在前面两篇MD系列的文章中,通过两个案例基本上能够掌握了CoordinatorLayout与AppBarLayout的配合使用。本文我们回过头来详细聊聊AppBarLayout的ScrollFlags属性,了解一下不同值之间的区别。至此,Android Material Design系列的学习已进行到第七篇,大家可以点击以下链接查看之前的文章:
- Android TabLayout 分分钟打造一个滑动标签页
- Android 一文告诉你到底是用Dialog,Snackbar,还是Toast
- Android FloatingActionButton 重要的操作不要太多,一个就好
- Android 初识AppBarLayout 和 CoordinatorLayout
- Android CoordinatorLayout实战案例学习《一》
- Android CoordinatorLayout 实战案例学习《二》
ScrollFlags共有五种常量值供AppBarLayout的Children View使用,在xml布局文件中通过app:layout_scrollFlags设置,对应的值为:scroll,enterAlways,enterAlwaysCollapsed,snap,exitUntilCollapsed;也可以在代码中通过setScrollFlags(int)方法使用,比如:
Toolbar toolbar = ... // your toolbar within an AppBarLayout
AppBarLayout.LayoutParams params =
(AppBarLayout.LayoutParams) toolbar.getLayoutParams();
params.setScrollFlags(AppBarLayout.LayoutParams.SCROLL_FLAG_SCROLL
| AppBarLayout.LayoutParams.SCROLL_FLAG_ENTER_ALWAYS);
下面我们通过官网介绍、XML代码和对应的效果图分别分析这五种值的使用(备注:代码中设置也一样,不再赘述):
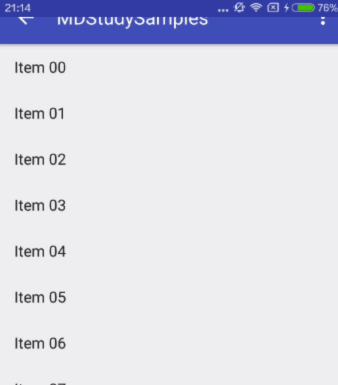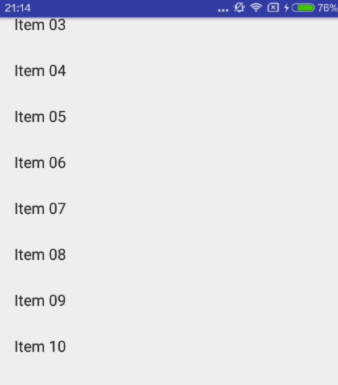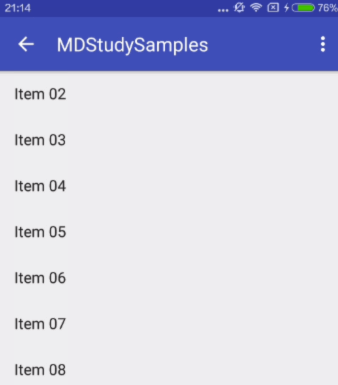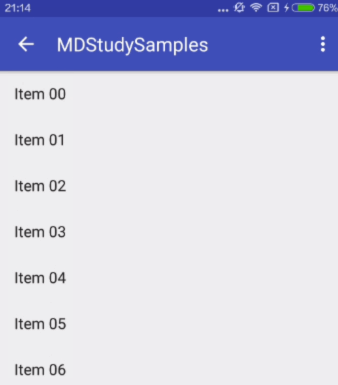
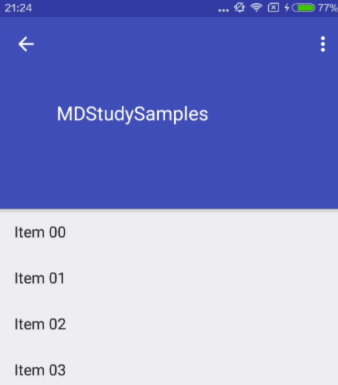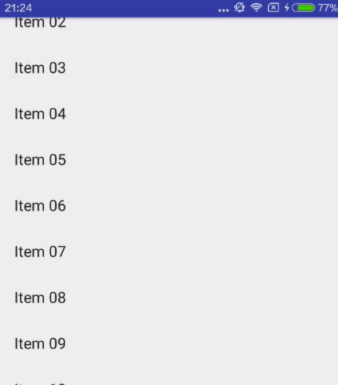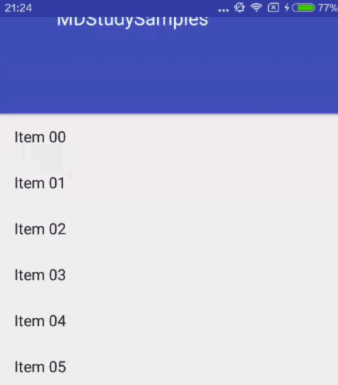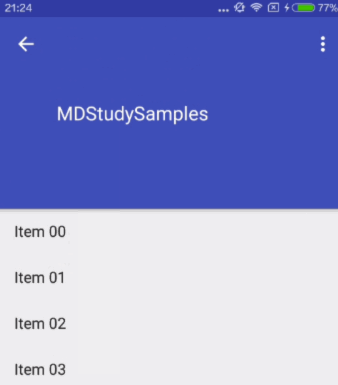
scroll
The view will be scroll in direct relation to scroll events. This flag needs to be set for any of the other flags to take effect. If any sibling views before this one do not have this flag, then this value has no effect.
