elem ptr); in lock order
cgoCtxt []uintptr // cgo traceback context
labels unsafe.Pointer // profiler labels
timer *timer // time.Sleep 缓存的定时器
selectDone uint32 // 该 g 是否正在参与 select,是否已经有人从 select 中胜出
gcAssistBytes int64
}
G里面比较重要的成员如下
- stack: 当前g使用的栈空间, 有lo和hi两个成员
- stackguard0: 检查栈空间是否足够的值, 低于这个值会扩张栈, 0是go代码使用的
- stackguard1: 检查栈空间是否足够的值, 低于这个值会扩张栈, 1是原生代码使用的
- m: 当前g对应的m
- sched: g的调度数据, 当g中断时会保存当前的pc和rsp等值到这里, 恢复运行时会使用这里的值
- atomicstatus: g的当前状态
- schedlink: 下一个g, 当g在链表结构中会使用
- preempt: g是否被抢占中
- lockedm: g是否要求要回到这个M执行, 有的时候g中断了恢复会要求使用原来的M执行
G的状态:
- 空闲中(_Gidle): 表示G刚刚新建, 仍未初始化
- 待运行(_Grunnable): 表示G在运行队列中, 等待M取出并运行
- 运行中(_Grunning): 表示M正在运行这个G, 这时候M会拥有一个P
- 系统调用中(_Gsyscall): 表示M正在运行这个G发起的系统调用, 这时候M并不拥有P
- 等待中(_Gwaiting): 表示G在等待某些条件完成, 这时候G不在运行也不在运行队列中(可能在channel的等待队列中)
- 已中止(_Gdead): 表示G未被使用, 可能已执行完毕(并在freelist中等待下次复用)
- 栈复制中(_Gcopystack): 表示G正在获取一个新的栈空间并把原来的内容复制过去(用于防止GC扫描)
sudog
当 g 遇到阻塞,或需要等待的场景时,会被打包成 sudog 这样一个结构。一个 g 可能被打包为多个 sudog 分别挂在不同的等待队列上:
// sudog 代表在等待列表里的 g,比如向 channel 发送/接收内容时
// 之所以需要 sudog 是因为 g 和同步对象之间的关系是多对多的
// 一个 g 可能会在多个等待队列中,所以一个 g 可能被打包为多个 sudog
// 多个 g 也可以等待在同一个同步对象上
// 因此对于一个同步对象就会有很多 sudog 了
// sudog 是从一个特殊的池中进行分配的。用 acquireSudog 和 releaseSudog 来分配和释放 sudog
type sudog struct {
// 之后的这些字段都是被该 g 所挂在的 channel 中的 hchan.lock 来保护的
// shrinkstack depends on
// this for sudogs involved in channel ops.
g *g
// isSelect 表示一个 g 是否正在参与 select 操作
// 所以 g.selectDone 必须用 CAS 来操作,以胜出唤醒的竞争
isSelect bool
next *sudog
prev *sudog
elem unsafe.Pointer
// 下面这些字段则永远都不会被并发访问
// 对于 channel 来说,waitlink 只会被 g 访问
// 对于信号量来说,所有的字段,包括上面的那些字段都只在持有 semaRoot 锁时才可以访问
acquiretime int64
releasetime int64
ticket uint32
parent *sudog // semaRoot binary tree
waitlink *sudog // g.waiting list or semaRoot
waittail *sudog // semaRoot
c *hchan // channel
}
m
线程在 runtime 中的结构,对应一个 pthread,pthread 也会对应唯一的内核线程(task_struct):
type m struct {
g0 *g // 用来执行调度指令的 goroutine
morebuf gobuf // gobuf arg to morestack
divmod uint32 // div/mod denominator for arm - known to liblink
procid uint64 // for debuggers, but offset not hard-coded
gsignal *g // 处理信号的goroutine
goSigStack gsignalStack // Go-allocated signal handling stack
sigmask sigset // storage for saved signal mask
// thread-local storage
tls [6]uintptr // thread-local storage (for x86 extern register)
mstartfn func()
curg *g // 当前运行的用户 goroutine
caughtsig guintptr // goroutine running during fatal signal
// 关联p和执行的go代码
p puintptr // attached p for executing go code (nil if not executing go code)
nextp puintptr
id int64
mallocing int32
throwing int32
preemptoff string // 该字段不等于空字符串的话,要保持 curg 始终在这个 m 上运行
locks int32 // locks表示该M是否被锁的状态,M被锁的状态下该M无法执行gc
softfloat int32
dying int32
profilehz int32
helpgc int32
spinning bool // 是否自旋,自旋就表示M正在找G来运行
blocked bool // m是否被阻塞
inwb bool // m是否在执行写屏蔽
newSigstack bool // minit on C thread called sigaltstack
printlock int8
incgo bool // m在执行cgo吗
freeWait uint32 // if == 0, safe to free g0 and delete m (atomic)
fastrand [2]uint32
needextram bool
traceback uint8
ncgocall uint64 // cgo调用的总数
ncgo int32 // 当前cgo调用的数目
cgoCallersUse uint32 // if non-zero, cgoCallers in use temporarily
cgoCallers *cgoCallers // cgo traceback if crashing in cgo call
park note
alllink *m //用于链接allm
schedlink muintptr
mcache *mcache // 当前m的内存缓存
lockedg guintptr // 锁定g在当前m上执行,而不会切换到其他m,一般cgo调用或者手动调用LockOSThread()才会有值
// thread创建的栈
createstack [32]uintptr // stack that created this thread.
