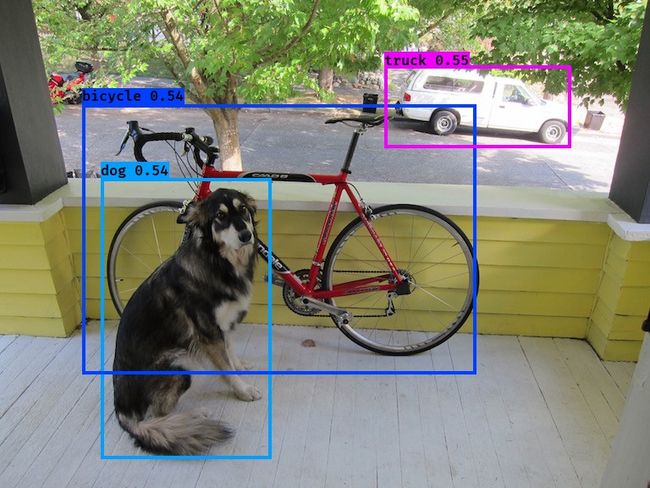
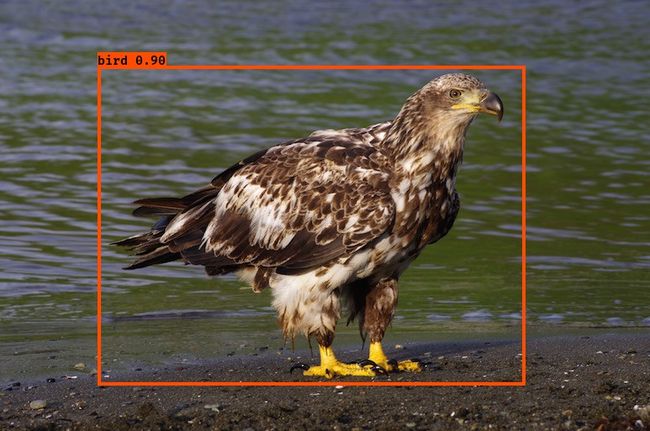
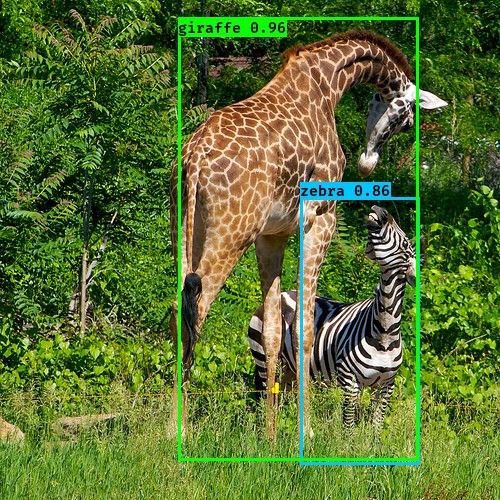
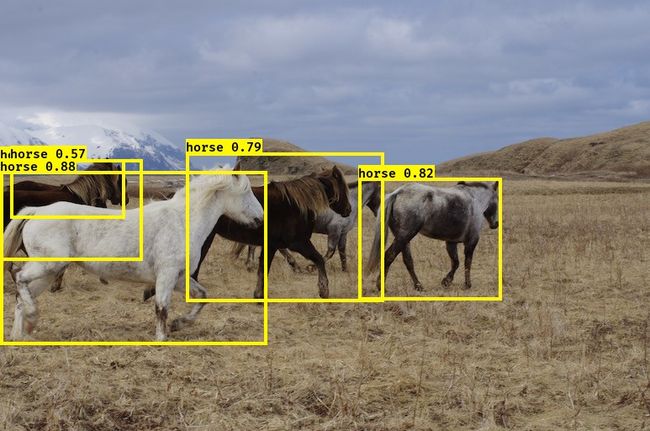
YOLOv2是Joseph Redmon提出的针对YOLO算法不足的改进版本,作者使用了一系列的方法对原来的YOLO多目标检测框架进行了改进,在保持原有速度的优势之下,精度上得以提升,此外作者提出了一种目标分类与检测的联合训练方法,通过这种方法YOLO9000可以同时在COCO和ImageNet数据集中进行训练,训练后的模型可以实现多达9000种物体的实时检测。
Paper:https://arxiv.org/abs/1612.08242
Github:https://github.com/pjreddie/darknet
Website:https://pjreddie.com/darknet/yolo
作者为YOLO算法设计了独有的深度学习框架darknet,因此没有提供Python的接口。在实验中,我找到了两种在Python 3中使用YOLOv2网络的方法。
第一种:为darknet添加Python接口
Github:https://github.com/SidHard/py-yolo2
该项目使用了原始的darknet网络,需要使用cmake重新编译源码,因此在Linux上使用更为方便一些。
首先从git上下载该项目
git clone https://github.com/SidHard/py-yolo2.git
执行cmake生成项目
cmake .. && make
最后执行yolo.py测试项目,相应的网络结构.cfg文件保存在cfg文件夹中,权值.weight文件放在根目录下,这些可以从darknet的官方网站上下载使用。
第二种:使用keras
Github:https://github.com/allanzelener/YAD2K
该项目使用了keras与tensorflow-gpu,因此可以在任何使用该框架的环境下运行,我在自己的程序中使用的该种方法。
首先下载源文件并且配置环境,可以使用anaconda环境或者在全局安装。
git clone https://github.com/allanzelener/yad2k.git
cd yad2k
# [Option 1] To replicate the conda environment:
conda env create -f environment.yml
source activate yad2k
# [Option 2] Install everything globaly.
pip install numpy
pip install tensorflow-gpu # CPU-only: conda install -c conda-forge tensorflow
pip install keras # Possibly older release: conda install keras
快速开始
- 从Darknet官方下载model:official YOLO website.
wget http://pjreddie.com/media/files/yolo.weights - 将 Darknet YOLO_v2 model转换为Keras model.
