基于pytorch的CNN、LSTM神经网络模型调参小结
(一篇有用的笔记,转载下)
-
这是最近两个月来的一个小总结,实现的demo已经上传github,里面包含了CNN、LSTM、BiLSTM、GRU以及CNN与LSTM、BiLSTM的结合还有多层多通道CNN、LSTM、BiLSTM等多个神经网络模型的的实现。这篇文章总结一下最近一段时间遇到的问题、处理方法和相关策略,以及经验(其实并没有什么经验)等,白菜一枚。
-
Demo Site: https://github.com/bamtercelboo/cnn-lstm-bilstm-deepcnn-clstm-in-pytorch
(一) Pytorch简述
-
Pytorch是一个较新的深度学习框架,是一个 Python 优先的深度学习框架,能够在强大的 GPU 加速基础上实现张量和动态神经网络。
-
对于没有学习过pytorch的初学者,可以先看一下官网发行的60分钟入门pytorch,参考地址 :http://pytorch.org/tutorials/beginner/deep_learning_60min_blitz.html
(二) CNN、LSTM
-
卷积神经网络CNN理解参考(https://www.zybuluo.com/hanbingtao/note/485480)
-
长短时记忆网络LSTM理解参考(https://zybuluo.com/hanbingtao/note/581764)
(三)数据预处理
1、我现在使用的语料是基本规范的数据(例如下),但是加载语料数据的过程中仍然存在着一些需要预处理的地方,像一些数据的大小写、数字的处理以及“\n \t”等一些字符,现在使用torchtext第三方库进行加载数据预处理。
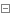
You Should Pay Nine Bucks for This : Because you can hear about suffering Afghan refugees on the news and still be unaffected . ||| 2 Dramas like this make it human . ||| 4
2、torch建立词表、处理语料数据的大小写:

import torchtext.data as data # lower word text_field = data.Field(lower=True)
3、处理语料数据数字等特殊字符:


1 from torchtext import data 2 def clean_str(string): 3 string = re.sub(r"[^A-Za-z0-9(),!?\'\`]", " ", string) 4 string = re.sub(r"\'s", " \'s", string) 5 string = re.sub(r"\'ve", " \'ve", string) 6 string = re.sub(r"n\'t", " n\'t", string) 7 string = re.sub(r"\'re", " \'re", string) 8 string = re.sub(r"\'d", " \'d", string) 9 string = re.sub(r"\'ll", " \'ll", string) 10 string = re.sub(r",", " , ", string) 11 string = re.sub(r"!", " ! ", string) 12 string = re.sub(r"\(", " \( ", string) 13 string = re.sub(r"\)", " \) ", string) 14 string = re.sub(r"\?", " \? ", string) 15 string = re.sub(r"\s{2,}", " ", string) 16 return string.strip() 17 18 text_field.preprocessing = data.Pipeline(clean_str)
4、需要注意的地方:
-
加载数据集的时候可以使用random打乱数据

1 if shuffle: 2 random.shuffle(examples_train) 3 random.shuffle(examples_dev) 4 random.shuffle(examples_test)
-
torchtext建立训练集、开发集、测试集迭代器的时候,可以选择在每次迭代的时候是否去打乱数据


1 class Iterator(object): 2 """Defines an iterator that loads batches of data from a Dataset. 3 4 Attributes: 5 dataset: The Dataset object to load Examples from. 6 batch_size: Batch size. 7 sort_key: A key to use for sorting examples in order to batch together 8 examples with similar lengths and minimize padding. The sort_key 9 provided to the Iterator constructor overrides the sort_key 10 attribute of the Dataset, or defers to it if None. 11 train: Whether the iterator represents a train set. 12 repeat: Whether to repeat the iterator for multiple epochs. 13 shuffle: Whether to shuffle examples between epochs. 14 sort: Whether to sort examples according to self.sort_key. 15 Note that repeat, shuffle, and sort default to train, train, and 16 (not train). 17 device: Device to create batches on. Use -1 for CPU and None for the 18 currently active GPU device. 19 """