freglo [16]uint32 // d[i] lsb and f[i]
freghi [16]uint32 // d[i] msb and f[i+16]
fflag uint32 // floating point compare flags
// 用户锁定M的标记
lockedExt uint32 // tracking for external LockOSThread
// runtime 内部锁定M的标记
lockedInt uint32 // tracking for internal lockOSThread
nextwaitm muintptr // next m waiting for lock
waitunlockf unsafe.Pointer // todo go func(*g, unsafe.pointer) bool
waitlock unsafe.Pointer
waittraceev byte
waittraceskip int
startingtrace bool
syscalltick uint32
thread uintptr // thread handle
freelink *m // on sched.freem
// these are here because they are too large to be on the stack
// of low-level NOSPLIT functions.
libcall libcall
libcallpc uintptr // for cpu profiler
libcallsp uintptr
libcallg guintptr
syscall libcall // stores syscall parameters on windows
mOS
}
M里面比较重要的成员如下
- g0: 用于调度的特殊g, 调度和执行系统调用时会切换到这个g,避免和
- curg: 当前运行的gp: 当前拥有的P
- nextp: 唤醒M时, M会拥有这个P
- park: M休眠时使用的信号量, 唤醒M时会通过它唤醒
- schedlink: 下一个m, 当m在链表结构中会使用
- mcache: 分配内存时使用的本地分配器, 和p.mcache一样(拥有P时会复制过来)
- lockedg: lockedm的对应值
M并没有像G和P一样的状态标记, 但可以认为一个M有以下的状态:
- 自旋中(spinning): M正在从运行队列获取G, 这时候M会拥有一个P
- 执行go代码中: M正在执行go代码, 这时候M会拥有一个P
- 执行原生代码中: M正在执行原生代码或者阻塞的syscall, 这时M并不拥有P
- 休眠中: M发现无待运行的G时会进入休眠, 并添加到空闲M链表中, 这时M并不拥有P
M可以运行两种代码:
- go代码, 即goroutine, M运行go代码需要一个P(运行常规的g)
- 原生代码, 例如阻塞的syscall, M运行原生代码不需要P(运行在m的go上)
自旋中(spinning)这个状态非常重要, 是否需要唤醒或者创建新的M取决于当前自旋中的M的数量.通常创建一个M的原因是由于没有足够的M来关联P并运行其中可运行的G。而且运行时系统执行系统监控的时候,或者GC的时候也会创建M。
p
抽象数据结构,可以认为是 processor 的抽象,代表了任务执行时的上下文,m 必须获得 p 才能执行:
type p struct {
lock mutex
id int32 // id也是allp的数组下标
status uint32 // one of pidle/prunning/...
link puintptr // 单向链表,指向下一个P的地址
schedtick uint32 // 每调度一次加1
syscalltick uint32 // 每一次系统调用加1
sysmontick sysmontick // 上次 sysmon 观察到的 tick 时间
m muintptr// 回链到关联的m
mcache *mcache
racectx uintptr
deferpool [5][]*_defer // pool of available defer structs of different sizes (see panic.go)
deferpoolbuf [5][32]*_defer
// goroutine的ID的缓存
goidcache uint64
goidcacheend uint64
// runnable 状态的 goroutine。访问时是不加锁的
runqhead uint32
runqtail uint32
runq [256]guintptr
// 下一个运行的g,优先级最高
runnext guintptr
// Available G's (status == Gdead)
gfree *g
gfreecnt int32
sudogcache []*sudog
sudogbuf [128]*sudog
tracebuf traceBufPtr
// traceSweep indicates the sweep events should be traced.
