1. 算法检测所给graph是否有Euler Path
a) 假设点都是连续的
b) 假设每点的degree是已知的,我们不需要一个点一个点的数 O(1)
假设degree需要自己计算,每个vertex的cost是O(V), 总cost是O(V^2)
c) 用循环检测所有vertices O(V)
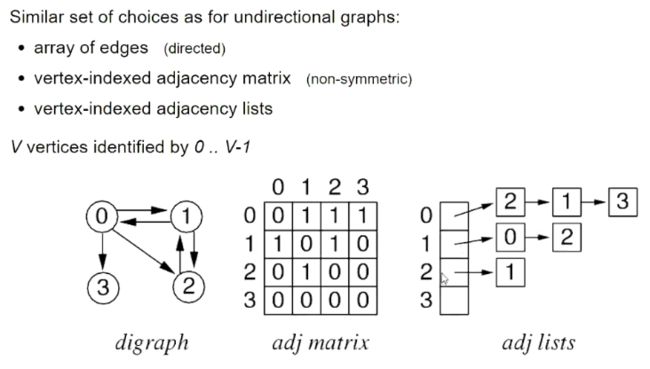
2. 通常array of edges最高效,adjacency matrix占地方最多
3. comman name and silly name
& and/snowman
* star/spider
" double quote/rabbit-ears
^ hat/shark-fin
@ at/spider monkey(German),cabbage
! exclamation/wow
# hash/grid
% percent sign,mod/grapes
4. reachable: can find a path from v to w(directed)
6. transitive closure
通过haspath(G, s, t), 利用DFS, BFS
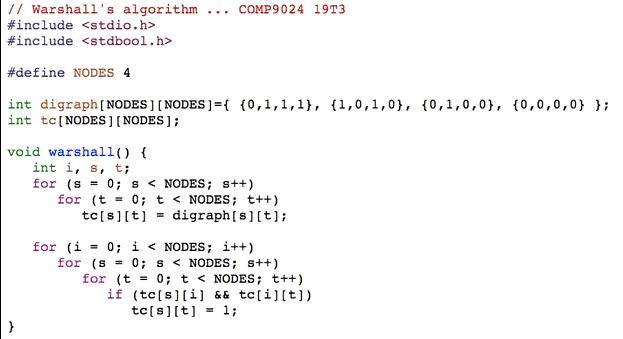
7. Warshall's algorithm: 如果tc[s][i]=1, tc[i][t]=1, 则tc[s][t]=1
computation of transitive closure: V^3
8. weighted graphs
若不可能为负数,no edge可写成
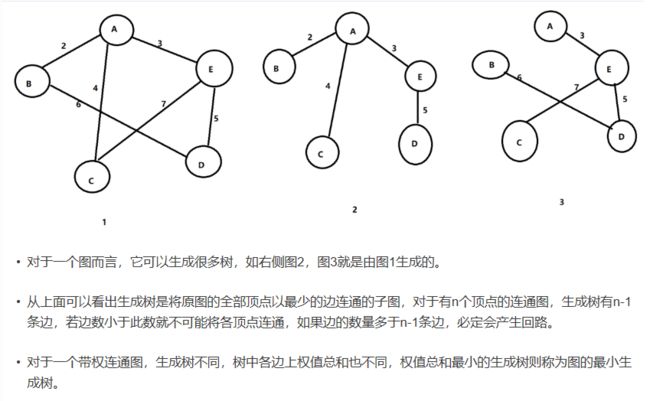
9. minimum spanning trees
spanning tree: 将所有点连接且不构成cycle
minimum spanning trees的例子有如,不同城市之间建造通信联络的成本不同,如A直接到C需要1000,但是A到B需要200,B到C需要300,就不需要直接连接A到C了,但是实际的问题要考虑整体graph而不是单独几个点,并且不能形成cycle。MST就是计算成本最少的情况
一般做法是将MST设为无穷大,然后遍历所有spanning tree,如果更小就替换掉之前的MST,直到结束得到最小的
10. MST的两种算法(Graph G with V nodes)
a) Kruskal's Algorithm(不一定只有一种结果)
从一个空的MST开始,从weight最小的edge开始不断加入,并保证新加进来的edge不会形成cycle
不断重复直到加入了V-1个edges
对edges进行排序的时间复杂度为O(E*logE)
b) Prim's Algorithm