(四)Word Embedding
1、word embedding简单来说就是语料中每一个单词对应的其相应的词向量,目前训练词向量的方式最使用的应该是word2vec(参考 http://www.cnblogs.com/bamtercelboo/p/7181899.html)
2、上文中已经通过torchtext建立了相关的词汇表,加载词向量有两种方式,一个是加载外部根据语料训练好的预训练词向量,另一个方式是随机初始化词向量,两种方式相互比较的话当时是使用预训练好的词向量效果会好很多,但是自己训练的词向量并不见得会有很好的效果,因为语料数据可能不足,像已经训练好的词向量,像Google News那个词向量,是业界公认的词向量,但是由于数量巨大,如果硬件设施(GPU)不行的话,还是不要去尝试这个了。
3、提供几个下载预训练词向量的地址
-
word2vec-GoogleNews-vectors(https://github.com/mmihaltz/word2vec-GoogleNews-vectors)
-
glove-vectors (https://nlp.stanford.edu/projects/glove/)
4、加载外部词向量方式
-
加载词汇表中在词向量里面能够找到的词向量


1 # load word embedding 2 def load_my_vecs(path, vocab, freqs): 3 word_vecs = {} 4 with open(path, encoding="utf-8") as f: 5 count = 0 6 lines = f.readlines()[1:] 7 for line in lines: 8 values = line.split(" ") 9 word = values[0] 10 # word = word.lower() 11 count += 1 12 if word in vocab: # whether to judge if in vocab 13 vector = [] 14 for count, val in enumerate(values): 15 if count == 0: 16 continue 17 vector.append(float(val)) 18 word_vecs[word] = vector 19 return word_vecs
-
处理词汇表中在词向量里面找不到的word,俗称OOV(out of vocabulary),OOV越多,可能对加过的影响也就越大,所以对OOV词的处理就显得尤为关键,现在有几种策略可以参考:
-
对已经找到的词向量平均化


1 # solve unknown by avg word embedding 2 def add_unknown_words_by_avg(word_vecs, vocab, k=100): 3 # solve unknown words inplaced by zero list 4 word_vecs_numpy = [] 5 for word in vocab: 6 if word in word_vecs: 7 word_vecs_numpy.append(word_vecs[word]) 8 print(len(word_vecs_numpy)) 9 col = [] 10 for i in range(k): 11 sum = 0.0 12 # for j in range(int(len(word_vecs_numpy) / 4)): 13 for j in range(int(len(word_vecs_numpy))): 14 sum += word_vecs_numpy[j][i] 15 sum = round(sum, 6) 16 col.append(sum) 17 zero = [] 18 for m in range(k): 19 # avg = col[m] / (len(col) * 5) 20 avg = col[m] / (len(word_vecs_numpy)) 21 avg = round(avg, 6) 22 zero.append(float(avg)) 23 24 list_word2vec = [] 25 oov = 0 26 iov = 0 27 for word in vocab: 28 if word not in word_vecs: 29 # word_vecs[word] = np.random.uniform(-0.25, 0.25, k).tolist() 30 # word_vecs[word] = [0.0] * k 31 oov += 1 32 word_vecs[word] = zero 33 list_word2vec.append(word_vecs[word]) 34 else: 35 iov += 1 36 list_word2vec.append(word_vecs[word]) 37 print("oov count", oov) 38 print("iov count", iov) 39 return list_word2vec
-
随机初始化或者全部取zero,随机初始化或者是取zero,可以是所有的OOV都使用一个随机值,也可以每一个OOV word都是随机的,具体效果看自己效果
-
随机初始化的值看过几篇论文,有的随机初始化是在(-0.25,0.25)或者是(-0.1,0.1)之间,具体的效果可以自己去测试一下,不同的数据集,不同的外部词向量估计效果不一样,我测试的结果是0.25要好于0.1


