上一篇文章主要讲述了TUN/TAP设备的一些原理,你可能会好奇,TUN/TAP设备究竟有什么用处呢?所以这篇文章,我想用一些实际的例子来回答这个问题。
例子源自陈硕老师的博客,博文中关于TUN/TAP设备的使用非常典型,对原文感兴趣的同学可以查看这里:http://blog.csdn.net/solstice/article/details/6579232
背景:在一台 PC 机上模拟 TCP 客户端程序发起连接请求,同时在该 PC 上创建虚拟网卡 tun0,接收连接请求
并送至 faketcp 应用程序,用于模拟 TCP 服务器端进行响应。
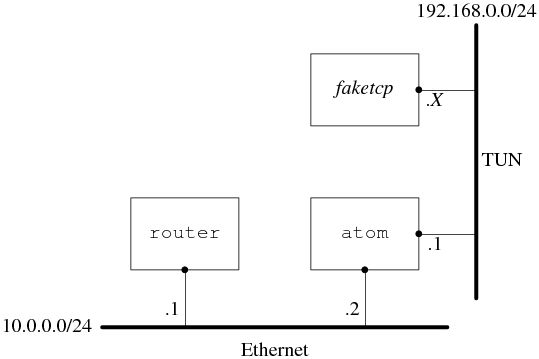
网络的拓扑结构如下:
具体做法是:在主机 atom 上通过打开 /dev/net/tun 设备来创建一个 tun0 虚拟网卡,然后把这个网卡的地址设为192.168.0.1/24,这样 faketcp 程序就扮演了192.168.0.0/24 这个网段上的所有机器。atom 发给192.168.0.2 ~ 192.168.0.254的 IP 数据包都会发给 faketcp 程序,faketcp 程序可以模拟其中任何一个IP 给atom 发 IP 数据包。
程序分成几步来实现。
第一步:实现 icmp echo 协议,这样就能 ping 通 faketcp 了:
faketcp.h:
#include // std::swap
#include
#include
#include
#include // inet_ntop
#include
struct SocketAddr
{
uint32_t saddr, daddr; // 源地址和目的地址
uint16_t sport, dport; // 源端口和目的端口
bool operator==(const SocketAddr& rhs) const
{
return saddr == rhs.saddr && daddr == rhs.daddr &&
sport == rhs.sport && dport == rhs.dport;
}
bool operator<(const SocketAddr& rhs) const
{
return memcmp(this, &rhs, sizeof(rhs)) < 0;
}
};
int tun_alloc(char dev[IFNAMSIZ]);
uint16_t in_checksum(const void* buf, int len);
void icmp_input(int fd, const void* input, const void* payload, int len);
faketcp.cc:
#include "faketcp.h"
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
int sethostaddr(const char* dev)
{
struct ifreq ifr;
bzero(&ifr, sizeof(ifr));
strcpy(ifr.ifr_name, dev);
struct sockaddr_in addr;
bzero(&addr, sizeof addr);
addr.sin_family = AF_INET;
inet_pton(AF_INET, "192.168.0.1", &addr.sin_addr);
//addr.sin_addr.s_addr = htonl(0xc0a80001);
bcopy(&addr, &ifr.ifr_addr, sizeof addr);
int sockfd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_DGRAM, 0);
if (sockfd < 0)
return sockfd;
int err = 0;
// ifconfig tun0 192.168.0.1
if ((err = ioctl(sockfd, SIOCSIFADDR, (void *) &ifr)) < 0)
{
perror("ioctl SIOCSIFADDR");
goto done;
}
// ifup tun0 其实就是启动tun0
if ((err = ioctl(sockfd, SIOCGIFFLAGS, (void *) &ifr)) < 0)
{
perror("ioctl SIOCGIFFLAGS");
goto done;
}
ifr.ifr_flags |= IFF_UP;
if ((err = ioctl(sockfd, SIOCSIFFLAGS, (void *) &ifr)) < 0)
{
perror("ioctl SIOCSIFFLAGS");
goto done;
}
// ifconfig tun0 192.168.0.1/24 # 配置子网掩码
inet_pton(AF_INET, "255.255.255.0", &addr.sin_addr);
bcopy(&addr, &ifr.ifr_netmask, sizeof addr);
if ((err = ioctl(sockfd, SIOCSIFNETMASK, (void *) &ifr)) < 0)
{
perror("ioctl SIOCSIFNETMASK");
goto done;
}
done:
close(sockfd);
return err;
}
int tun_alloc(char dev[IFNAMSIZ])
{
struct ifreq ifr;
int fd, err;
if ((fd = open("/dev/net/tun", O_RDWR)) < 0)
{
perror("open");
return -1;
}
bzero(&ifr, sizeof(ifr));
ifr.ifr_flags = IFF_TUN | IFF_NO_PI; // tun设备不包含以太网头部,而tap包含,仅此而已
if (*dev)
{
strncpy(ifr.ifr_name, dev, IFNAMSIZ);
}
