深入理解 ThreadLocal
前言
ThreadLocal是一个本地线程副本变量工具类。主要用于将私有线程和该线程存放的副本对象做一个映射,各个线程之间的变量互不干扰,在高并发场景下,可以实现无状态的调用,特别适用于各个线程依赖不通的变量值完成操作的场景。
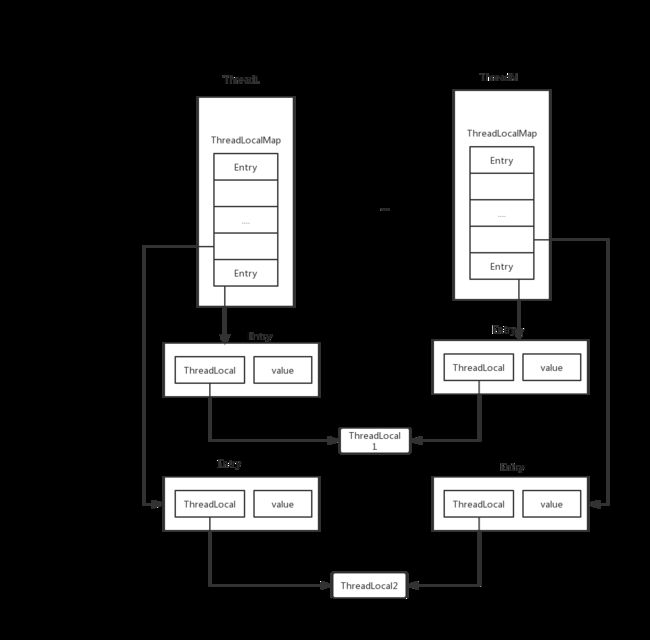
ThreadLocal 内部结构
/* ThreadLocal values pertaining to this thread. This map is maintained
* by the ThreadLocal class. */
ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap threadLocals = null;
/*
* InheritableThreadLocal values pertaining to this thread. This map is
* maintained by the InheritableThreadLocal class.
*/
ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap inheritableThreadLocals = null;
- 每一个 Thread 里都有一个 ThreadLocalMap
ThreadLocalMap 是 ThreadLocal 的一个静态类
static class ThreadLocalMap {
/**
* The entries in this hash map extend WeakReference, using
* its main ref field as the key (which is always a
* ThreadLocal object). Note that null keys (i.e. entry.get()
* == null) mean that the key is no longer referenced, so the
* entry can be expunged from table. Such entries are referred to
* as "stale entries" in the code that follows.
*/
static class Entry extends WeakReference> {
/** The value associated with this ThreadLocal. */
Object value;
Entry(ThreadLocal k, Object v) {
super(k);
value = v;
}
}
....
- ThreadLocalMap 存储了线程本地对象(key)和线程的变量副本(value)
- Thread内部的Map是由ThreadLocal维护的,由ThreadLocal负责向map获取和设置线程的变量值
所以对于不同的线程,每次获取副本值时,别的线程并不能获取到当前线程的副本值,形成了副本的隔离,互不干扰。
深入解析ThreadLocal
ThreadLocal类提供如下几个核心方法:
public T get()
public void set(T value)
public void remove()
- get()方法用于获取当前线程的副本变量值。
- set()方法用于保存当前线程的副本变量值。
- initialValue()为当前线程初始副本变量值。
- remove()方法移除当前前程的副本变量值。
get() 方法
/**
* Returns the value in the current thread's copy of this
* thread-local variable. If the variable has no value for the
* current thread, it is first initialized to the value returned
* by an invocation of the {@link #initialValue} method.
*
* @return the current thread's value of this thread-local
*/
public T get() {
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null) {
ThreadLocalMap.Entry e = map.getEntry(this);
if (e != null) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
T result = (T)e.value;
return result;
}
}
return setInitialValue();
}
在你去调用 get() 的时候,会拿到当前的线程,调用 getMap(t) 来获取 ThreadLocalMap
/**
* Get the map associated with a ThreadLocal. Overridden in
* InheritableThreadLocal.
*
* @param t the current thread
* @return the map
*/
ThreadLocalMap getMap(Thread t) {
return t.threadLocals;
}
从这里我们知道 Thread 中的 ThreadLocalMap 是交给 ThreadLocal 进行管理的。
如果 map 是 null, 那么会调用 setInitialValue( )
/**
* Variant of set() to establish initialValue. Used instead
* of set() in case user has overridden the set() method.
