搭建内网yum服务器
yum介绍
为什么要使用yum
Linux系统维护中令管理员很头疼的就是软件包之间的依赖性了,往往是你要安装A软件,但是编译的时候告诉你X软件安装之前需要B软件,而当你安装Y软件的时候,又告诉你需要Z库了,好不容易安装好Z库,发现版本还有问题等。由于历史原因,RPM软件包管理系统对软件之间的依存关系没有内部定义,造成安装RPM软件时经常出现令人无法理解的软件依赖问题。其实开源社区早就对这个问题尝试进行解决了,不同的发行版推出了各自的工具,比如Yellow Dog的YUM(Yellow dog Updater, Modified),Debian的APT(Advanced Packaging Tool)等。开发这些工具的目的都是为了要解决安装RPM时的依赖性问题,而不是额外再建立一套安装模式。这些软件也被开源软件爱好者们逐渐移植到别的发行版上。
目前,APT和YUM都可以运行在Red Hat系统上。目前 yum 是Red Hat/Fedora系统上默认安装的更新系统。
什么是yum
YUM是Yellow dog Updater, Modified 的简称,起初是由yellow dog 发行版的开发者 Terra Soft 研发,用 python 写成,那时叫做 yup (yellow dog updater),后经杜克大学的 Linux@Duke 开发团队进行改进,遂有此名。yum 的宗旨是自动化地升级,安装/移除rpm包,收集rpm包的相关信息,检查依赖性并自动提示用户解决。yum 的关键之处是要有可靠的 repository,顾名思义,这是软件的仓库,它可以是 http 或 ftp 站点,也可以是本地软件池,但必须包含 rpm 的 header,header 包括了rpm 包的各种信息,包括描述,功能,提供的文件,依赖性等.正是收集了这些 header并加以分析,才能自动化地完成余下的任务。
yum 具有如下特点:
- 自动解决包的倚赖性问题能更方便的添加/删除/更新RPM包
- 便于管理大量系统的更新问题
- 可以同时配置多个资源库(Repository)
- 简洁的配置文件(/etc/yum.conf)
- 保持与RPM数据库的一致性
- 有一个比较详细的log,可以查看何时升级安装了什么软件包等
- 使用方便
yum使用流程
CentOS 先将释出的软件放置到 YUM 服务器内,然后分析这些软件的相依属性问题,将软件内的记录资讯写下来 (header)。 然后再将这些资讯分析后记录成软件相关性的清单列表。这些列表数据与软件所在的位置可以称呼为容器 (repository)。 当用户端有软件安装的需求时,用户端主机会主动的向网络上面的 yum 服务器的容器网址下载清单列表, 然后透过清单列表的数据与本机 RPM 数据库已存在的软件数据相比较,就能够一口气安装所有需要的具有相依属性的软件了。
整个流程可以简单的如下图说明:
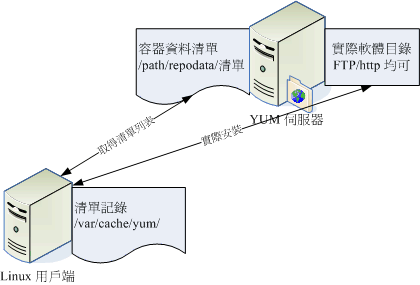
当用户端有升级、安装的需求时, yum 会向容器要求清单的升级,等到清单升级到本机的 /var/cache/yum 里面后, 等一下升级时就会用这个本机清单与本机的 RPM 数据库进行比较,这样就知道该下载什么软件。接下来 yum 会跑到容器服务器 (yum server) 下载所需要的软件,然后再透过 RPM 的机制开始安装软件啦!这就是整个流程。
内网YUM配置
在很多公司中,出于网络安全、维护成本等方面的考虑,服务器并没有接入到公共网络。从”yum使用流程”示意图可以看出,没有接入公网的服务器默认是无法访问外部的yum服务器的,这样yum带给系统管理员的维护便利似乎一下子荡然无存了。好在yum提供了简洁的资源库配置,结合ftp、http服务,我们就可以很方便快速的打造出一个内网的yum服务器,以供其他内网Linux系统使用。
以下即是一个简单的内网yum环境搭建示例。
环境
- YUM Server: CentOS 6.2,httpd-2.2.15,192.168.1.111(yum.egolife.com)
- YUM Client: CentOS 6.2,192.168.2.111
仓库规划
仓库(repository)是一个预备好的目录,或是一个网站,包含了软件包和索引文件。 yum 可以在仓库中自动地定位并获取正确的 RPM 软件包。这样,您就不必手动搜索和安装新应用程序和升级补丁了。只用一个命令,您就可以更新系统中所有软件,也可以根据指定搜索目标来查找安装新软件。
[root@yum]# pwd
/apps/yum
[root@yum]# tree -L 3 .