if ((err = ioctl(fd, TUNSETIFF, (void *) &ifr)) < 0)
{
perror("ioctl TUNSETIFF");
close(fd);
return err;
}
strcpy(dev, ifr.ifr_name);
if ((err = sethostaddr(dev)) < 0) // 设定地址等信息
return err;
return fd;
}
uint16_t in_checksum(const void* buf, int len)
{
assert(len % 2 == 0);
const uint16_t* data = static_cast(buf);
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < len; i+=2)
{
sum += *data++;
}
while (sum >> 16)
sum = (sum & 0xFFFF) + (sum >> 16);
assert(sum <= 0xFFFF);
return ~sum;
}
void icmp_input(int fd, const void* input, const void* payload, int len)
{
const struct iphdr* iphdr = static_cast(input); // ip头部
const struct icmphdr* icmphdr = static_cast(payload); // icmp头部
// const int icmphdr_size = sizeof(*icmphdr);
const int iphdr_len = iphdr->ihl*4;
if (icmphdr->type == ICMP_ECHO)
{
char source[INET_ADDRSTRLEN];
char dest[INET_ADDRSTRLEN];
inet_ntop(AF_INET, &iphdr->saddr, source, INET_ADDRSTRLEN);
inet_ntop(AF_INET, &iphdr->daddr, dest, INET_ADDRSTRLEN);
printf("%s > %s: ", source, dest);
printf("ICMP echo request, id %d, seq %d, length %d\n",
ntohs(icmphdr->un.echo.id),
ntohs(icmphdr->un.echo.sequence),
len - iphdr_len);
union
{
unsigned char output[ETH_FRAME_LEN]; // 以太网头部
struct
{
struct iphdr iphdr;
struct icmphdr icmphdr;
} out;
};
memcpy(output, input, len);
out.icmphdr.type = ICMP_ECHOREPLY;
out.icmphdr.checksum += ICMP_ECHO; // FIXME: not portable
std::swap(out.iphdr.saddr, out.iphdr.daddr);
write(fd, output, len);
}
}
icmpecho.cc:
#include "faketcp.h"
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
int main()
{
char ifname[IFNAMSIZ] = "tun%d";
int fd = tun_alloc(ifname); // tun_alloc函数主要用于开启
if (fd < 0)
{
fprintf(stderr, "tunnel interface allocation failed\n");
exit(1);
}
printf("allocted tunnel interface %s\n", ifname);
sleep(1);
for (;;)
{
union
{
unsigned char buf[ETH_FRAME_LEN]; // 以太网头部
struct iphdr iphdr; // ip头部
};
const int iphdr_size = sizeof iphdr; // ip头部默认是20字节
int nread = read(fd, buf, sizeof(buf));
if (nread < 0)
{
perror("read");
close(fd);
exit(1);
}
printf("read %d bytes from tunnel interface %s.\n", nread, ifname);
const int iphdr_len = iphdr.ihl*4;
if (nread >= iphdr_size
&& iphdr.version == 4
&& iphdr_len >= iphdr_size
&& iphdr_len <= nread
&& iphdr.tot_len == htons(nread)
&& in_checksum(buf, iphdr_len) == 0)
{
const void* payload = buf + iphdr_len;
if (iphdr.protocol == IPPROTO_ICMP) // icmp协议
{
icmp_input(fd, buf, payload, nread);
}
}
else
{
printf("bad packet\n");
for (int i = 0; i < nread; ++i)
{
if (i % 4 == 0) printf("\n");
printf("%02x ", buf[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
}
return 0;
}
运行方法,打开3个命令行窗口:
- 在第1个窗口运行
sudo ./icmpecho,程序显示:
allocted tunnel interface tun0
- 在第2个窗口运行:
$ sudo ifconfig tun0 192.168.0.1/24 # 设定ip地址
$ sudo tcpdump -i tun0 # 用tcpdump抓取通过接口tun0的数据包
- 在第3个窗口运行:
$ ping 192.168.0.2
$ ping 192.168.0.3
$ ping 192.168.0.234
发现每个192.168.0.X 的IP 都能 ping 通。
第二步:实现拒接 TCP 连接的功能,即在收到SYN TCP segment的时候发送RST segment。
rejectall.cc:
#include "faketcp.h"
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
void tcp_input(int fd, const void* input, const void* payload, int tot_len)
{
const struct iphdr* iphdr = static_cast(input); // ip头部
const struct tcphdr* tcphdr = static_cast(payload); // tcp头部
const int iphdr_len = iphdr->ihl*4; // ip头部的大小
const int tcp_seg_len = tot_len - iphdr_len; // tcp报文的大小
const int tcphdr_size = sizeof(*tcphdr);
if (tcp_seg_len >= tcphdr_size
&& tcp_seg_len >= tcphdr->doff*4)
{
const int tcphdr_len = tcphdr->doff*4;
if (tcphdr->syn) // 收到了SYN分节
{
char source[INET_ADDRSTRLEN];
char dest[INET_ADDRSTRLEN];
inet_ntop(AF_INET, &iphdr->saddr, source, INET_ADDRSTRLEN); // 将ip转化为可读的字符串
inet_ntop(AF_INET, &iphdr->daddr, dest, INET_ADDRSTRLEN);
printf("IP %s.%d > %s.%d: ",
source, ntohs(tcphdr->source), dest, ntohs(tcphdr->dest));
printf("Flags [S], seq %u, win %d, length %d\n",
ntohl(tcphdr->seq), // 序列号
ntohs(tcphdr->window), // 窗口大小
tot_len - iphdr_len - tcphdr_len);
union
{
unsigned char output[ETH_FRAME_LEN];
struct
{
struct iphdr iphdr;
struct tcphdr tcphdr;
} out;
};
assert(sizeof(out) == sizeof(struct iphdr) + sizeof(struct tcphdr));
int output_len = sizeof(out);
bzero(&out, output_len + 4);
memcpy(output, input, sizeof(struct iphdr));
out.iphdr.tot_len = htons(output_len);
std::swap(out.iphdr.saddr, out.iphdr.daddr);
out.iphdr.check = 0;
out.iphdr.check = in_checksum(output, sizeof(struct iphdr));
out.tcphdr.source = tcphdr->dest; // 源地址和目的地址对调
out.tcphdr.dest = tcphdr->source;
out.tcphdr.seq = 0;
out.tcphdr.ack_seq = htonl(ntohl(tcphdr->seq)+1); // 确认序列号
out.tcphdr.doff = sizeof(struct tcphdr) / 4;
out.tcphdr.ack = 1;
out.tcphdr.rst = 1; // 注意这里的RST分节
out.tcphdr.window = 0;
unsigned char* pseudo = output + output_len;
pseudo[0] = 0;
pseudo[1] = IPPROTO_TCP;
pseudo[2] = 0;
pseudo[3] = sizeof(struct tcphdr);
out.tcphdr.check = in_checksum(&out.iphdr.saddr, sizeof(struct tcphdr)+12);
write(fd, output, output_len);
}
}
}
int main()
{
char ifname[IFNAMSIZ] = "tun%d";
int fd = tun_alloc(ifname);
if (fd < 0)
{
fprintf(stderr, "tunnel interface allocation failed\n");
exit(1);
}
printf("allocted tunnel interface %s\n", ifname);
sleep(1);
for (;;)
{
union
{
unsigned char buf[ETH_FRAME_LEN];
struct iphdr iphdr;
};
const int iphdr_size = sizeof iphdr;
int nread = read(fd, buf, sizeof(buf));
if (nread < 0)
{
perror("read");
close(fd);
exit(1);
}
printf("read %d bytes from tunnel interface %s.\n", nread, ifname);
const int iphdr_len = iphdr.ihl*4;
if (nread >= iphdr_size
&& iphdr.version == 4
&& iphdr_len >= iphdr_size
&& iphdr_len <= nread
&& iphdr.tot_len == htons(nread)
&& in_checksum(buf, iphdr_len) == 0)
{
const void* payload = buf + iphdr_len;
if (iphdr.protocol == IPPROTO_ICMP)
{
icmp_input(fd, buf, payload, nread);
}
else if (iphdr.protocol == IPPROTO_TCP)
{
tcp_input(fd, buf, payload, nread);
}
}
else
{
printf("bad packet\n");
for (int i = 0; i < nread; ++i)
{
if (i % 4 == 0) printf("\n");
printf("%02x ", buf[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
}
return 0;
}
运行方法,打开3个命令行窗口,头两个窗口的操作与前面相同,运行的faketcp 程序是 ./rejectall。
- 在第3个窗口运行
$ nc 192.168.0.2 2000
$ nc 192.168.0.2 3333
$ nc 192.168.0.7 5555
发现向其中任意一个 IP 发起的 TCP 连接都被拒接了。
第三步:实现接受 TCP 连接的功能,即在接收到SYN TCP segment的时候发回 SYN + ACK。这个程序同时处理了连接断开的情况,即在收到FIN segment的时候发回 FIN + ACK。
acceptall.cc:
#include "faketcp.h"
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
void tcp_input(int fd, const void* input, const void* payload, int tot_len)
{
const struct iphdr* iphdr = static_cast(input);
const struct tcphdr* tcphdr = static_cast(payload);
const int iphdr_len = iphdr->ihl*4;
const int tcp_seg_len = tot_len - iphdr_len;
const int tcphdr_size = sizeof(*tcphdr);
if (tcp_seg_len >= tcphdr_size
&& tcp_seg_len >= tcphdr->doff*4)
{
const int tcphdr_len = tcphdr->doff*4;
char source[INET_ADDRSTRLEN];
char dest[INET_ADDRSTRLEN];
inet_ntop(AF_INET, &iphdr->saddr, source, INET_ADDRSTRLEN);
inet_ntop(AF_INET, &iphdr->daddr, dest, INET_ADDRSTRLEN);
printf("IP %s.%d > %s.%d: ",
source, ntohs(tcphdr->source), dest, ntohs(tcphdr->dest));
printf("Flags [%c], seq %u, win %d, length %d\n",
tcphdr->syn ? 'S' : (tcphdr->fin ? 'F' : '.'),
ntohl(tcphdr->seq),
ntohs(tcphdr->window),
tot_len - iphdr_len - tcphdr_len);
union
{
unsigned char output[ETH_FRAME_LEN];
struct
{
struct iphdr iphdr;
struct tcphdr tcphdr;
} out;
};
assert(sizeof(out) == sizeof(struct iphdr) + sizeof(struct tcphdr));
int output_len = sizeof(out);
bzero(&out, output_len + 4);
memcpy(output, input, sizeof(struct iphdr));
out.iphdr.tot_len = htons(output_len);
std::swap(out.iphdr.saddr, out.iphdr.daddr);
out.iphdr.check = 0;
out.iphdr.check = in_checksum(output, sizeof(struct iphdr));
out.tcphdr.source = tcphdr->dest;
out.tcphdr.dest = tcphdr->source;
out.tcphdr.ack_seq = htonl(ntohl(tcphdr->seq)+1);
out.tcphdr.doff = sizeof(struct tcphdr) / 4;
out.tcphdr.window = htons(5000);
bool response = false;
if (tcphdr->syn)
{
out.tcphdr.seq = htonl(123456); // 序列号随机产生
out.tcphdr.syn = 1; // SYN
out.tcphdr.ack = 1; // ACK
response = true;
}
else if (tcphdr->fin) // 对于对方发送的FIN也需要接收是吧!