1 # solve unknown word by uniform(-0.25,0.25) 2 def add_unknown_words_by_uniform(word_vecs, vocab, k=100): 3 list_word2vec = [] 4 oov = 0 5 iov = 0 6 # uniform = np.random.uniform(-0.25, 0.25, k).round(6).tolist() 7 for word in vocab: 8 if word not in word_vecs: 9 oov += 1 10 word_vecs[word] = np.random.uniform(-0.25, 0.25, k).round(6).tolist() 11 # word_vecs[word] = np.random.uniform(-0.1, 0.1, k).round(6).tolist() 12 # word_vecs[word] = uniform 13 list_word2vec.append(word_vecs[word]) 14 else: 15 iov += 1 16 list_word2vec.append(word_vecs[word]) 17 print("oov count", oov) 18 print("iov count", iov) 19 return list_word2vec
-
特别需要注意处理后的OOV词向量是否在一定的范围之内,这个一定要在处理之后手动或者是demo查看一下,想处理出来的词向量大于15,30的这种,可能就是你自己处理方式的问题,也可以是说是你自己demo可能存在bug,对结果的影响很大。
5、model中使用外部词向量
-
 View Code
View Code
(五)参数初始化
-
对于pytorch中的nn.Conv2d()卷积函数来说,有weight and bias,对weight初始化是很有必要的,不对其初始化可能减慢收敛速度,影响最终效果等
-
对weight初始化,一般可以使用
torch.nn.init.uniform()、torch.nn.init.normal()、torch.nn.init.xavier_uniform(),具体使用参考 http://pytorch.org/docs/master/nn.html#torch-nn-init 
1 init.xavier_normal(conv.weight.data, gain=np.sqrt(args.init_weight_value)) 2 init.uniform(conv.bias, 0, 0)
-
对于pytorch中的nn.LSTM(),有all_weights属性,其中包括weight and bias,是一个多维矩阵

1 if args.init_weight: 2 print("Initing W .......") 3 init.xavier_normal(self.bilstm.all_weights[0][0], gain=np.sqrt(args.init_weight_value)) 4 init.xavier_normal(self.bilstm.all_weights[0][1], gain=np.sqrt(args.init_weight_value)) 5 init.xavier_normal(self.bilstm.all_weights[1][0], gain=np.sqrt(args.init_weight_value)) 6 init.xavier_normal(self.bilstm.all_weights[1][1], gain=np.sqrt(args.init_weight_value))
(六)调参及其策略
-
神经网络参数设置
-
CNN中的kernel-size:看过一篇paper(A Sensitivity Analysis of (and Practitioners’ Guide to)Convolutional Neural Networks for Sentence Classification),论文上测试了kernel的使用,根据其结果,设置大部分会在1-10随机组合,具体的效果还好根据自己的任务。
-
CNN中的kernel-num,就是每个卷积窗口的特征数目,大致设置在100-600,我一般会设置200,300
-
Dropout:Dropout大多数论文上设置都是0.5,据说0.5的效果很好,能够防止过拟合问题,但是在不同的task中,还需要适当的调整dropout的大小,出来要调整dropout值之外,dropout在model中的位置也是很关键的,可以尝试不同的dropout位置,或许会收到惊人的效果。
-
batch size:batch size这个还是需要去适当调整的,看相关的blogs,一般设置不会超过128,有可能也很小,在我目前的任务中,batch size =16有不错的效果。
-
learning rate:学习率这个一般初值对于不同的优化器设置是不一样的,据说有一些经典的配置,像Adam :lr = 0.001
-
迭代次数:根据自己的task、model、收敛速度、拟合效果设置不同的值
-
LSTM中的hidden size:LSTM中的隐藏层维度大小也对结果有一定的影响,如果使用300dim的外部词向量的话,可以考虑hidden size =150或者是300,对于hidden size我最大设置过600,因为硬件设备的原因,600训练起来已经是很慢了,如果硬件资源ok的话,可以尝试更多的hidden size值,但是尝试的过程中还是要考虑一下hidden size 与词向量维度的关系(自认为其是有一定的关系影响的)
-
二范式约束:pytorch中的Embedding中的max-norm 和norm-type就是二范式约束

1 if args.max_norm is not None: 2 print("max_norm = {} ".format(args.max_norm)) 3 self.embed = nn.Embedding(V, D, max_norm=args.max_norm)-
pytorch中实现了L2正则化,也叫做权重衰减,具体实现是在优化器中,参数是 weight_decay(pytorch中的L1正则已经被遗弃了,可以自己实现),一般设置1e-8

1 if args.Adam is True: 2 print("Adam Training......") 3 optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=args.lr, weight_decay=args.init_weight_decay)-
梯度消失、梯度爆炸问题

1 import torch.nn.utils as utils 2 if args.init_clip_max_norm is not None: 3 utils.clip_grad_norm(model.parameters(), 4 max_norm=args.init_clip_max_norm)
-
神经网络提升Acc的策略
-
数据预处理,建立词汇表的过程中可以把词频为1的单词剔除,这也是一个超参数,如果剔除之后发现准确率下降的话,可以尝试以一定的概率剔除或者是以一定的概率对这部分词向量进行不同的处理
-
动态学习率:pytorch最新的版本0.2已经实现了动态学习率,具体使用参考 http://pytorch.org/docs/master/optim.html#how-to-adjust-learning-rate
-
批量归一化(batch normalizations),pytorch中也提供了相应的函数 BatchNorm1d() 、BatchNorm2d() 可以直接使用,其中有一个参数(momentum)可以作为超参数调整


1 if args.batch_normalizations is True: 2 print("using batch_normalizations in the model......") 3 self.convs1_bn = nn.BatchNorm2d(num_features=Co, momentum=args.bath_norm_momentum, 4 affine=args.batch_norm_affine) 5 self.fc1_bn = nn.BatchNorm1d(num_features=in_fea//2, momentum=args.bath_norm_momentum, 6 affine=args.batch_norm_affine) 7 self.fc2_bn = nn.BatchNorm1d(num_features=C, momentum=args.bath_norm_momentum, 8 affine=args.batch_norm_affine)
-
宽卷积、窄卷积,在深层卷积model中应该需要使用的是宽卷积,使用窄卷积的话会出现维度问题,我现在使用的数据使用双层卷积神经网络就会出现维度问题,其实也是和数据相关的


1 if args.wide_conv is True: 2 print("using wide convolution") 3 self.convs1 = [nn.Conv2d(in_channels=Ci, out_channels=Co, kernel_size=(K, D), stride=(1, 1), 4 padding=(K//2, 0), dilation=1, bias=True) for K in Ks] 5 else: 6 print("using narrow convolution") 7 self.convs1 = [nn.Conv2d(in_channels=Ci, out_channels=Co, kernel_size=(K, D), bias=True) for K in Ks]
-
character-level的处理,最开始的处理方式是使用词进行处理(也就是单词),可以考虑根据字符去划分,划分出来的词向量可以采用随机初始化的方式,这也是一种策略,我试过这种策略,对我目前的任务来说是没有提升的。
-
优化器:pytorch提供了多个优化器,我们最常用的是Adam,效果还是很不错的,具体的可以参考 http://pytorch.org/docs/master/optim.html#algorithms
-
fine-tune or no-fine-tune:这是一个很重要的策略,一般情况下fine-tune是有很不错的效果的相对于no-fine-tune来说。
(七)参考致谢
-
你有哪些deep learning(rnn、cnn)调参的经验?
-
有谁可以解释下word embedding?
-
零基础入门深度学习
-
PyTorch参数初始化和Finetune
-
过拟合与正则
-
Batch Normalitions