学习笔记:来源慕课网 https://www.imooc.com/learn/1086
Synchronized methods enable a simple strategy for preventing thread interference and memory consistency errors : if an object is visible to more than one thread ,all reads or writes to that object's variables are done throught synchronized methods
同步方法支持的一种简单的策瑜来防止线程干扰和内存一致性错误,如果一个对象对多个线程可见,则对该对象变量的所有读取或写入都是通过同步方法完成的。
synchronized 的作用
能够保证在同一时刻最多只有一个线程执行该段代码,以达到保证并发安全的效果。
synchronized 是java 的关键字,被java 语言原生支持。
是最基本互斥同步手段。
是并发编程中的元老级别角色,是并发编程的必学内容。
不使用并发手段会有什么后果。
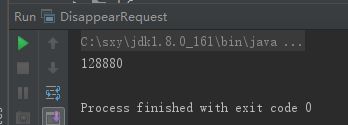
代码实战:两个线程同时a++ ,最后结果会比预计的少。
上代码:一
/**
* @author sxylml
* @Date : 2019/2/25 16:47
* @Description:
* 消失的请求
* 不采用并发控制,执行结果就不是我们所预计的效果。
*
* 原因:count ++ 看上去是一个操作,实际上包含三个动作
* 1:读取count
* 2: 将count +1
* 3:将count 的值写入内存
*/
public class DisappearRequest implements Runnable {
static DisappearRequest instance = new DisappearRequest();
static int count = 0;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread thread1 = new Thread(instance);
Thread thread2 = new Thread(instance);
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
try {
thread1.join();
thread2.join();
System.out.println(count);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) {
// 不加锁运行结果基本都是小于 200000
// synchronized (this){
count++;
// }
}
}
}
synchronized 的两个用法
对象锁:包括方法锁,(默认对象为this为当前实例对象)和同步代码块(自己指定锁对象)
类锁:指synchronized修饰静态的方法或指定锁为Class 对象
第一个用法:
对象锁
/**
* @author sxylml
* @Date : 2019/2/25 16:55
* @Description: 对象锁
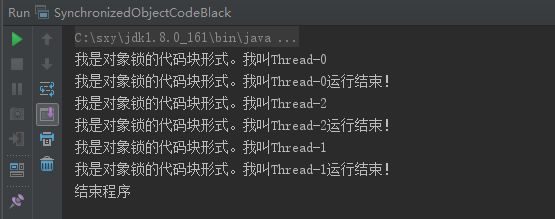
* 对象锁形式1.代码块形式,如果没有加锁,则运行结果,线程结束顺序就不确定
*/
public class SynchronizedObjectCodeBlack implements Runnable {
static SynchronizedObjectCodeBlack instance = new SynchronizedObjectCodeBlack();
@Override
public void run() {
String threadName = Thread.currentThread().getName();
System.out.println("我是对象锁的代码块形式。我叫" + threadName);
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("我是对象锁的代码块形式。我叫" + threadName+ "运行结束!");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread thread1 = new Thread(instance);
Thread thread2 = new Thread(instance);
Thread thread3 = new Thread(instance);
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
thread3.start();
while (thread1.isAlive() || thread2.isAlive() || thread3.isAlive()) {
}
System.out.println("结束程序");
}
}
/**
* @author sxylml
* @Date : 2019/2/25 16:55
* @Description: 对象锁
* 对象锁形式1.代码块形式,加锁,则运行结果,线程开始-结束 都是顺序执行的
*/
public class SynchronizedObjectCodeBlack implements Runnable {
static SynchronizedObjectCodeBlack instance = new SynchronizedObjectCodeBlack();
@Override
public void run() {
// 当前对象做为锁
synchronized (this) {
String threadName = Thread.currentThread().getName();
System.out.println("我是对象锁的代码块形式。我叫" + threadName);
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("我是对象锁的代码块形式。我叫" + threadName + "运行结束!");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread thread1 = new Thread(instance);
Thread thread2 = new Thread(instance);
Thread thread3 = new Thread(instance);
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
thread3.start();
while (thread1.isAlive() || thread2.isAlive() || thread3.isAlive()) {
}
System.out.println("结束程序");
}
}
·
使用自己创建的对象加锁:
/**
* @author sxylml
* @Date : 2019/2/26 09:09
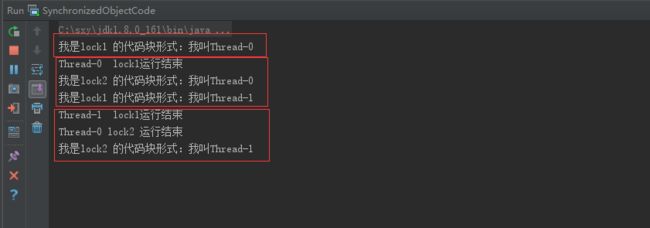
* @Description: 保护时机不相同的情况,可以使用2个锁...
*/
public class SynchronizedObjectCode implements Runnable {
Object lock1 = new Object();
Object lock2 = new Object();
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (lock1) {
System.out.println("我是lock1 的代码块形式:我叫" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() +" lock1运行结束");
}
synchronized (lock2) {
System.out.println("我是lock2 的代码块形式:我叫" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() +" lock2 运行结束");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
Runnable instance = new SynchronizedObjectCode();
Thread t1 = new Thread(instance);
Thread t2 = new Thread(instance);
t1.start();
t2.start();
while (t1.isAlive() || t2.isAlive()) {
}
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("finished 用时:" + (endTime - startTime));
}
}
/**
* @author sxylml
* @Date : 2019/2/26 09:29
* @Description: synchronized 修饰方式
*/
public class SynchronizedObjectMethod implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
method();
}
public synchronized void method() {
System.out.println("对象锁的方法修饰符形式,我叫:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 休眠3秒");
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "运行结束");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
Runnable instance = new SynchronizedObjectMethod();
Thread t1 = new Thread(instance);
Thread t2 = new Thread(instance);
t1.start();
t2.start();
while (t1.isAlive() || t2.isAlive()) {
}
Long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("整个程序运行结束! 用时" + (endTime - startTime));
}
}
结果会是:顺序执行完毕。
总结:
第一个用法:对象锁
代码块形式:手动指定锁对象
方法锁形式:synchronized 修饰普通方法,锁对象默认为this,不能是静态方法哦。