
import numpy as np
from w2v_utils import *

words, word_to_vec_map = read_glove_vecs('data/glove.6B.50d.txt')

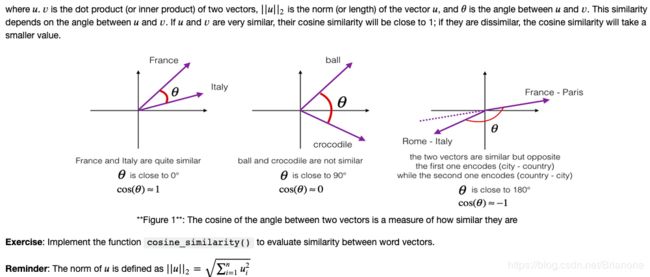
# GRADED FUNCTION: cosine_similarity
def cosine_similarity(u, v):
"""
Cosine similarity reflects the degree of similariy between u and v
Arguments:
u -- a word vector of shape (n,)
v -- a word vector of shape (n,)
Returns:
cosine_similarity -- the cosine similarity between u and v defined by the formula above.
"""
distance = 0.0
### START CODE HERE ###
# Compute the dot product between u and v (≈1 line)
dot = np.dot(u,v)
# Compute the L2 norm of u (≈1 line)
norm_u = np.linalg.norm(u)
# Compute the L2 norm of v (≈1 line)
norm_v = np.linalg.norm(v)
# Compute the cosine similarity defined by formula (1) (≈1 line)
cosine_similarity = dot/(norm_u * norm_v)
### END CODE HERE ###
return cosine_similarity
father = word_to_vec_map["father"]
mother = word_to_vec_map["mother"]
ball = word_to_vec_map["ball"]
crocodile = word_to_vec_map["crocodile"]
france = word_to_vec_map["france"]
italy = word_to_vec_map["italy"]
paris = word_to_vec_map["paris"]
rome = word_to_vec_map["rome"]
print("cosine_similarity(father, mother) = ", cosine_similarity(father, mother))
print("cosine_similarity(ball, crocodile) = ",cosine_similarity(ball, crocodile))
print("cosine_similarity(france - paris, rome - italy) = ",cosine_similarity(france - paris, rome - italy))


# GRADED FUNCTION: complete_analogy
def complete_analogy(word_a, word_b, word_c, word_to_vec_map):
"""
Performs the word analogy task as explained above: a is to b as c is to ____.
Arguments:
word_a -- a word, string
word_b -- a word, string
word_c -- a word, string
word_to_vec_map -- dictionary that maps words to their corresponding vectors.
Returns:
best_word -- the word such that v_b - v_a is close to v_best_word - v_c, as measured by cosine similarity
"""
# convert words to lower case
word_a, word_b, word_c = word_a.lower(), word_b.lower(), word_c.lower()
### START CODE HERE ###
# Get the word embeddings v_a, v_b and v_c (≈1-3 lines)
e_a, e_b, e_c = word_to_vec_map[word_a], word_to_vec_map[word_b], word_to_vec_map[word_c]
### END CODE HERE ###
words = word_to_vec_map.keys()
max_cosine_sim = -100 # Initialize max_cosine_sim to a large negative number
best_word = None # Initialize best_word with None, it will help keep track of the word to output
# loop over the whole word vector set
for w in words:
# to avoid best_word being one of the input words, pass on them.
if w in [word_a, word_b, word_c] :
continue
### START CODE HERE ###
# Compute cosine similarity between the vector (e_b - e_a) and the vector ((w's vector representation) - e_c) (≈1 line)
cosine_sim = cosine_similarity(e_b-e_a, word_to_vec_map[w]-e_c)
# If the cosine_sim is more than the max_cosine_sim seen so far,
# then: set the new max_cosine_sim to the current cosine_sim and the best_word to the current word (≈3 lines)
if cosine_sim > max_cosine_sim:
max_cosine_sim = cosine_sim
best_word = w
### END CODE HERE ###
return best_word
triads_to_try = [('italy', 'italian', 'spain'), ('india', 'delhi', 'japan'), ('man', 'woman', 'boy'), ('small', 'smaller', 'large')]
for triad in triads_to_try:
print ('{} -> {} :: {} -> {}'.format( *triad, complete_analogy(*triad,word_to_vec_map)))


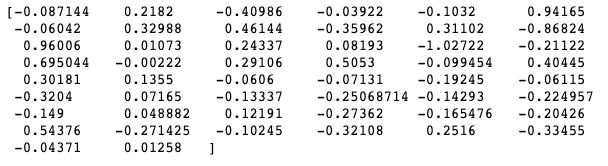
g = word_to_vec_map['woman'] - word_to_vec_map['man']
print(g)

print ('List of names and their similarities with constructed vector:')
# girls and boys name
name_list = ['john', 'marie', 'sophie', 'ronaldo', 'priya', 'rahul', 'danielle', 'reza', 'katy', 'yasmin']
for w in name_list:
print (w, cosine_similarity(word_to_vec_map[w], g))


print('Other words and their similarities:')
word_list = ['lipstick', 'guns', 'science', 'arts', 'literature', 'warrior','doctor', 'tree', 'receptionist',
'technology', 'fashion', 'teacher', 'engineer', 'pilot', 'computer', 'singer']
for w in word_list:
print (w, cosine_similarity(word_to_vec_map[w], g))


