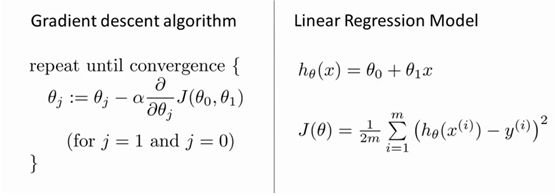
假设房子的面积和价格的对应关系如下图所示,那么如何 面积和价格的关系呢?
假设 训练集如下:
面积 : 150 , 200 , 250 , 300, 350, 400, 600
价格 : 6450,6450,8450,9450,11450,15450,18450
假设我们设定为线性:Y=θ0+θ1x
使用梯度下降的方法求解线性回归
梯度下降的原理:
也就是说使用梯度下降寻找代价函数的最小值的原理就是给J求关于θ0和θ1的偏导。
手写Y=θ0+θ1x,梯度下降的θ0,θ1的迭代过程。
实验
假设存在x=[1,2,3,4,5,6],y=[4,7,10,13,16,19] (它们的关系是y=3x+1),然后使用梯度下降求解线性回归。
x=[1,2,3,4,5,6]
y=[4,7,10,13,16,19]
#θ的参数设置,这个一般是随机取的
theta0=0.1
theta1=0.2
#α 是学习率,代表的是迭代的步长
alpha=0.01
m=len(x)
def h(i):
return theta0+theta1*x[i]
def diff(i):
return h(i)-y[i]
#times 表示迭代1000次,那么基本上可以下降到梯度的最小值了
#每次迭代做的事情,就是我上面手写的那个公式,不停的去修改theta0,theta1
for times in range(1000):
sum1=0
sum2=0
for i in range(m):
sum1=sum1+diff(i)
sum2=sum2+diff(i)*x[i]
theta0=theta0-(alpha/m)*sum1
theta1=theta1-(alpha/m)*sum2
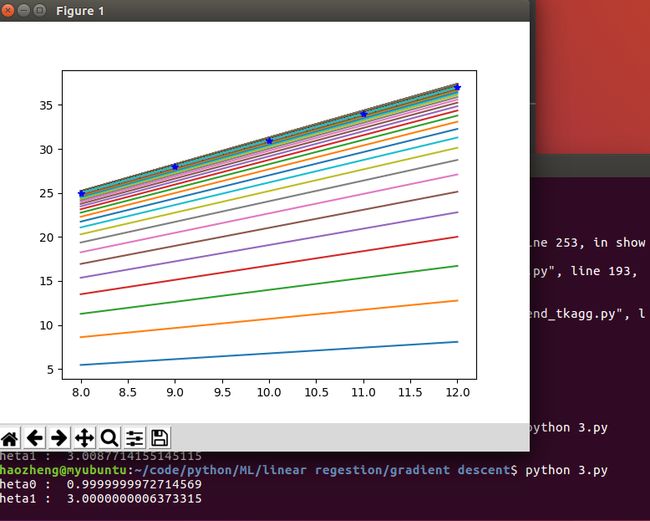
print ("theta0 : ",theta0)
print ("theta1 : ",theta1)
输出结果:
后来想到,把每次迭代计算出来的theta0 ,theta1 画出来:
源码:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x=[1,2,3,4,5,6]
y=[4,7,10,13,16,19]
test_x=[8,9,10,11,12]
#参数,这个是随机的
theta0=0.1
theta1=0.2
#学习率
alpha=0.01
m=len(x)
def h_(x):
return theta0+theta1*x
def h(i):
return theta0+theta1*x[i]
def diff(i):
return h(i)-y[i]
for times in range(1000):
sum1=0
sum2=0
for i in range(m):
sum1=sum1+diff(i)
sum2=sum2+diff(i)*x[i]
theta0=theta0-(alpha/m)*sum1
theta1=theta1-(alpha/m)*sum2
plt.plot(test_x, [h_(xi) for xi in test_x ])
plt.plot(test_x, [h_(xi) for xi in test_x ],'b*')
print ("theta0 : ",theta0)
print ("theta1 : ",theta1)
plt.show()
Part two
刚才的问题是Y=θ0+θ1x,当时问题也有可能是Y=theta0+theta1*x1+theta*x2 。这样的到的代价函数就是一个和θ0,θ1,θ2有关的函数了。问题可能会稍稍复杂一点。
代码:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
#y=2 * (x1) + (x2) + 3
x_train = np.array([ [1, 2], [2, 1], [2, 3], [3, 5], [1, 3], [4, 2], [7, 3], [4, 5], [11, 3], [8, 7] ])
y_train = np.array([7, 8, 10, 14, 8, 13, 20, 16, 28, 26])
x_test = np.array([ [1, 4], [2, 2], [2, 5], [5, 3], [1, 5], [4, 1] ])
alpha = 0.001
theta0=np.random.normal()
theta1=np.random.normal()
theta2=np.random.normal()
m=len(x_train)
def h_(x):
return theta0+theta1*x[0]+theta2*x[1]
def h(i):
return theta0+theta1*x_train[i][0]+theta2*x_train[i][1]
def diff(i):
return h(i)-y_train[i]
for times in range(10000):
sum1=0
sum2=0
sum3=0
for i in range(len(x_train)):
sum1=sum1+diff(i)
sum2=sum2+diff(i)*x_train[i][0]
sum3=sum3+diff(i)*x_train[i][1]
theta0=theta0-(alpha/m)*sum1
theta1=theta1-(alpha/m)*sum2
theta2=theta2-(alpha/m)*sum3
"""
for i in range(len(x_train)):
sum1=sum1+alpha*diff(i)
sum2=sum2+alpha*diff(i)*x_train[i][0]
sum3=sum3+alpha*diff(i)*x_train[i][1]
theta0=theta0-sum1
theta1=theta1-sum2
theta2=theta2-sum3
"""
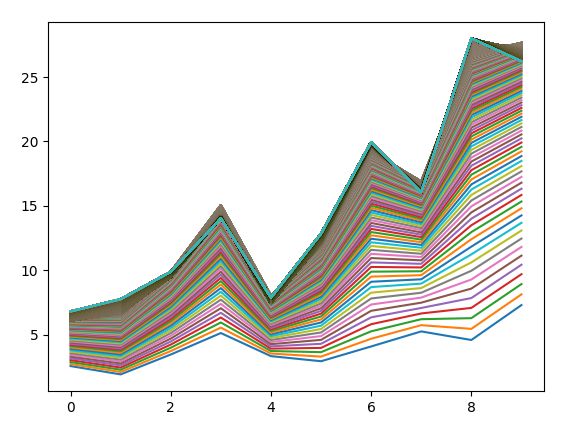
#plt.plot([x_train],[h_(xi) for xi in x_train ])
plt.plot([h_(xi) for xi in x_train ])
#plt.plot([h_(xi) for xi in x_train ])
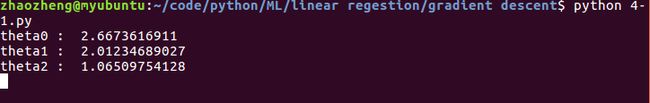
print ("theta0 : ",theta0)
print ("theta1 : ",theta1)
print ("theta2 : ",theta2)
plt.show()
实验结果: