目录
- socket 简介
- 创建连接
- 接收消息
- 发送消息
- 断开连接
- 进度灰色保活
- IPC
- 自定义权限广播
- 重试机制
- 进程异常恢复
前段时间公司项目有个大版本准备对IM(消息通信)模块升级。虽然需求紧急但server同事任坚持自定义消息协议来实现一套通信框架。这里对Android端实现做下总结,仅供交流。
socket 简介
socket就是我们常说的套接字。网络上具有唯一标识的IP地址和端口组合在一起才能构成唯一能识别的标识符套接字。根据不同的的底层协议,Socket的实现是多样化的。常见的Socket类型为流套接字(streamsocket)和数据报套接字(datagramsocket);数据报套接字使用UDP协议,提供数据打包发送服务。流套接字将TCP作为其端对端协议,提供了一个可信赖的字节流服务,本文将介绍流套接字的简单应用。
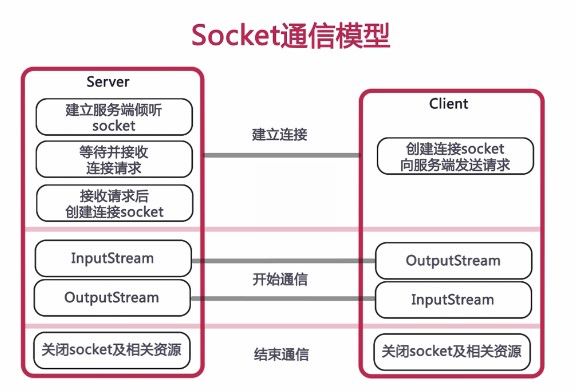
创建连接
这里给出一个简单通信模型,图片来源于网络。
- sample code 这里只贴出了client端代码
try {
LogUtil.d(TAG, " connecting ip=%s , port = %d", ip, port);
while (true) {
try {
mSocket = new Socket();
mSocket.setKeepAlive(true);
mSocket.setSoTimeout(2 * 3 * 60 * 1000);//inputStream read 超时时间
mSocket.setTcpNoDelay(true);
mSocket.connect(new InetSocketAddress(ip, port));
if (mSocket.isConnected()) {
dataIS = new DataInputStream(mSocket.getInputStream());
dataOS = new DataOutputStream(mSocket.getOutputStream());
connectState = true;
}
this.mCallback.onConnect(this);
break;//connect sucess
} catch (IOException e) {
mRetryPolicy.retry(e);
//间隔5秒,重连。
Thread.sleep(5000);
LogUtil.e(TAG, " connect IOException =%s , and retry count = %d", e.getMessage(), mRetryPolicy.getCurrentRetryCount());
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
//重试后,仍然失败了。回调失败。
connectState = false;
e.printStackTrace();
LogUtil.e(TAG, " connect IOException = " + e.getMessage());
mCallback.onConnectFailed(e);
}
接收消息
创建成功后就开始接收处理消息。
while (isConnected()) {
try {
int type = dataIS.readByte();//读取1位
int length = dataIS.readChar();//读取2位标记第三段数据长度
byte[] data = new byte[length];
LogUtil.i(TAG, " receiveData connected receiveData type = %d, ", type);
dataIS.readFully(data);
mCallback.onReceive(type, data);
} catch (SocketTimeoutException e) {
LogUtil.e(TAG, " receiveData SocketTimeoutException = " + e.getMessage());
e.printStackTrace();
break;
} catch (IOException e) {
LogUtil.e(TAG, " receiveData IOException = " + e.getMessage());
e.printStackTrace();
break;//异常后,退出循环
}
}
//通知异常,并重连。
发送消息
在连接状态下向服务器发送字节流消息。
// 1.同步处理 2.异常或未连接状态下,则回调并通知重连
final byte[] bytes = {1,2,3,4,5}; //test data
synchronized (TcpClient.class) {
if (isConnected()) {
try {
byte type = 1;
dataOS.writeByte(type);
dataOS.writeChar(bytes.length);
dataOS.write(bytes);
dataOS.flush();
LogUtil.i(TAG, "send success msg : %s", Arrays.toString(bytes));
} catch (final IOException e) {
callback.onFailed(e);
disConnect(true);
e.printStackTrace();
}
} else {
callback.onFailed(new Exception("socket is not connected"));
disConnect(true);