.
└── centos
└── 6.2_64
├── addons
├── base
├── centosplus
├── contrib
├── extras
└── updates
8 directories, 0 files
在本例中,YUM镜像服务器为每个版本的 CentOS 分别提供了一些仓库。其中,为CentOS 6.2 64bit提供了以下几个仓库:
- base: 构成 CentOS 发行版的软件包,和光盘上内容相同
- updates: base 仓库中软件包的更新版本
- addons: 已编译的但不在发行版中的软件包
- extras: 一大批附加的软件包
- centosplus: 用于增强一些现有软件包的功能
- contrib:社区用户构建贡献的软件包
创建仓库
CentOS提供了createrepo工具,可以从rpm包来创建yum仓库。
拷贝CentOS ISO镜像,创建仓库
[root@yum]# createrepo centos/6.2_64/base
2762/6295 - gthumb-2.10.11-8.el6.x86_64.rpm
当需要增加RPM包时,拷贝到相应的路径,并使用createrepo更新仓库即可
[root@yum]# pwd
/apps/yum/centos/6.2_64/extras
[root@server extras]# ll
total 92
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 92328 Dec 13 11:02 rlwrap-0.37-1.el6.x86_64.rpm
[root@yum]# createrepo --update .
1/1 - rlwrap-0.37-1.el6.x86_64.rpm
Saving Primary metadata
Saving file lists metadata
Saving other metadata
[root@yum]# ll
total 96
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Apr 1 18:09 repodata
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 92328 Dec 13 11:02 rlwrap-0.37-1.el6.x86_64.rpm
配置http
这里以Apache HTTP作为http服务器,其他Web服务器配置可以自行查询参考手册。
创建连接文件,指向/apps/yum
[root@server html]# grep DocumentRoot /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
# DocumentRoot: The directory out of which you will serve your
DocumentRoot "/var/www/html"
# This should be changed to whatever you set DocumentRoot to.
# DocumentRoot /www/docs/dummy-host.example.com
[root@server html]# pwd
/var/www/html
[root@server html]# ln -s /apps/yum/ yum
[root@server html]# ll
total 0
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 10 Apr 1 17:39 yum -> /apps/yum/
开启http服务
[root@yum]# service httpd start
Starting httpd:
yum测试
服务端测试
1.确认连接
[root@client]# ping yum.egolife.com
PING yum.egolife.com (192.168.1.111) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from yum.egolife.com (192.168.1.111): icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=0.041 ms
64 bytes from yum.egolife.com (192.168.1.111): icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=0.039 ms