{
out.tcphdr.seq = htonl(123457);
out.tcphdr.fin = 1;
out.tcphdr.ack = 1;
response = true;
}
unsigned char* pseudo = output + output_len;
pseudo[0] = 0;
pseudo[1] = IPPROTO_TCP;
pseudo[2] = 0;
pseudo[3] = sizeof(struct tcphdr);
out.tcphdr.check = in_checksum(&out.iphdr.saddr, sizeof(struct tcphdr)+12);
if (response)
{
write(fd, output, output_len);
}
}
}
int main()
{
char ifname[IFNAMSIZ] = "tun%d";
int fd = tun_alloc(ifname);
if (fd < 0)
{
fprintf(stderr, "tunnel interface allocation failed\n");
exit(1);
}
printf("allocted tunnel interface %s\n", ifname);
sleep(1);
for (;;)
{
union
{
unsigned char buf[ETH_FRAME_LEN];
struct iphdr iphdr;
};
const int iphdr_size = sizeof iphdr;
int nread = read(fd, buf, sizeof(buf));
if (nread < 0)
{
perror("read");
close(fd);
exit(1);
}
printf("read %d bytes from tunnel interface %s.\n", nread, ifname);
const int iphdr_len = iphdr.ihl*4;
if (nread >= iphdr_size
&& iphdr.version == 4
&& iphdr_len >= iphdr_size
&& iphdr_len <= nread
&& iphdr.tot_len == htons(nread)
&& in_checksum(buf, iphdr_len) == 0)
{
const void* payload = buf + iphdr_len;
if (iphdr.protocol == IPPROTO_ICMP)
{
icmp_input(fd, buf, payload, nread);
}
else if (iphdr.protocol == IPPROTO_TCP)
{
tcp_input(fd, buf, payload, nread);
}
}
else
{
printf("bad packet\n");
for (int i = 0; i < nread; ++i)
{
if (i % 4 == 0) printf("\n");
printf("%02x ", buf[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
}
return 0;
}
运行方法,打开3个命令行窗口,步骤与前面相同,运行的 faketcp 程序是 ./acceptall。
这次会发现 nc 能和192.168.0.X中的每一个 IP 每一个 PORT 都能连通。还可以在第4个窗口中运行 netstat -tpn,以确认连接确实建立起来了。
如果在 nc 中输入数据,数据会堆积在操作系统中,表现为netstat 显示的发送队列 (Send-Q)的长度增加。
第四步:在第三步接受TCP连接的基础上,实现接收数据,即在收到包含 payload 数据的 TCP segment时发回ACK。
discardall.cc:
#include "faketcp.h"
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
void tcp_input(int fd, const void* input, const void* payload, int tot_len)
{
const struct iphdr* iphdr = static_cast(input);
const struct tcphdr* tcphdr = static_cast(payload);
const int iphdr_len = iphdr->ihl*4;
const int tcp_seg_len = tot_len - iphdr_len;
const int tcphdr_size = sizeof(*tcphdr);
if (tcp_seg_len >= tcphdr_size
&& tcp_seg_len >= tcphdr->doff*4)
{
const int tcphdr_len = tcphdr->doff*4;
const int payload_len = tot_len - iphdr_len - tcphdr_len;
char source[INET_ADDRSTRLEN];
char dest[INET_ADDRSTRLEN];
inet_ntop(AF_INET, &iphdr->saddr, source, INET_ADDRSTRLEN); // 将ip地址变得可读
inet_ntop(AF_INET, &iphdr->daddr, dest, INET_ADDRSTRLEN);
printf("IP %s.%d > %s.%d: ",
source, ntohs(tcphdr->source), dest, ntohs(tcphdr->dest));
printf("Flags [%c], seq %u, win %d, length %d\n",
tcphdr->syn ? 'S' : (tcphdr->fin ? 'F' : '.'),
ntohl(tcphdr->seq),
ntohs(tcphdr->window),
payload_len);
union
{
unsigned char output[ETH_FRAME_LEN];
struct
{
struct iphdr iphdr;
struct tcphdr tcphdr;
} out;
};
assert(sizeof(out) == sizeof(struct iphdr) + sizeof(struct tcphdr));
int output_len = sizeof(out);
bzero(&out, output_len + 4);
memcpy(output, input, sizeof(struct iphdr));
out.iphdr.tot_len = htons(output_len);
std::swap(out.iphdr.saddr, out.iphdr.daddr);
out.iphdr.check = 0;
out.iphdr.check = in_checksum(output, sizeof(struct iphdr));
out.tcphdr.source = tcphdr->dest; // 目的地址和源地址倒换
out.tcphdr.dest = tcphdr->source;
out.tcphdr.doff = sizeof(struct tcphdr) / 4;
out.tcphdr.window = htons(5000);
bool response = false;
if (tcphdr->syn)
{
out.tcphdr.seq = htonl(123456);
out.tcphdr.ack_seq = htonl(ntohl(tcphdr->seq)+1);
out.tcphdr.syn = 1;
out.tcphdr.ack = 1;
response = true;
}
else if (tcphdr->fin)
{
out.tcphdr.seq = htonl(123457);
out.tcphdr.ack_seq = htonl(ntohl(tcphdr->seq)+1);
out.tcphdr.fin = 1;
out.tcphdr.ack = 1;
response = true;
}
else if (payload_len > 0)
{
out.tcphdr.seq = htonl(123457);
out.tcphdr.ack_seq = htonl(ntohl(tcphdr->seq)+payload_len); // 确认的序列号
out.tcphdr.ack = 1; // ack,不发送数据,仅发送确认号
response = true;
}
unsigned char* pseudo = output + output_len;
pseudo[0] = 0;
pseudo[1] = IPPROTO_TCP;
pseudo[2] = 0;
pseudo[3] = sizeof(struct tcphdr);
out.tcphdr.check = in_checksum(&out.iphdr.saddr, sizeof(struct tcphdr)+12);
if (response)
{
write(fd, output, output_len);
}
}
}
int main()
{
char ifname[IFNAMSIZ] = "tun%d";
int fd = tun_alloc(ifname);
if (fd < 0)
{
fprintf(stderr, "tunnel interface allocation failed\n");
exit(1);
}
printf("allocted tunnel interface %s\n", ifname);
sleep(1);
for (;;)
{
union
{
unsigned char buf[ETH_FRAME_LEN];
struct iphdr iphdr;
};
const int iphdr_size = sizeof iphdr;
int nread = read(fd, buf, sizeof(buf));
if (nread < 0)
{
perror("read");
close(fd);
exit(1);
}
printf("read %d bytes from tunnel interface %s.\n", nread, ifname);
const int iphdr_len = iphdr.ihl*4;
if (nread >= iphdr_size
&& iphdr.version == 4
&& iphdr_len >= iphdr_size
&& iphdr_len <= nread
&& iphdr.tot_len == htons(nread)
&& in_checksum(buf, iphdr_len) == 0)
{
const void* payload = buf + iphdr_len;
if (iphdr.protocol == IPPROTO_ICMP)
{
icmp_input(fd, buf, payload, nread);
}
else if (iphdr.protocol == IPPROTO_TCP)
{
tcp_input(fd, buf, payload, nread);
}
}
else
{
printf("bad packet\n");
for (int i = 0; i < nread; ++i)
{
if (i % 4 == 0) printf("\n");
printf("%02x ", buf[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
}
return 0;
}
运行方法,打开3个命令行窗口,步骤与前面相同,运行的faketcp程序是./acceptall。
这次会发现 nc 能和192.168.0.X中的每一个IP 每一个PORT 都能连通,数据也能发出去。还可以在第4个窗口中运行netstat -tpn,以确认连接确实建立起来了,并且发送队列的长度为0;
这一步已经解决了前面的问题2,扮演任意 TCP 服务端。
第五步:解决前面的问题1,扮演客户端向atom 发起任意多的连接。
connectmany.cc:
#include "faketcp.h"
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
void tcp_input(int fd, const void* input, const void* payload, int tot_len, bool passive)
{
const struct iphdr* iphdr = static_cast(input);
const struct tcphdr* tcphdr = static_cast(payload);
const int iphdr_len = iphdr->ihl*4;
const int tcp_seg_len = tot_len - iphdr_len;
const int tcphdr_size = sizeof(*tcphdr);
if (tcp_seg_len >= tcphdr_size
&& tcp_seg_len >= tcphdr->doff*4)
{
const int tcphdr_len = tcphdr->doff*4;
const int payload_len = tot_len - iphdr_len - tcphdr_len;