./yad2k.py cfg/yolo.cfg yolo.weights model_data/yolo.h5 - 测试图片位于
images/文件夹.
./test_yolo.py model_data/yolo.h5
最后执行test_yolo就可以执行网络,在images/out/文件夹里可以看到执行效果。
为了方便模型用于测试视频与图片,我对demo做了修改,相比原来的测试代码,能够直接移植到项目中去,对象化的程序也更易于修改,代码如下
#! /usr/bin/env python
"""Run a YOLO_v2 style detection model on test images."""
import cv2
import os
import time
import numpy as np
from keras import backend as K
from keras.models import load_model
from yad2k.models.keras_yolo import yolo_eval, yolo_head
class YOLO(object):
def __init__(self):
self.model_path = 'model_data/yolo.h5'
self.anchors_path = 'model_data/yolo_anchors.txt'
self.classes_path = 'model_data/coco_classes.txt'
self.score = 0.3
self.iou = 0.5
self.class_names = self._get_class()
self.anchors = self._get_anchors()
self.sess = K.get_session()
self.boxes, self.scores, self.classes = self.generate()
def _get_class(self):
classes_path = os.path.expanduser(self.classes_path)
with open(classes_path) as f:
class_names = f.readlines()
class_names = [c.strip() for c in class_names]
return class_names
def _get_anchors(self):
anchors_path = os.path.expanduser(self.anchors_path)
with open(anchors_path) as f:
anchors = f.readline()
anchors = [float(x) for x in anchors.split(',')]
anchors = np.array(anchors).reshape(-1, 2)
return anchors
def generate(self):
model_path = os.path.expanduser(self.model_path)
assert model_path.endswith('.h5'), 'Keras model must be a .h5 file.'
self.yolo_model = load_model(model_path)
# Verify model, anchors, and classes are compatible
num_classes = len(self.class_names)
num_anchors = len(self.anchors)
# TODO: Assumes dim ordering is channel last
model_output_channels = self.yolo_model.layers[-1].output_shape[-1]
assert model_output_channels == num_anchors * (num_classes + 5), \
'Mismatch between model and given anchor and class sizes'
print('{} model, anchors, and classes loaded.'.format(model_path))
# Check if model is fully convolutional, assuming channel last order.
self.model_image_size = self.yolo_model.layers[0].input_shape[1:3]
self.is_fixed_size = self.model_image_size != (None, None)
# Generate output tensor targets for filtered bounding boxes.
# TODO: Wrap these backend operations with Keras layers.
yolo_outputs = yolo_head(self.yolo_model.output, self.anchors, len(self.class_names))
self.input_image_shape = K.placeholder(shape=(2, ))
boxes, scores, classes = yolo_eval(yolo_outputs, self.input_image_shape, score_threshold=self.score, iou_threshold=self.iou)
return boxes, scores, classes
def detect_image(self, image):
start = time.time()
y, x, _ = image.shape
if self.is_fixed_size: # TODO: When resizing we can use minibatch input.
resized_image = cv2.resize(image, tuple(reversed(self.model_image_size)), interpolation=cv2.INTER_CUBIC)
image_data = np.array(resized_image, dtype='float32')
else:
image_data = np.array(image, dtype='float32')
image_data /= 255.
image_data = np.expand_dims(image_data, 0) # Add batch dimension.
out_boxes, out_scores, out_classes = self.sess.run(
[self.boxes, self.scores, self.classes],
feed_dict={
self.yolo_model.input: image_data,
self.input_image_shape: [image.shape[0], image.shape[1]],
K.learning_phase(): 0
})
print('Found {} boxes for {}'.format(len(out_boxes), 'img'))
for i, c in reversed(list(enumerate(out_classes))):
predicted_class = self.class_names[c]
box = out_boxes[i]
score = out_scores[i]
label = '{} {:.2f}'.format(predicted_class, score)
top, left, bottom, right = box
top = max(0, np.floor(top + 0.5).astype('int32'))
left = max(0, np.floor(left + 0.5).astype('int32'))
bottom = min(y, np.floor(bottom + 0.5).astype('int32'))
right = min(x, np.floor(right + 0.5).astype('int32'))
print(label, (left, top), (right, bottom))
cv2.rectangle(image, (left, top), (right, bottom), (255, 0, 0), 2)
cv2.putText(image, label, (left, int(top - 4)), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, (0, 0, 255), 1, cv2.LINE_AA)
end = time.time()
print(end - start)
return image
def close_session(self):
self.sess.close()
def detect_vedio(video, yolo):
camera = cv2.VideoCapture(video)
cv2.namedWindow("detection", cv2.WINDOW_NORMAL)
while True:
res, frame = camera.read()
if not res:
break
image = yolo.detect_image(frame)
cv2.imshow("detection", image)
if cv2.waitKey(110) & 0xff == 27:
break
yolo.close_session()
def detect_img(img, yolo):
image = cv2.imread(img)
r_image = yolo.detect_image(image)
cv2.namedWindow("detection")
while True:
cv2.imshow("detection", r_image)
if cv2.waitKey(110) & 0xff == 27:
break
yolo.close_session()
if __name__ == '__main__':
yolo = YOLO()
img = 'E:\Documents\Downloads\YAD2K-master\YAD2K-master\images\horses.jpg'
video = 'E:\Documents\Documents\python\Traffic\data\person.avi'
detect_img(img, yolo)
detect_vedio(video, yolo)