Dagger2在MVP中的应用
转载说明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/a15286856575/article/details/53405630
需要基础
- Dagger2
- MVP
建议把基础学会再看下面文章好理解点。
为什么MVP中要用Dagger2?
我们首先看一下传统的mvp有什么缺点?
-
presenter在Activity的耦合
我们知道在传统的MVP中Preseter是在Activity中初始化的,也就是显式的new了一个对象,那么这里面在这个Activity中就有了耦合在里面。为什么会有耦合呢?
- 场景1: 假如你的项目中多次用到了这个Presetner,现在有这么个需求,这个Presenter依赖某个对象,需要在构造方法中传入这个对象,我们是不是要找到所有找到所有初始化这个Presenter的对象,然后去修改它,小项目还可以如果是大项目,我们是不是要找到所有的去修改。这就产生了耦合。怎么解决?Daggger2是个依赖注入框架,当前的Activity不用关心Presenter,是怎么创建的,具体的创建交给module.我们只需要修改module. .
- 场景2:假如Presenter需要对象A,对象A需要对象B,对象B需要对象C,我们是不是先C c= new B(),B b = new B(c),A a = new A(B) 然后在初始化Presenter。像这种情况,我们是不是每次都需要这样写,在Activity中还要关系他们的创建顺序。很繁琐,用Dagger2就可以解决这个问题。我们通过依赖注入,注入我们需要的对象,就大功告成了。
-
model在Presenter中的耦合
传统的的mvp中的model是在Presenter中进行初始化的,这里面也是显示的new了一个对象。同样也会有一个耦合在里面。
- 场景1:多个Presenter用了同一个model类,有同样的需求,model需要传入一个对象,我们是不是要找到用了这个model的所有Presenter,一个一个修改。里面是不是有耦合。同样我们可以通过dagger2注入model,在dagger2的module修改这个model就行了。
- 场景2:初始化一个Model,需要对象A,对象A需要对象B,对象B需要对象C,我们是不是先C c= new B(),B b = new B(c),A a = new A(B),然后初始化Model。我们在对model进行重用的时候,每次都要这样做很繁琐,通过dagger2中提供的创建的Module,我们可以注入这个model,是不是很省事。
注意module是Dagger2中的,model是mvp中的
当然Dagger2不仅仅局限于MVP,在有耦合的地方都可以用。
Dagger2在MVP中的具体实现
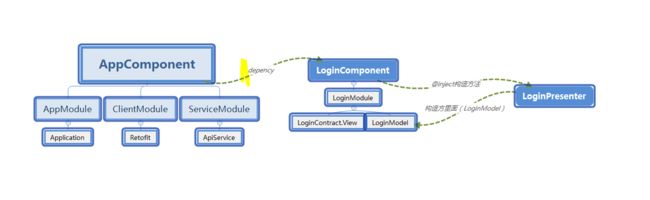
架构思路:对于上面两种情况。他们可以有同一个Module提供,那我们就可以有一套依赖体系实现,例如登录,我们LoginModule提供Presenter和Model,LoginComponent负责注入,就行了。但是我们还需要一个全局的AppModule,提供OkHttpClient ,Sevivce,Retofit。然后让LoginComponent依赖他就行了。那么我们在LoginComponent,就能够拿到所有的Module.如图:
我们需要两个Component:
AppComponent
AppCompponet是在Applcation中初始化的所有是个全局的Component代码如下
@Singleton
@Component(modules = {AppModule.class, ClientModule.class, ServiceModule.class})
public interface AppComponent {
Application Application();
ApiService apiService();
}
这个组件相当于工厂管理员,他管理着AppModule,ClentModule,ServiceModule
通过他我们能找到这些Module所提供的实例。如果在其他Component依赖此Component,我们有需要那些module所提供的实例,那么我们就需要在AppComponent暴露这些对象,在这里我们暴露了Application ApiService;
- AppModule 主要提供Application对象。
@Module
public class AppModule {
private Application mApplication;
public AppModule(Application application) {
this.mApplication = application;
}
@Singleton
@Provides
public Application provideApplication() {
return mApplication;
}
@Singleton
@Provides
public Gson provideGson(){return new Gson();}
}
- ClientModule 主要提供Retofit对象.其中包括了配置我们需要的Retofit
@Module
public class ClientModule {
private static final int TOME_OUT = 10;
public static final int HTTP_RESPONSE_DISK_CACHE_MAX_SIZE = 10 * 1024 * 1024;//缓存文件最大值为10Mb
private HttpUrl mApiUrl;
private GlobeHttpHandler mHandler;
private Interceptor[] mInterceptors;
/**
* @author: jess
* @date 8/5/16 11:03 AM
* @description: 设置baseurl
*/
private ClientModule(Buidler buidler) {
this.mApiUrl = buidler.apiUrl;
this.mHandler = buidler.handler;
this.mInterceptors = buidler.interceptors;
}
public static Buidler buidler() {
return new Buidler();
}
/**
* @param cache 缓存
* @param intercept 拦截器
* @return
* @author: jess
* @date 8/30/16 1:12 PM
* @description:提供OkhttpClient
*/
@Singleton
@Provides
OkHttpClient provideClient(Cache cache, Interceptor intercept) {
final OkHttpClient.Builder okHttpClient = new OkHttpClient.Builder();
return configureClient(okHttpClient, cache, intercept);
}
/**
* @param client
* @param httpUrl
* @return
* @author: jess
* @date 8/30/16 1:13 PM
* @description: 提供retrofit
*/
@Singleton
@Provides
Retrofit provideRetrofit(OkHttpClient client, HttpUrl httpUrl) {