*
* @return the initial value
*/
private T setInitialValue() {
T value = initialValue();
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null)
map.set(this, value);
else
createMap(t, value);
return value;
}
这里会在去根据当前线程拿一次 map,如果没有就调用 createMap(t, value)
/**
* Create the map associated with a ThreadLocal. Overridden in
* InheritableThreadLocal.
*
* @param t the current thread
* @param firstValue value for the initial entry of the map
*/
void createMap(Thread t, T firstValue) {
t.threadLocals = new ThreadLocalMap(this, firstValue);
}
可以看到其new 了一个 ThreadLocalMap,并将当前的 ThreadLocal(this) 传了进去。
set( ) 方法
/**
* Sets the current thread's copy of this thread-local variable
* to the specified value. Most subclasses will have no need to
* override this method, relying solely on the {@link #initialValue}
* method to set the values of thread-locals.
*
* @param value the value to be stored in the current thread's copy of
* this thread-local.
*/
public void set(T value) {
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null)
map.set(this, value);
else
createMap(t, value);
}
判断逻辑和 get( ) 方法一样,首先调用 getMap(t),判断是否有 map,没有就创建一个。
从 get 和 set 方法我们可以看到,线程的ThreadLocalMap 是懒加载的
remove( ) 方法
/**
* Removes the current thread's value for this thread-local
* variable. If this thread-local variable is subsequently
* {@linkplain #get read} by the current thread, its value will be
* reinitialized by invoking its {@link #initialValue} method,
* unless its value is {@linkplain #set set} by the current thread
* in the interim. This may result in multiple invocations of the
* {@code initialValue} method in the current thread.
*
* @since 1.5
*/
public void remove() {
ThreadLocalMap m = getMap(Thread.currentThread());
if (m != null)
m.remove(this);
}
remove 的实现就比较简单了,获取map将当前的删除。
代码示例:
/*
* ThreadLocal 每个线程的一个副本,互相不受影响
*
* InheritableThreadLocal 可以允许线程及该线程创建的子线程均可以访问同一个变量
*
* @author apple
*/
public class ThreadLocalTest {
private static ThreadLocal threadLocal = new ThreadLocal<>();
// private static InheritableThreadLocal threadLocal = new
// InheritableThreadLocal();
private static class Task implements Runnable {
private ThreadLocal threadLocal = new ThreadLocal<>();
private String taskName;
public Task(String taskName) {
this.taskName = taskName;
}
@Override
public void run() {
threadLocal.set(Thread.currentThread().getName());
System.out.println(this.taskName + ":" + threadLocal.get());
}
}
private static class Task1 implements Runnable {
private ThreadLocal threadLocal = new ThreadLocal<>();
private String taskName;
public Task1(String taskName) {
threadLocal.set(Thread.currentThread().getName());
this.taskName = taskName;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":" + threadLocal.get());
}
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(this.taskName + ":" + threadLocal.get());
}
}
private static class Task2 implements Runnable {
private String taskName;
public Task2(String taskName) {
this.taskName = taskName;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":" + threadLocal.get());
}
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(this.taskName + ":" + threadLocal.get());
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Task task1 = new Task("任务1");
Thread t1 = new Thread(task1);
Task task2 = new Task("任务2");
Thread t2 = new Thread(task2);
t1.start();
t2.start(); // 任务1:Thread-0
// 任务2:Thread-1
// Task1 的构造函数由 main 线程调用,所以 threadLocal.set() 是在 main 线程中完成的,但是在 子线程
// run() 方法中没有调用 threadLocal.set() 所以 其 get() 到的值为 null
// Task1 task1 = new Task1("任务1");
// Thread t1 = new Thread(task1);
//
// Task1 task2 = new Task1("任务2");
// Thread t2 = new Thread(task2);
//
// t1.start();
// t2.start(); // main:main
// main:main
// 任务1:null
// 任务2:null
// threadLocal.set(10);
// Task2 task1 = new Task2("任务1");
// Thread t1 = new Thread(task1);
//
// Task2 task2 = new Task2("任务2");
// Thread t2 = new Thread(task2);
//
// t1.start();
// t2.start();
}
}
参考博文:
- https://www.jianshu.com/p/98b68c97df9b
- https://blog.csdn.net/duchao123duchao/article/details/50989773