64 bytes from yum.egolife.com (192.168.1.111): icmp_seq=3 ttl=64 time=0.038 ms
^C
--- yum.egolife.com ping statistics ---
3 packets transmitted, 3 received, 0% packet loss, time 2879ms
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 0.038/0.039/0.041/0.005 ms
2.更改yum仓库配置
[root@yum]# vim /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo
# CentOS-Base.repo
#
# The mirror system uses the connecting IP address of the client and the
# update status of each mirror to pick mirrors that are updated to and
# geographically close to the client. You should use this for CentOS updates
# unless you are manually picking other mirrors.
#
# If the mirrorlist= does not work for you, as a fall back you can try the
# remarked out baseurl= line instead.
#
#
[base]
name=CentOS-$releasever - Base
#mirrorlist=http://mirrorlist.centos.org/?release=$releasever&arch=$basearch&repo=os
#baseurl=http://mirror.centos.org/centos/$releasever/os/$basearch/
baseurl=http://yum.egolife.com/yum/centos/6.2_64/base
gpgcheck=0
enabled=1
#gpgkey=file:///etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-CentOS-6
#released updates
[updates]
name=CentOS-$releasever - Updates
#mirrorlist=http://mirrorlist.centos.org/?release=$releasever&arch=$basearch&repo=updates
#baseurl=http://mirror.centos.org/centos/$releasever/updates/$basearch/
baseurl=http://yum.egolife.com/yum/centos/6.2_64/updates
gpgcheck=0
enabled=0
#gpgkey=file:///etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-CentOS-6
#additional packages that may be useful
[extras]
name=CentOS-$releasever - Extras
#mirrorlist=http://mirrorlist.centos.org/?release=$releasever&arch=$basearch&repo=extras
#baseurl=http://mirror.centos.org/centos/$releasever/extras/$basearch/
baseurl=http://yum.egolife.com/yum/centos/6.2_64/extras
gpgcheck=0
enabled=1
#gpgkey=file:///etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-CentOS-6
#additional packages that extend functionality of existing packages
[centosplus]
name=CentOS-$releasever - Plus
mirrorlist=http://mirrorlist.centos.org/?release=$releasever&arch=$basearch&repo=centosplus
#baseurl=http://mirror.centos.org/centos/$releasever/centosplus/$basearch/
baseurl=http://yum.egolife.com/yum/centos/6.2_64/centosplus
gpgcheck=0
enabled=0
gpgkey=file:///etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-CentOS-6
#contrib - packages by Centos Users
[contrib]
name=CentOS-$releasever - Contrib
mirrorlist=http://mirrorlist.centos.org/?release=$releasever&arch=$basearch&repo=contrib
#baseurl=http://mirror.centos.org/centos/$releasever/contrib/$basearch/
baseurl=http://yum.egolife.com/yum/centos/6.2_64/contrib
gpgcheck=0
enabled=0
gpgkey=file:///etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-CentOS-6
以上配置主要说明如下:
- repositoryid : 用于指定一个仓库
- name: 用于指定易读的仓库名称
- mirrorlist: 用于指定仓库的镜像站点
- baseurl: 用于指定本仓库的 URL,可以是如下的几种类型:
- http: 用于指定远程 HTTP 协议的源
- ftp: 用于指定远程 FTP 协议的源
- file: 用于本地镜像或 NFS 挂装文件系统
- enabled: 用于指定是否使用本仓库,默认值为1,即可用
- gpgcheck: 用于指定是否检查软件包的 GPG 签名
- gpgkey: 用于指定 GPG 签名文件的 URL
在本例中,baseurl为http://yum.egolife.com/yum/centos/6.2_64/repositoryid。
注:
在此次测试中,以硬编码的形式指定了具体的URL,包括yum服务器,Linux平台和发行版。在yum配置中,releasever,basearch以变量的形式从OS中获取,来确定不同Linux的平台和发行版本,从很大程度上保证了配置的灵活性。
在配置baseurl=http://mirror.centos.org/centos/$releasever/os/$basearch/中,可以看到有几个变量,releaseve和basearch,该变量的值,即对应当前的Linux发行版,可以从/etc/yum.conf中找到。
[root@server etc]# head /etc/yum.conf
[main]
cachedir=/var/cache/yum/$basearch/$releasever
keepcache=0
debuglevel=2
logfile=/var/log/yum.log
exactarch=1
obsoletes=1
gpgcheck=1
plugins=1
installonly_limit=5
[root@server etc]# ll /var/cache/yum/x86_64/6/
total 12
drwxr-xr-x. 3 root root 4096 Apr 1 17:15 base
drwxr-xr-x. 3 root root 4096 Apr 1 17:15 extras
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Apr 1 17:15 timedhosts.txt
drwxr-xr-x. 3 root root 4096 Jan 7 00:03 updates
从以上输出,可以看到本例中,releasever=6,basearch=x86_64。
3.yum测试
[root@server conf]# yum info yum
Loaded plugins: downloadonly, fastestmirror, refresh-packagekit, security
Determining fastest mirrors
base | 1.3 kB 00:00
extras | 1.3 kB 00:00
Installed Packages
Name : yum
Arch : noarch
Version : 3.2.29
Release : 22.el6.centos
Size : 4.5 M
Repo : installed
From repo : anaconda-CentOS-201112091719.x86_64
Summary : RPM package installer/updater/manager
URL : http://yum.baseurl.org/
License : GPLv2+
Description : Yum is a utility that can check for and automatically download and
: install updated RPM packages. Dependencies are obtained and downloaded
: automatically, prompting the user for permission as necessary.
客户端测试
其他Linux客户机中,在保证到yum.egolife.com正常的网络连接的前提下,按照上述配置,即可以正常使用yum服务。
root@oabak ~]# yum install -y lrzsz
Loaded plugins: fastestmirror, refresh-packagekit
Loading mirror speeds from cached hostfile
Setting up Install Process
Resolving Dependencies
There are unfinished transactions remaining. You might consider running yum-complete-transaction first to finish them.
The program yum-complete-transaction is found in the yum-utils package.
--> Running transaction check
---> Package lrzsz.x86_64 0:0.12.20-27.1.el6 will be installed
--> Finished Dependency Resolution
Dependencies Resolved
============================================================================================
Package Arch Version Repository Size
============================================================================================
Installing:
lrzsz x86_64 0.12.20-27.1.el6 base 71 k
Transaction Summary
============================================================================================
Install 1 Package(s)
Total download size: 71 k
Installed size: 159 k
Downloading Packages:
lrzsz-0.12.20-27.1.el6.x86_64.rpm