final Retrofit.Builder builder = new Retrofit.Builder();
return configureRetrofit(builder, client, httpUrl);
}
@Singleton
@Provides
HttpUrl provideBaseUrl() {
return mApiUrl;
}
/**
* @param builder
* @param client
* @param httpUrl
* @return
* @author: jess
* @date 8/30/16 1:15 PM
* @description:配置retrofit
*/
private Retrofit configureRetrofit(Retrofit.Builder builder, OkHttpClient client, HttpUrl httpUrl) {
return builder
.baseUrl(httpUrl)//域名
.client(client)//设置okhttp
.addCallAdapterFactory(RxJavaCallAdapterFactory.create())//使用rxjava
.addConverterFactory(GsonConverterFactory.create())//使用Gson
.build();
}
@Singleton
@Provides
Cache provideCache(File cacheFile) {
return new Cache(cacheFile, HTTP_RESPONSE_DISK_CACHE_MAX_SIZE);//设置缓存路径和大小
}
/**
* 提供缓存地址
*/
@Singleton
@Provides
File provideCacheFile(Application application) {
return DataHelper.getCacheFile(application);
}
@Singleton
@Provides
Interceptor provideIntercept() {
return new RequestIntercept(mHandler);//打印请求信息的拦截器
}
/**
* 配置okhttpclient
*
* @param okHttpClient
* @return
*/
private OkHttpClient configureClient(OkHttpClient.Builder okHttpClient, Cache cache, Interceptor intercept) {
OkHttpClient.Builder builder = okHttpClient
.connectTimeout(TOME_OUT, TimeUnit.SECONDS)
.readTimeout(TOME_OUT, TimeUnit.SECONDS)
.cache(cache)//设置缓存
.addNetworkInterceptor(intercept);
if (mInterceptors != null && mInterceptors.length > 0) {//如果外部提供了interceptor的数组则遍历添加
for (Interceptor interceptor : mInterceptors) {
builder.addInterceptor(interceptor);
}
}
return builder
.build();
}
public static final class Buidler {
private HttpUrl apiUrl = HttpUrl.parse("https://api.github.com/");
private GlobeHttpHandler handler;
private Interceptor[] interceptors;
private Buidler() {
}
public Buidler baseurl(String baseurl) {//基础url
if (TextUtils.isEmpty(baseurl)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("baseurl can not be empty");
}
this.apiUrl = HttpUrl.parse(baseurl);
return this;
}
public Buidler globeHttpHandler(GlobeHttpHandler handler) {//用来处理http响应结果
this.handler = handler;
return this;
}
public Buidler interceptors(Interceptor[] interceptors) {//动态添加任意个interceptor
this.interceptors = interceptors;
return this;
}
public ClientModule build() {
if (apiUrl == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("baseurl is required");
}
return new ClientModule(this);
}
}
}
在ClientModule中我们找到了一个加了@providers注解返为Retofit的方法
@Singleton
@Provides
Retrofit provideRetrofit(OkHttpClient client, HttpUrl httpUrl) {
final Retrofit.Builder builder = new Retrofit.Builder();
return configureRetrofit(builder, client, httpUrl);
}
里面需要传入OkHttpClient,HttpUrl对象。他们是怎么初始化的呢。在当前的ClientModule我们又发现了
@Singleton
@Provides
OkHttpClient provideClient(Cache cache, Interceptor intercept) {
final OkHttpClient.Builder okHttpClient = new OkHttpClient.Builder();
return configureClient(okHttpClient, cache, intercept);
}
@Singleton
@Provides
HttpUrl provideBaseUrl() {
return mApiUrl;
}
里面待参数的依次查找完成初始化工作,这里就不写了
- ServiceModule 主要是提供ApiSevice对象
@Module
public class ServiceModule {
@Singleton
@Provides
ApiService provideCommonService(Retrofit retrofit) {
return retrofit.create(ApiService.class);
}
}
ApiService初始化需要一个Retofit,这个Retrofit是有
- AppComponent初始化
既然AppComponent是个全局的组件那我们就需要在Applcation中进行初始化的工作,那么它的生命周期就和Application一样长
首先是BaseApplication
public abstract class BaseApplication extends Application {
static private BaseApplication mApplication;
public LinkedList mActivityList;
private ClientModule mClientModule;
private AppModule mAppModule;
private ServiceModule serviceModule;
protected final String TAG = this.getClass().getSimpleName();
@Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
mApplication = this;
this.mClientModule = ClientModule//用于提供okhttp和retrofit的单列
.buidler()
.baseurl(getBaseUrl())
.globeHttpHandler(getHttpHandler())
.interceptors(getInterceptors())
.build();
this.mAppModule = new AppModule(this);//提供application
this.serviceModule = new ServiceModule();
}
/**
* 提供基础url给retrofit
*
* @return
*/
protected abstract String getBaseUrl();
public ServiceModule getServiceModule() {
return serviceModule;
}
public ClientModule getClientModule() {
return mClientModule;
}
public AppModule getAppModule() {
return mAppModule;
}
/**
* 这里可以提供一个全局处理http响应结果的处理类,
* 这里可以比客户端提前一步拿到服务器返回的结果,可以做一些操作,比如token超时,重新获取
* 默认不实现,如果有需求可以重写此方法
*
* @return
*/
protected GlobeHttpHandler getHttpHandler() {
return null;
}
/**
* 用来提供interceptor,如果要提供额外的interceptor可以让子application实现此方法
*
* @return
*/
protected Interceptor[] getInterceptors() {
return null;
}
/**
* 返回上下文
*
* @return
*/
public static Context getContext() {
return mApplication;
}
}
我们的Application:App
public class App extends BaseApplication{
private AppComponent appComponent;
@Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
appComponent = DaggerAppComponent.builder().clientModule(getClientModule()).appModule(getAppModule()).serviceModule(getServiceModule()).build();
}
@Override
protected String getBaseUrl() {
return API.BASE_URL;
}
public AppComponent getAppComponent() {
return appComponent;
}
}
在这里我们完成了AppComponent的初始化工作。从这我们可以看出App我们可以通过getAppComponent拿到AppComponent;
LoginComponent
@ActivityScope
@Component(modules = LoginModule.class,dependencies = AppComponent.class)
public interface LoginComponent {
public void inject(MainActivity activity);
}
此组件是Login的工厂管理员,从图上可以看出,它不但管理着LoginModule,而且还依赖AppComponent,就是说他能够提供 Application,ApiService,loginModel,LoginContract.View(这个是通过构造方法传进来的),从而完成LoginPresenter的注入。当然我们是通过@inject构造方法注入的。不懂的请看dagger2的几种注入方式。
- LoginModule
注意其是dagger2中的Module,这是重点,从图中可以看出它提供了View和model,看代码,初始化过程是LoginContract使我们通过构造方法传入过来的,而ApiService是有上个AppCompoent提供。然后就完成了LoginContract.Model的初始化。
@Module
public class LoginModule {
private LoginContract.View view;
public LoginModule(LoginContract.View view) {
this.view = view;
}
@ActivityScope
@Provides
LoginContract.View providerContract() {
return view;
}
@ActivityScope
@Provides
LoginContract.Model providerModel(ApiService service){
return new LoginModel(service);
}
}
- LoginModel
注意其是我们MVP中的Model,我们首先分析下,在loginModel中我们要联网请求,必然需要ApiService,而ApiSevice,是不是我们在ServiceModule,中是不是已经初始化好了,拿来用就好了。代码如下:
BaseModel
public class BaseModel {
public BaseModel() {
}
private ApiService apiService;
public BaseModel(ApiService apiService) {
this.apiService = apiService;
}
public ApiService getApiService() {
return apiService;
}
}
LoginModel
public class LoginModel extends BaseModel implements LoginContract.Model {
public LoginModel(ApiService service) {
super(service);
}
@Override
public Observable<_User.LoginResult> login(String name, String password) {
_User user = new _User();
user.setUsername(name);
user.setPassword(password);
return getApiService().login(user).compose(RxsRxSchedulers.<_User.LoginResult>io_main());
}
}
我们需要ApiService进行联网请求,所以我们要传进来一个ApiService对象。在LoginModule中我们初始化了这个LoginModel.
-
LoginPresenter
首先是BasePresenter
public class BasePresenter implements Ipresenter {
protected final String TAG = this.getClass().getSimpleName();
protected M mModel;
protected V mView;
public BasePresenter() {
}
public BasePresenter(M model, V mView) {
this.mModel = model;
this.mView = mView;
onStart();
}
public M getmModel() {
return mModel;
}
public V getmView() {
return mView;
}
public BasePresenter(V rootView) {
this.mView = rootView;
onStart();
}
public void onStart() {
}
LoginPresenter
@ActivityScope
public class LoginPresenter extends BasePresenter {
@Inject
public LoginPresenter(LoginContract.Model model, LoginContract.View mView) {
super(model, mView);
}
public void login(String name, String password){
getmModel().login(name,password).subscribe(new Action1<_User.LoginResult>() {
@Override
public void call(_User.LoginResult loginResult) {
Log.e(TAG, "call() called with: loginResult = [" + loginResult + "]");
getmView().loginSucess();
}
}, new Action1() {
@Override
public void call(Throwable throwable) {
Log.e(TAG, "call() called with: throwable = [" + throwable + "]");
getmView().loginFailed();
}
});
}
}
我们看到我们通过@inject构造方法完成LoginPresenter的初始化操作。LoginPresenter是怎样初始化的呢?当初始化该构造方法的时候里面有两个参数LoginContract.Model 和LoginContract.View,我们知道这两个参数初始化在LoginModule完成的也就完成了LoginPresenter的初始化。
- MainActivity
目标类也就是我们要注入的目的地
首先看BaseActivity
public abstract class BaseActiviy extends AppCompatActivity{
@Inject
protected p mPresenter;
private App application;
@Override
protected void onCreate(@Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
application = ((App) getApplication());
setContentView(getContentViewId());
componentInject(application.getAppComponent());//依赖注入
initData();
}
protected abstract void componentInject(AppComponent appComponent);
componentInject(AppComponent appComponent)方法传入了我们需要的AppComponent;
MainActivity
初始化
@Override
protected void componentInject(AppComponent appComponent) {
DaggerLoginComponent.builder().appComponent(appComponent).loginModule(new LoginModule(this)).build().inject(this);
}
在此方法中完成了LoginComponent的初始化,并注入目标类中。
具体注入过程
首先是在BaseActivity中的 @Inject
protected p mPresenter;此时会在LoginModule中查找对应的LoginPresenter,没有的话会从查找对应的构造方法,我们这里没有所有知道了加了@inject注释的构造方法。找到
@Inject
public LoginPresenter(LoginContract.Model model, LoginContract.View mView) {
super(model, mView);
}
构造方法里面面有两个参数LoginContract.Model,LoginContract.View,那就初始化这两个对象也就知道了LoginModule
- 在LoginModule中我们看到LoginContract.View 是我们通过构造方法传进来的,我们在初始化LoginComponent的时候
DaggerLoginComponent.builder().appComponent(appComponent).loginModule(new LoginModule(this)).build().inject(this);
new LoginModule(this))传进来了这个this就是我们的Activity也就是我们的View.对于LoginContract.Model我们发现提供这个对象的方法里面有个参数是ApiService,那么它在哪里初始化的呢?我们发现在我们的LoginComponent依赖于AppComponet,而AppComponent暴露了APiService对象,我们也就查找到了ServiceModule.
- 在ServiceModule中我们发现其提供了一个返回值为ApiServce的方法,里面需要传入Retorfit对象。这个对象在哪里初始化的呢,因为AppComponent管理着ServiceModule,ClientModule,我们发现了ClientModule提供了Retofit对象。
- 在ClientModule中我们找到了一个加了@providers注解返为Retofit的方法
@Singleton
@Provides
Retrofit provideRetrofit(OkHttpClient client, HttpUrl httpUrl) {
final Retrofit.Builder builder = new Retrofit.Builder();
return configureRetrofit(builder, client, httpUrl);
}
里面需要传入OkHttpClient,HttpUrl对象。他们是怎么初始化的呢。在当前的ClientModule我们又发现了
@Singleton
@Provides
OkHttpClient provideClient(Cache cache, Interceptor intercept) {
final OkHttpClient.Builder okHttpClient = new OkHttpClient.Builder();
return configureClient(okHttpClient, cache, intercept);
}
@Singleton
@Provides
HttpUrl provideBaseUrl() {
return mApiUrl;
}
里面待参数的依次查找完成初始化工作,这里就不写了。基本就完成了所有的注入过程,其他没写到的请大家见谅。
当然这些工作不是我们做的是有Dagger2自动生成代码完成的,想要知道原理的可以看前面基础部分的原理。
源码传入门