// This is used to defer the sweep start event until a span
// has actually been swept.
traceSweep bool
// traceSwept and traceReclaimed track the number of bytes
// swept and reclaimed by sweeping in the current sweep loop.
traceSwept, traceReclaimed uintptr
palloc persistentAlloc // per-P to avoid mutex
// Per-P GC state
gcAssistTime int64 // Nanoseconds in assistAlloc
gcFractionalMarkTime int64 // Nanoseconds in fractional mark worker
gcBgMarkWorker guintptr
gcMarkWorkerMode gcMarkWorkerMode
// 当前标记 worker 的开始时间,单位纳秒
gcMarkWorkerStartTime int64
// gcw is this P's GC work buffer cache. The work buffer is
// filled by write barriers, drained by mutator assists, and
// disposed on certain GC state transitions.
gcw gcWork
// wbBuf is this P's GC write barrier buffer.
//
// TODO: Consider caching this in the running G.
wbBuf wbBuf
runSafePointFn uint32 // if 1, run sched.safePointFn at next safe point
pad [sys.CacheLineSize]byte
}
P里面比较重要的成员如下
- status: p的当前状态
- link: 下一个p, 当p在链表结构中会使用
- m: 拥有这个P的M
- mcache: 分配内存时使用的本地分配器
- runqhead: 本地运行队列的出队序号
- runqtail: 本地运行队列的入队序号
- runq: 本地运行队列的数组, 可以保存256个G
- gfree: G的自由列表, 保存变为_Gdead后可以复用的G实例
- gcBgMarkWorker: 后台GC的worker函数, 如果它存在M会优先执行它
- gcw: GC的本地工作队列
P的状态
- 空闲中(_Pidle): 当M发现无待运行的G时会进入休眠, 这时M拥有的P会变为空闲并加到空闲P链表中
- 运行中(_Prunning): 当M拥有了一个P后, 这个P的状态就会变为运行中, M运行G会使用这个P中的资源
- 系统调用中(_Psyscall): 当go调用原生代码, 原生代码又反过来调用go代码时, 使用的P会变为此状态
- GC停止中(_Pgcstop): 当gc停止了整个世界(STW)时, P会变为此状态
- 已中止(_Pdead): 当P的数量在运行时改变, 且数量减少时多余的P会变为此状态
schedt
全局调度器,全局只有一个 schedt 类型的实例:
type schedt struct {
// accessed atomically. keep at top to ensure alignment on 32-bit systems.
goidgen uint64
lastpoll uint64
lock mutex
// When increasing nmidle, nmidlelocked, nmsys, or nmfreed, be
// sure to call checkdead().
// idle状态的m
midle muintptr // idle m's waiting for work
// idle状态的m个数
nmidle int32 // number of idle m's waiting for work
// lockde状态的m个数
nmidlelocked int32 // number of locked m's waiting for work
mnext int64 // number of m's that have been created and next M ID
// m允许的最大个数
maxmcount int32 // maximum number of m's allowed (or die)
nmsys int32 // number of system m's not counted for deadlock
nmfreed int64 // cumulative number of freed m's
// 系统中goroutine的数目,会自动更新
ngsys uint32 // number of system goroutines; updated atomically
// idle的p列表
pidle puintptr // idle p's
// 有多少个状态为idle的p
npidle uint32
// 有多少个m自旋
nmspinning uint32 // See "Worker thread parking/unparking" comment in proc.go.
// Global runnable queue.
// 全局的可运行的g队列
runqhead guintptr
runqtail guintptr
// 全局队列的大小
runqsize int32
// Global cache of dead G's.
// dead的G的全局缓存
gflock mutex
gfreeStack *g
gfreeNoStack *g
ngfree int32
// Central cache of sudog structs.
// sudog的缓存中心
sudoglock mutex
sudogcache *sudog
// Central pool of available defer structs of different sizes.
deferlock mutex
deferpool [5]*_defer
// freem is the list of m's waiting to be freed when their
// m.exited is set. Linked through m.freelink.
freem *m
gcwaiting uint32 // gc is waiting to run
stopwait int32
stopnote note
sysmonwait uint32
sysmonnote note
// safepointFn should be called on each P at the next GC
// safepoint if p.runSafePointFn is set.
safePointFn func(*p)
safePointWait int32
safePointNote note
profilehz int32 // cpu profiling rate
procresizetime int64 // nanotime() of last change to gomaxprocs
totaltime int64 // ∫gomaxprocs dt up to procresizetime
}