Child View 伴随着滚动事件而滚出或滚进屏幕。注意两点:第一点,如果使用了其他值,必定要使用这个值才能起作用;第二点:如果在这个child View前面的任何其他Child View没有设置这个值,那么这个Child View的设置将失去作用。
示例XML代码:
对应效果图:
enterAlways
When entering (scrolling on screen) the view will scroll on any downwards scroll event, regardless of whether the scrolling view is also scrolling. This is commonly referred to as the 'quick return' pattern.
快速返回模式。其实就是向下滚动时Scrolling View和Child View之间的滚动优先级问题。对比scroll和scroll | enterAlways设置,发生向下滚动事件时,前者优先滚动Scrolling View,后者优先滚动Child View,当优先滚动的一方已经全部滚进屏幕之后,另一方才开始滚动。
示例XML代码:
...
app:layout_scrollFlags="scroll|enterAlways"
...
对应效果图:
enterAlwaysCollapsed
An additional flag for 'enterAlways' which modifies the returning view to only initially scroll back to it's collapsed height. Once the scrolling view has reached the end of it's scroll range, the remainder of this view will be scrolled into view. The collapsed height is defined by the view's minimum height.
enterAlways的附加值。这里涉及到Child View的高度和最小高度,向下滚动时,Child View先向下滚动最小高度值,然后Scrolling View开始滚动,到达边界时,Child View再向下滚动,直至显示完全。
示例XML代码:
...
android:layout_height="@dimen/dp_200"
android:minHeight="@dimen/dp_56"
...
app:layout_scrollFlags="scroll|enterAlways|enterAlwaysCollapsed"
...
对应效果图:
exitUntilCollapsed
When exiting (scrolling off screen) the view will be scrolled until it is 'collapsed'. The collapsed height is defined by the view's minimum height.
这里也涉及到最小高度。发生向上滚动事件时,Child View向上滚动退出直至最小高度,然后Scrolling View开始滚动。也就是,Child View不会完全退出屏幕。
示例SML代码:
...
android:layout_height="@dimen/dp_200"
android:minHeight="@dimen/dp_56"
...
app:layout_scrollFlags="scroll|exitUntilCollapsed"
...
对应效果图:
snap
Upon a scroll ending, if the view is only partially visible then it will be snapped and scrolled to it's closest edge. For example, if the view only has it's bottom 25% displayed, it will be scrolled off screen completely. Conversely, if it's bottom 75% is visible then it will be scrolled fully into view.
简单理解,就是Child View滚动比例的一个吸附效果。也就是说,Child View不会存在局部显示的情况,滚动Child View的部分高度,当我们松开手指时,Child View要么向上全部滚出屏幕,要么向下全部滚进屏幕,有点类似ViewPager的左右滑动。
示例XML代码:
...
android:layout_height="@dimen/dp_200"
...
app:layout_scrollFlags="scroll|snap"
...
对应效果图:
示例源码
我在GitHub上建立了一个Repository,用来存放整个Android Material Design系列控件的学习案例,会伴随着文章逐渐更新完善,欢迎大家补充交流,Star地址:
https://github.com/Mike-bel/MDStudySamples