char source[INET_ADDRSTRLEN];
char dest[INET_ADDRSTRLEN];
inet_ntop(AF_INET, &iphdr->saddr, source, INET_ADDRSTRLEN);
inet_ntop(AF_INET, &iphdr->daddr, dest, INET_ADDRSTRLEN);
printf("IP %s.%d > %s.%d: ",
source, ntohs(tcphdr->source), dest, ntohs(tcphdr->dest));
printf("Flags [%c], seq %u, win %d, length %d\n",
tcphdr->syn ? 'S' : (tcphdr->fin ? 'F' : '.'),
ntohl(tcphdr->seq),
ntohs(tcphdr->window),
payload_len);
union
{
unsigned char output[ETH_FRAME_LEN];
struct
{
struct iphdr iphdr;
struct tcphdr tcphdr;
} out;
};
assert(sizeof(out) == sizeof(struct iphdr) + sizeof(struct tcphdr));
int output_len = sizeof(out);
bzero(&out, output_len + 4);
memcpy(output, input, sizeof(struct iphdr));
out.iphdr.tot_len = htons(output_len);
std::swap(out.iphdr.saddr, out.iphdr.daddr);
out.iphdr.check = 0;
out.iphdr.check = in_checksum(output, sizeof(struct iphdr));
out.tcphdr.source = tcphdr->dest;
out.tcphdr.dest = tcphdr->source;
out.tcphdr.doff = sizeof(struct tcphdr) / 4;
out.tcphdr.window = htons(5000);
bool response = false;
if (tcphdr->syn) // 对方发起连接,或者对方发送了确认的syn和ack
{
out.tcphdr.seq = htonl(passive ? 123456 : 123457);
out.tcphdr.ack_seq = htonl(ntohl(tcphdr->seq)+1);
if (passive) // passive==true表示被动接收连接,表示对方连过来
{
out.tcphdr.syn = 1;
}
// 否则的话,表示自己主动发送的连接,接收到了对方的syn和ack,我们只需要发送一个ack即可
out.tcphdr.ack = 1;
response = true;
}
else if (tcphdr->fin) // 对方关闭连接
{
out.tcphdr.seq = htonl(123457);
out.tcphdr.ack_seq = htonl(ntohl(tcphdr->seq)+1);
out.tcphdr.fin = 1;
out.tcphdr.ack = 1;
response = true;
}
else if (payload_len > 0)
{
out.tcphdr.seq = htonl(123457);
out.tcphdr.ack_seq = htonl(ntohl(tcphdr->seq)+payload_len);
out.tcphdr.ack = 1;
response = true;
}
unsigned char* pseudo = output + output_len;
pseudo[0] = 0;
pseudo[1] = IPPROTO_TCP;
pseudo[2] = 0;
pseudo[3] = sizeof(struct tcphdr);
out.tcphdr.check = in_checksum(&out.iphdr.saddr, sizeof(struct tcphdr)+12);
if (response)
{
write(fd, output, output_len);
}
}
}
// connect_one 发起一个tcp连接?
bool connect_one(int fd, uint32_t daddr, int dport, uint32_t saddr, int sport)
{
{
union
{
unsigned char output[ETH_FRAME_LEN];
struct
{
struct iphdr iphdr;
struct tcphdr tcphdr;
} out;
};
bzero(&out, (sizeof out)+4);
out.iphdr.version = IPVERSION;
out.iphdr.ihl = sizeof(out.iphdr)/4;
out.iphdr.tos = 0;
out.iphdr.tot_len = htons(sizeof(out));
out.iphdr.id = 55564;
out.iphdr.frag_off |= htons(IP_DF);
out.iphdr.ttl = IPDEFTTL;
out.iphdr.protocol = IPPROTO_TCP;
out.iphdr.saddr = saddr;
out.iphdr.daddr = daddr;
out.iphdr.check = in_checksum(output, sizeof(struct iphdr));
out.tcphdr.source = sport; // 端口号
out.tcphdr.dest = dport;
out.tcphdr.seq = htonl(123456);
out.tcphdr.ack_seq = 0;
out.tcphdr.doff = sizeof(out.tcphdr)/4;
out.tcphdr.syn = 1; // 主动发起连接
out.tcphdr.window = htons(4096);
unsigned char* pseudo = output + sizeof out;
pseudo[0] = 0;
pseudo[1] = IPPROTO_TCP;
pseudo[2] = 0;
pseudo[3] = sizeof(struct tcphdr);
out.tcphdr.check = in_checksum(&out.iphdr.saddr, sizeof(struct tcphdr)+12);
write(fd, output, sizeof out); // 发送连接
