上次我们说了,要进行多线程编程,我们可以使用最原始的方式也是最灵活的方式进行,那就是Thread(ThreadPool)+信号量+锁+Control.Invoke。.NET的异步编程模型给我们提供了一种基于IAsyncResult的编程模式,它尤其适用于处理下面的应用场景:
1) 被阻止,正在等待一个 IAsyncResult
2) 被阻止,正在等待多个 IAsyncResult 对象
3) 轮询 IAsyncResult 上的完成情形
.NET还提供了基于事件的异步编程模式(EAP),它能够提供:
1) 后台执行耗时任务(例如下载和数据库操作),但不会中断应用程序
2) 同时执行多个操作,每个操作完成时都会接到通知
下面是一个符合基于事件的异步编程模式的类:
public class AsyncExample { public int Method1(string param); public void Method2(double param); public void Method1Async(string param); public void Method1Async(string param, object userState); public event Method1CompletedEventHandler Method1Completed; public void Method2Async(double param); public void Method2Async(double param, object userState); public event Method2CompletedEventHandler Method2Completed; public void CancelAsync(object userState); public bool IsBusy { get; } }
我们看到它的操作一般提供同步和异步两种模式,异步操作提供一个完成事件,还提供了取消异步操作的方法。对于某些更高级的组件还提供了汇报进度的功能,通过一个进度汇报事件来完成,此事件通常将叫做 ProgressChanged 或 方法名称ProgressChanged,它对应的事件处理程序会带有一个 ProgressChangedEventArgs 参数。ProgressChanged 事件的事件处理程序可以检查 ProgressChangedEventArgs.ProgressPercentage 属性来确定异步任务完成的百分比。此属性的范围是 0 到 100,可用来更新 ProgressBar 的 Value 属性。
说到这里您可能想到了,BackgroundWorker就是遵从这种模式的组件。那么我们在设计组件的时候如何来选择实现基于事件的APM还是基于IAsyncResult的APM呢,MSDN上有这么一段指导原则:
1) 将基于事件的模式用作默认API 以公开类的异步行为。
2) 当类主要用在客户端应用程序(例如 Windows 窗体)中时,不要公开 IAsyncResult 模式。 (比如PictureBox的LoadAsync 方法以及LoadCompleted 事件)
3) 仅在必须公开 IAsyncResult 模式才能满足要求时公开该模式。例如,需要与现有 API 兼容时可能需要公开 IAsyncResult 模式。
4) 不要在不公开基于事件的模式时公开 IAsyncResult 模式。 如果必须公开 IAsyncResult 模式,应将其作为高级选项公开。例如,如果生成一个代理对象,则应默认生成基于事件的模式,其中具有一个生成 IAsyncResult 模式的选项。
5) 在 IAsyncResult 模式实现上生成基于事件的模式实现。
6) 避免在同一个类上同时公开基于事件的模式和 IAsyncResult 模式。在“较高级别”的类上公开基于事件的模式,在“较低级别”的类上公开 IAsyncResult 模式。例如,比较 WebClient 组件上的基于事件的模式与 HttpRequest 类上的 IAsyncResult 模式。
来看一个WebClient的例子:
WebClient wc = new WebClient(); wc.Encoding = Encoding.UTF8; wc.DownloadStringCompleted += new DownloadStringCompletedEventHandler(wc_DownloadStringCompleted); wc.DownloadProgressChanged += new DownloadProgressChangedEventHandler(wc_DownloadProgressChanged); wc.DownloadStringAsync(new Uri("http://www.cnblogs.com"), "test"); Console.WriteLine(DateTime.Now.ToString("mm:ss")); Console.ReadLine();
进度更新事件处理方法:
static void wc_DownloadProgressChanged(object sender, DownloadProgressChangedEventArgs e) { Console.WriteLine("{0} downloaded {1} of {2} bytes. {3} % complete...", (string)e.UserState, e.BytesReceived, e.TotalBytesToReceive, e.ProgressPercentage); }
完成下载事件处理方法:
static void wc_DownloadStringCompleted(object sender, DownloadStringCompletedEventArgs e) { Console.WriteLine(DateTime.Now.ToString("mm:ss")); Console.WriteLine(e.Result.Substring(0, 300)); }
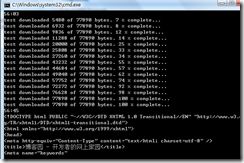
程序输出结果:
我们可以看到WebClient的DownloadStringAsync方法在内部使用了WebRequest:
public void DownloadStringAsync(Uri address, object userToken) { if (Logging.On) { Logging.Enter(Logging.Web, this, "DownloadStringAsync", address); } if (address == null) { throw new ArgumentNullException("address"); } this.InitWebClientAsync(); this.ClearWebClientState(); AsyncOperation asyncOp = AsyncOperationManager.CreateOperation(userToken); this.m_AsyncOp = asyncOp; try { WebRequest request = this.m_WebRequest = this.GetWebRequest(this.GetUri(address)); this.DownloadBits(request, null, new CompletionDelegate(this.DownloadStringAsyncCallback), asyncOp); } catch (Exception exception) { if (((exception is ThreadAbortException) || (exception is StackOverflowException)) || (exception is OutOfMemoryException)) { throw; } if (!(exception is WebException) && !(exception is SecurityException)) { exception = new WebException(SR.GetString("net_webclient"), exception); } this.DownloadStringAsyncCallback(null, exception, asyncOp); } catch { Exception exception2 = new WebException(SR.GetString("net_webclient"), new Exception(SR.GetString("net_nonClsCompliantException"))); this.DownloadStringAsyncCallback(null, exception2, asyncOp); } if (Logging.On) { Logging.Exit(Logging.Web, this, "DownloadStringAsync", ""); } }
而且,使用了WebRequest的基于IAsyncResult的APM,可以看看DownloadBits的定义:
private byte[] DownloadBits(WebRequest request, Stream writeStream, CompletionDelegate completionDelegate, AsyncOperation asyncOp) { WebResponse response = null; DownloadBitsState state = new DownloadBitsState(request, writeStream, completionDelegate, asyncOp, this.m_Progress, this); if (state.Async) { request.BeginGetResponse(new AsyncCallback(WebClient.DownloadBitsResponseCallback), state); return null; } response = this.m_WebResponse = this.GetWebResponse(request); int bytesRetrieved = state.SetResponse(response); while (!state.RetrieveBytes(ref bytesRetrieved)) { } state.Close(); return state.InnerBuffer; }
在这里BeginGetResponse(),DownloadBitsResponseCallback回调方法如下:
private static void DownloadBitsResponseCallback(IAsyncResult result) { DownloadBitsState asyncState = (DownloadBitsState)result.AsyncState; WebRequest request = asyncState.Request; Exception exception = null; try { WebResponse webResponse = asyncState.WebClient.GetWebResponse(request, result); asyncState.WebClient.m_WebResponse = webResponse; asyncState.SetResponse(webResponse); } catch (Exception exception2) { if (((exception2 is ThreadAbortException) || (exception2 is StackOverflowException)) || (exception2 is OutOfMemoryException)) { throw; } exception = exception2; if (!(exception2 is WebException) && !(exception2 is SecurityException)) { exception = new WebException(SR.GetString("net_webclient"), exception2); } AbortRequest(request); if ((asyncState != null) && (asyncState.WriteStream != null)) { asyncState.WriteStream.Close(); } } finally { if (exception != null) { asyncState.CompletionDelegate(null, exception, asyncState.AsyncOp); } } }
很显然,在WebClient.GetWebResponse中我们会进行EndGetResponse()操作:
protected virtual WebResponse GetWebResponse(WebRequest request, IAsyncResult result) { WebResponse response = request.EndGetResponse(result); this.m_WebResponse = response; return response; }
那么继续看看SetResponse:
internal int SetResponse(WebResponse response) { this.ContentLength = response.ContentLength; if ((this.ContentLength == -1L) || (this.ContentLength > 0x10000L)) { this.Length = 0x10000L; } else { this.Length = this.ContentLength; } if (this.WriteStream == null) { if (this.ContentLength > 0x7fffffffL) { throw new WebException(SR.GetString("net_webstatus_MessageLengthLimitExceeded"), WebExceptionStatus.MessageLengthLimitExceeded); } this.SgBuffers = new ScatterGatherBuffers(this.Length); } this.InnerBuffer = new byte[(int)this.Length]; this.ReadStream = response.GetResponseStream(); if (this.Async && (response.ContentLength >= 0L)) { this.Progress.TotalBytesToReceive = response.ContentLength; } if (this.Async) { if ((this.ReadStream == null) || (this.ReadStream == Stream.Null)) { WebClient.DownloadBitsReadCallbackState(this, null); } else { this.ReadStream.BeginRead(this.InnerBuffer, this.Offset, ((int)this.Length) - this.Offset, new AsyncCallback(WebClient.DownloadBitsReadCallback), this); } return -1; } if ((this.ReadStream != null) && (this.ReadStream != Stream.Null)) { return this.ReadStream.Read(this.InnerBuffer, this.Offset, ((int)this.Length) - this.Offset); } return 0; }
关注下ReadStream.BeginRead()的回调方法:
private static void DownloadBitsReadCallback(IAsyncResult result) { DownloadBitsState asyncState = (DownloadBitsState)result.AsyncState; DownloadBitsReadCallbackState(asyncState, result); }
继续看看DownloadBitsReadCallbackState:
private static void DownloadBitsReadCallbackState(DownloadBitsState state, IAsyncResult result) { Stream readStream = state.ReadStream; Exception exception = null; bool flag = false; try { int bytesRetrieved = 0; if ((readStream != null) && (readStream != Stream.Null)) { bytesRetrieved = readStream.EndRead(result); } flag = state.RetrieveBytes(ref bytesRetrieved); } catch (Exception exception2) { flag = true; if (((exception2 is ThreadAbortException) || (exception2 is StackOverflowException)) || (exception2 is OutOfMemoryException)) { throw; } exception = exception2; state.InnerBuffer = null; if (!(exception2 is WebException) && !(exception2 is SecurityException)) { exception = new WebException(SR.GetString("net_webclient"), exception2); } AbortRequest(state.Request); if ((state != null) && (state.WriteStream != null)) { state.WriteStream.Close(); } } finally { if (flag) { if (exception == null) { state.Close(); } state.CompletionDelegate(state.InnerBuffer, exception, state.AsyncOp); } } }
在这里EndRead(),再来看看再来看看RetrieveBytes()方法:
internal bool RetrieveBytes(ref int bytesRetrieved) { if (bytesRetrieved > 0) { if (this.WriteStream != null) { this.WriteStream.Write(this.InnerBuffer, 0, bytesRetrieved); } else { this.SgBuffers.Write(this.InnerBuffer, 0, bytesRetrieved); } if (this.Async) { this.Progress.BytesReceived += (long)bytesRetrieved; } if (this.Offset != this.ContentLength) { if (this.Async) { this.WebClient.PostProgressChanged(this.AsyncOp, this.Progress); this.ReadStream.BeginRead(this.InnerBuffer, this.Offset, ((int)this.Length) - this.Offset, new AsyncCallback(WebClient.DownloadBitsReadCallback), this); } else { bytesRetrieved = this.ReadStream.Read(this.InnerBuffer, this.Offset, ((int)this.Length) - this.Offset); } return false; } } if (this.Async) { if (this.Progress.TotalBytesToReceive < 0L) { this.Progress.TotalBytesToReceive = this.Progress.BytesReceived; } this.WebClient.PostProgressChanged(this.AsyncOp, this.Progress); } if (this.ReadStream != null) { this.ReadStream.Close(); } if (this.WriteStream != null) { this.WriteStream.Close(); } else if (this.WriteStream == null) { byte[] dst = new byte[this.SgBuffers.Length]; if (this.SgBuffers.Length > 0) { BufferOffsetSize[] buffers = this.SgBuffers.GetBuffers(); int dstOffset = 0; for (int i = 0; i < buffers.Length; i++) { BufferOffsetSize size = buffers[i]; Buffer.BlockCopy(size.Buffer, 0, dst, dstOffset, size.Size); dstOffset += size.Size; } } this.InnerBuffer = dst; } return true; }
WebClient的PostProgressChanged方法,在汇报进度的时候调用了AsyncOperation的Post方法:
private void PostProgressChanged(AsyncOperation asyncOp, ProgressData progress) { if ((asyncOp != null) && ((progress.BytesSent + progress.BytesReceived) > 0L)) { int num; if (progress.HasUploadPhase) { if ((progress.TotalBytesToReceive < 0L) && (progress.BytesReceived == 0L)) { num = (progress.TotalBytesToSend < 0L) ? 0 : ((progress.TotalBytesToSend == 0L) ? 50 : ((int)((50L * progress.BytesSent) / progress.TotalBytesToSend))); } else { num = (progress.TotalBytesToSend < 0L) ? 50 : ((progress.TotalBytesToReceive == 0L) ? 100 : ((int)(((50L * progress.BytesReceived) / progress.TotalBytesToReceive) + 50L))); } asyncOp.Post(this.reportUploadProgressChanged, new UploadProgressChangedEventArgs(num, asyncOp.UserSuppliedState, progress.BytesSent, progress.TotalBytesToSend, progress.BytesReceived, progress.TotalBytesToReceive)); } else { num = (progress.TotalBytesToReceive < 0L) ? 0 : ((progress.TotalBytesToReceive == 0L) ? 100 : ((int)((100L * progress.BytesReceived) / progress.TotalBytesToReceive))); asyncOp.Post(this.reportDownloadProgressChanged, new DownloadProgressChangedEventArgs(num, asyncOp.UserSuppliedState, progress.BytesReceived, progress.TotalBytesToReceive)); } } }
MSDN中有这么一段描述:为了使类正确运行,应当使用给定应用程序模型(包括 ASP.NET 和 Windows 窗体应用程序)的适当线程或上下文调用客户端事件处理程序,这一点很重要。我们提供了两个重要的帮助器类,以确保您的异步类在任何应用程序模型中都能正确运行,这两个帮助器类是 AsyncOperation 和 AsyncOperationManager。AsyncOperationManager 提供了 CreateOperation 方法,该方法会返回一个 AsyncOperation。方法名称Async 方法调用 CreateOperation,类使用返回的 AsyncOperation 跟踪异步任务的生存期。若要向客户端报告进度、增量结果和完成,请调用 AsyncOperation 的 Post 和 OperationCompleted 方法。AsyncOperation 负责将对客户端事件处理程序的调用封送到适当的线程和上下文。
7) 当为了提供兼容性需要在同一个类上公开基于事件的模式和 IAsyncResult 模式时,同时公开这两种模式。例如,如果已经释放了一个使用 IAsyncResult 模式的 API,则需要保留 IAsyncResult 模式以提供向后兼容性。
8)如果得到的对象模型复杂性方面的优点大于分开实现的优点,则在同一个类上实现基于事件的模式和 IAsyncResult 模式。在一个类上同时公开两种模式比避免公开基于事件的模式效果更好。
9) 如果必须在同一个类上同时公开基于事件的模式和 IAsyncResult 模式,可使用设置为 Advanced 的 EditorBrowsableAttribute 将 IAsyncResult 模式实现标记为高级功能。这指示设计环境(如 Visual Studio IntelliSense)不显示 IAsyncResult 属性和方法。这些属性和方法仍然是完全可用的,但使用 IntelliSense 的开发人员能够更清楚地查看 API。
我们可以发现从自己实现异步编程,到使用基于IAsyncResult的APM到使用基于事件的APM,使用上越来越简单,封装的也越来越厉害(自己实现一个WebClient的工作量也很大)。之所以有APM这种模式是因为.NET的BCL不管是基于线程池的异步操作还是基于IOCP的异步操作都遵从了APM,对于开发人员来说不需要过多学习就可以掌握大多数提供了异步能力的类库的使用。而对于组件或类库设计师来说就更要遵循这个模式,并且要根据需要选择提供基于IAsyncResult的APM还是基于事件的APM还是两者都提供。通过这两篇文章的介绍您应该已经知道了如何去使用基于APM的类库,在之后高级系列文章中我们会介绍如何去实现自己的APM组件。
在这十篇文章中我们介绍了线程/线程池/线程同步/基于多线程的组件/异步编程模式,这些文章中用到的例子可以在这里下载(VS2008解决方案)。