LogUtil.i(TAG, "socket is not connected !");
}
}
断开连接
//关闭流
closeInputStream(dataIS);
closeOutputStream(dataOS);
if (mSocket != null) {
try {
mSocket.shutdownInput();
mSocket.shutdownOutput();
mSocket.close();
mSocket = null;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (mCallback != null && needRec) {
mCallback.onDisconnect();
}
mState = STATE_DISCONNECT;
进度灰色保活
由于项目中通信模块运行在独立的进程中,为避免进程被意外干掉,这里将其优先级提高已达到报活效果。
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT < 18) {//18以下,可直接设置为前台service
startForeground(GRAY_SERVICE_ID, new Notification());
} else if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT <= 24) {
Intent innerIntent = new Intent(this, GrayInnerService.class);
startService(innerIntent);
startForeground(GRAY_SERVICE_ID, new Notification());
}
在看看GrayInnerService实现
/**
* 测试结果:API<=24可行。25/7.1.1版本,通知栏正常状态下看不到icon,但滑下来就看得到icon。
* 给 API >= 18 的平台上用的灰色保活手段
*/
public static class GrayInnerService extends Service {
@Override
public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId) {
startForeground(GRAY_SERVICE_ID, new Notification());
stopSelf();
return super.onStartCommand(intent, flags, startId);
}
@Nullable
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
return null;
}
}
代码中可以看出,启动一个相同id的前台GrayInnerService然后立即stopSelf,再以同样方式启动主service,这样运行起来的service就已经是达到前台服务优先级了,一般情况都杀不了它。
IPC(进程间通信)
这里IPC比较简单,就是使用bundle实现service到broadcast之间的跨进程通信。此处略过,详细请查看代码。
自定义广播权限
出于安全考虑或者其它特殊需求,可能会限制广播接收者,所以这里就用到了自定义权限。
- manifest.xml中定义并使用
- 发送带权限的广播
contexts.sendBroadcast(intent, "android.intent.permission.im.receiver_permission");
这样只有申明了此权限的广播才能接收到消息。
重试机制
这里参考volley框架的重试机制,在创建连接时若失败5次之内会尝试重连。具体实现请参考DefaultRetryPolicy类。
进程异常恢复
实现Thread.UncaughtExceptionHandler接口,处理异常并恢复。
@Override
public void uncaughtException(Thread thread, Throwable ex) {
// crash统计打点
if (ex != null) {
ex.printStackTrace();
// 保存错误报告文件
saveCrashInfoToFile(ex);
}
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
LogUtil.i(TAG, "uncaughtException crash recovering");
// 检查socket状态并重连
ImServiceHelper.getInstance(mContext).reConnect();
}
代码地址
- demo 请戳这里
补充
- 弱网情况。
目前弱网情况未做处理,超时异常会捕获,然后进入重连机制。
给个处理建议:将所有未发送成功的请求缓存到队列,待网络恢复后自动发送。 - 连接异常断开,如何恢复。
除了上面提到了连接重试,及进程异常恢复;代码中捕获了任何socket异常,并进入重连机制。 - 健壮的心跳策略。
心跳策略最好是双向的,即服务器和客户端都应有心跳。
由于demo代码这块没完善,这里简单说下实现思路: 空闲状态,每三分钟发送一个心跳包。
server每三分钟发一次心跳"ping"到client,client收到后回发一
个"pong"给server,这就完成了一次心跳检测。但如果在这三分钟之
内收到client发来的数据,则证明长连接处于正常状态,需要重新记
时三分钟再发送心跳。 client处理策略可以和server一致。
参考
- 关于service的一切
- 进程保活
- 基于Android的socket通信
- 官方api等资料