}
union
{
unsigned char buf[ETH_FRAME_LEN];
struct iphdr iphdr;
};
const int iphdr_size = sizeof iphdr;
int nread = read(fd, buf, sizeof(buf)); // 接收到回复之后
if (nread < 0)
{
perror("read");
close(fd);
exit(1);
}
// printf("read %d bytes from tunnel interface %s.\n", nread, ifname);
if (nread >= iphdr_size
&& iphdr.version == 4
&& iphdr.ihl*4 >= iphdr_size
&& iphdr.ihl*4 <= nread
&& iphdr.tot_len == htons(nread)
&& in_checksum(buf, iphdr.ihl*4) == 0)
{
const void* payload = buf + iphdr.ihl*4;
if (iphdr.protocol == IPPROTO_ICMP)
{
icmp_input(fd, buf, payload, nread);
}
else if (iphdr.protocol == IPPROTO_TCP) // tcp 报文
{
tcp_input(fd, buf, payload, nread, false); // 注意到这里的false,表示是自己主动发起连接
}
}
return true;
}
void connect_many(int fd, const char* ipstr, int port, int count)
{
uint32_t destip;
inet_pton(AF_INET, ipstr, &destip); // 连接到目的ip
uint32_t srcip = ntohl(destip)+1;
int srcport = 1024; // 端口从1024开始
for (int i = 0; i < count; ++i)
{
connect_one(fd, destip, htons(port), htonl(srcip), htons(srcport));
srcport++; // 源端口在不断加1
if (srcport > 0xFFFF)
{
srcport = 1024;
srcip++;
}
}
}
void usage()
{
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
if (argc < 4)
{
usage();
return 0;
}
char ifname[IFNAMSIZ] = "tun%d";
int fd = tun_alloc(ifname);
if (fd < 0)
{
fprintf(stderr, "tunnel interface allocation failed\n");
exit(1);
}
const char* ip = argv[1]; // ip
int port = atoi(argv[2]); // 端口
int count = atoi(argv[3]); // 数量
printf("allocted tunnel interface %s\n", ifname);
printf("press enter key to start connecting %s:%d\n", ip, port);
getchar();
connect_many(fd, ip, port, count); // 发起连接
for (;;)
{
union
{
unsigned char buf[ETH_FRAME_LEN];
struct iphdr iphdr;
};
const int iphdr_size = sizeof iphdr;
int nread = read(fd, buf, sizeof(buf));
if (nread < 0)
{
perror("read");
close(fd);
exit(1);
}
printf("read %d bytes from tunnel interface %s.\n", nread, ifname);
const int iphdr_len = iphdr.ihl*4;
if (nread >= iphdr_size
&& iphdr.version == 4
&& iphdr_len >= iphdr_size
&& iphdr_len <= nread
&& iphdr.tot_len == htons(nread)
&& in_checksum(buf, iphdr_len) == 0)
{
const void* payload = buf + iphdr_len;
if (iphdr.protocol == IPPROTO_ICMP)
{
icmp_input(fd, buf, payload, nread);
}
else if (iphdr.protocol == IPPROTO_TCP)
{
tcp_input(fd, buf, payload, nread, true); // 注意到这里的true,表示是被动接收连接
}
}
else
{
printf("bad packet\n");
for (int i = 0; i < nread; ++i)
{
if (i % 4 == 0) printf("\n");
printf("%02x ", buf[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
}
return 0;
}
这一步的运行方法与前面不同,打开4个命令行窗口。
- 在第1个窗口运行
sudo ./connectmany 192.168.0.1 2007 1000,表示将向192.168.0.1:2007发起1000个并发连接。程序显示:
allocated tunnel interface tun0
press enter key to start connecting 192.168.0.1 2007
- 在第二个窗口运行
$ sudo ifconfig tun0 192.168.0.1/24
$ sudo tcpdump -i tun0
- 在第3个窗口运行一个能接收并发TCP 连接的服务程序,可以是httpd, 也可以是muduo 的echo 或 discard 示例,程序应listen 2007端口。
- 回到第1个窗口敲回车,然后在第4个窗口中用
netstat -tpn来观察并发连接。
文中代码目录连接:https://github.com/chenshuo/recipes/tree/master/faketcp