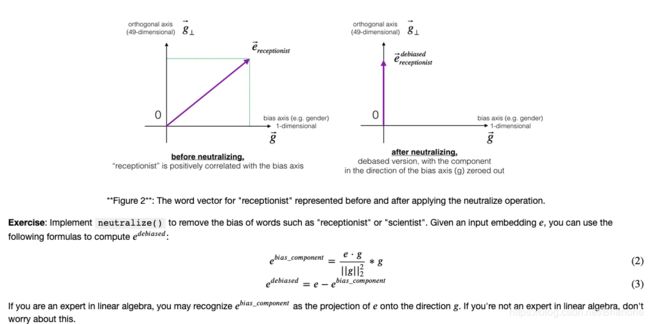
def neutralize(word, g, word_to_vec_map):
"""
Removes the bias of "word" by projecting it on the space orthogonal to the bias axis.
This function ensures that gender neutral words are zero in the gender subspace.
Arguments:
word -- string indicating the word to debias
g -- numpy-array of shape (50,), corresponding to the bias axis (such as gender)
word_to_vec_map -- dictionary mapping words to their corresponding vectors.
Returns:
e_debiased -- neutralized word vector representation of the input "word"
"""
### START CODE HERE ###
# Select word vector representation of "word". Use word_to_vec_map. (≈ 1 line)
e = word_to_vec_map[word]
# Compute e_biascomponent using the formula give above. (≈ 1 line)
e_biascomponent = np.dot(e, g) * g/np.square(np.linalg.norm(g))
# Neutralize e by substracting e_biascomponent from it
# e_debiased should be equal to its orthogonal projection. (≈ 1 line)
e_debiased = e - e_biascomponent
### END CODE HERE ###
return e_debiased
e = "receptionist"
print("cosine similarity between " + e + " and g, before neutralizing: ", cosine_similarity(word_to_vec_map["receptionist"], g))
e_debiased = neutralize("receptionist", g, word_to_vec_map)
print("cosine similarity between " + e + " and g, after neutralizing: ", cosine_similarity(e_debiased, g))

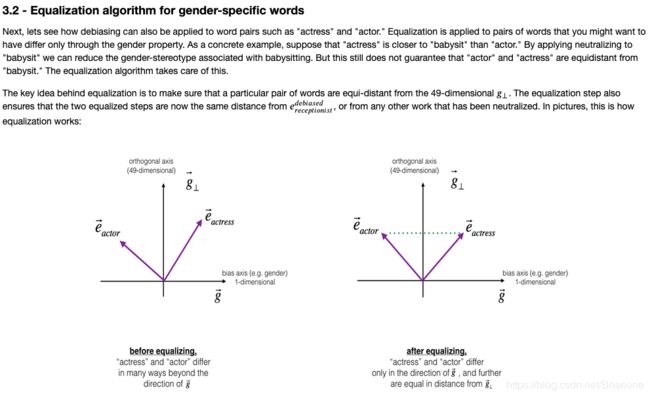

def equalize(pair, bias_axis, word_to_vec_map):
"""
Debias gender specific words by following the equalize method described in the figure above.
Arguments:
pair -- pair of strings of gender specific words to debias, e.g. ("actress", "actor")
bias_axis -- numpy-array of shape (50,), vector corresponding to the bias axis, e.g. gender
word_to_vec_map -- dictionary mapping words to their corresponding vectors
Returns
e_1 -- word vector corresponding to the first word
e_2 -- word vector corresponding to the second word
"""
### START CODE HERE ###
# Step 1: Select word vector representation of "word". Use word_to_vec_map. (≈ 2 lines)
w1, w2 = pair[0], pair[1]
e_w1, e_w2 = word_to_vec_map[w1], word_to_vec_map[w2]
# Step 2: Compute the mean of e_w1 and e_w2 (≈ 1 line)
mu = (e_w1 + e_w2) /2
# Step 3: Compute the projections of mu over the bias axis and the orthogonal axis (≈ 2 lines)
mu_B = np.dot(mu, bias_axis) * bias_axis/np.dot(bias_axis, bias_axis)
mu_orth = mu - mu_B
# Step 4: Use equations (7) and (8) to compute e_w1B and e_w2B (≈2 lines)
e_w1B = np.dot(e_w1, bias_axis) * bias_axis/np.dot(bias_axis, bias_axis)
e_w2B = np.dot(e_w2, bias_axis) * bias_axis/np.dot(bias_axis, bias_axis)
# Step 5: Adjust the Bias part of e_w1B and e_w2B using the formulas (9) and (10) given above (≈2 lines)
temp = np.sqrt(np.abs(1. - np.dot(mu_orth, mu_orth)))
corrected_e_w1B = temp * (e_w1B - mu_B) / np.abs( e_w1 - mu_orth - mu_B)
corrected_e_w2B = temp * (e_w2B - mu_B) / np.abs( e_w2 - mu_orth - mu_B)
# Step 6: Debias by equalizing e1 and e2 to the sum of their corrected projections (≈2 lines)
e1 = corrected_e_w1B + mu_orth
e2 = corrected_e_w2B + mu_orth
### END CODE HERE ###
return e1, e2
print("cosine similarities before equalizing:")
print("cosine_similarity(word_to_vec_map[\"man\"], gender) = ", cosine_similarity(word_to_vec_map["man"], g))
print("cosine_similarity(word_to_vec_map[\"woman\"], gender) = ", cosine_similarity(word_to_vec_map["woman"], g))
print()
e1, e2 = equalize(("man", "woman"), g, word_to_vec_map)
print("cosine similarities after equalizing:")
print("cosine_similarity(e1, gender) = ", cosine_similarity(e1, g))
print("cosine_similarity(e2, gender) = ", cosine_similarity(e2, g))


![]()
![]()
















